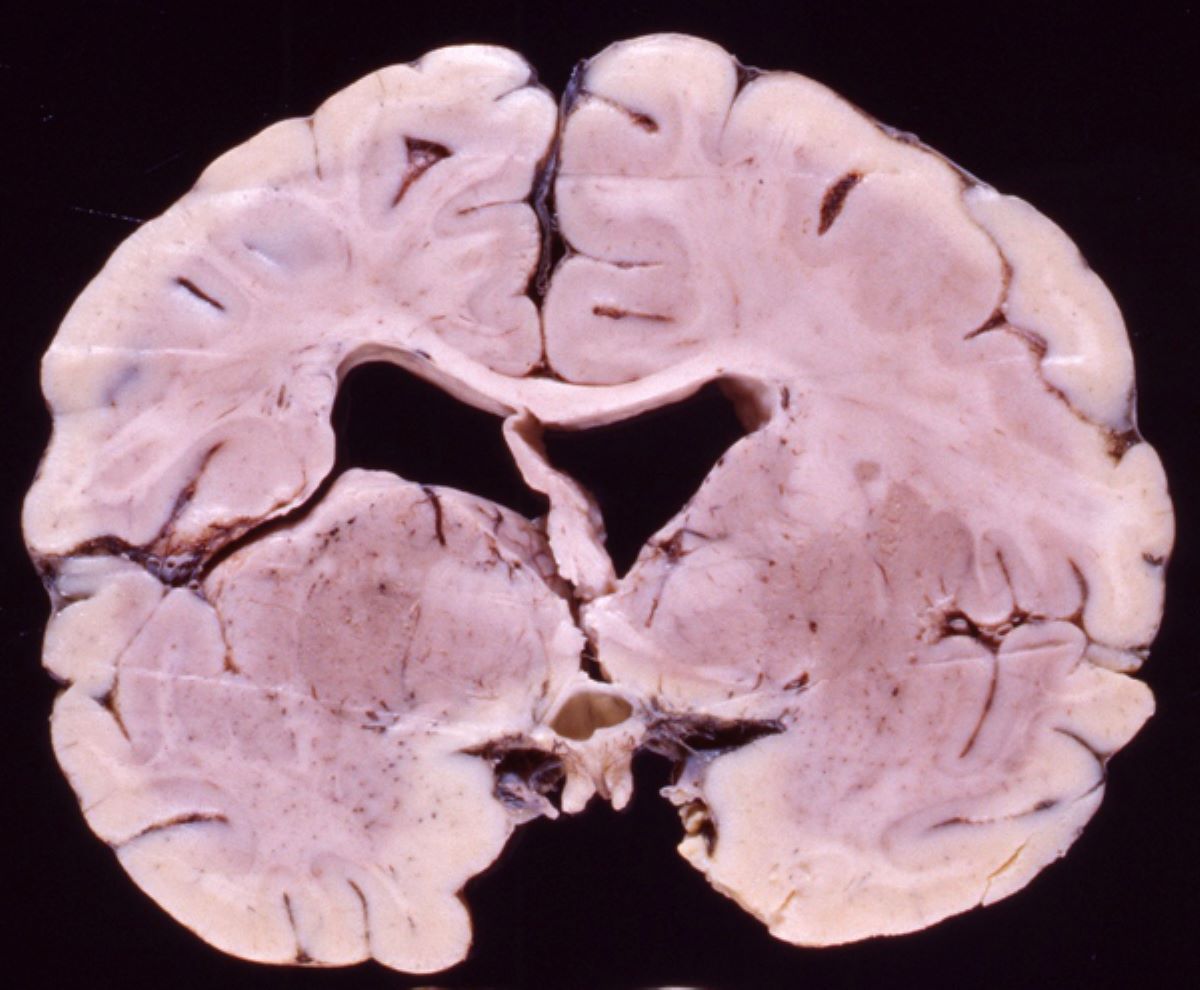
What is schizencephaly? Schizencephaly is a rare brain disorder where clefts or deep grooves form in the brain's cerebral hemispheres. These clefts can be present on one or both sides of the brain, leading to a variety of symptoms. Symptoms can include developmental delays, seizures, and muscle weakness. The severity of these symptoms often depends on the size and location of the clefts. Causes of schizencephaly are not fully understood, but it is believed to be linked to genetic mutations or environmental factors during pregnancy. Diagnosing this condition typically involves imaging tests like MRI scans. While there's no cure, treatment focuses on managing symptoms through therapies and medications. Understanding schizencephaly helps in providing better care and support for those affected. This condition highlights the complexity of brain development and the importance of early diagnosis and intervention.
Key Takeaways:
- Schizencephaly is a rare brain condition with clefts in the cerebral hemispheres, causing challenges in development. Early diagnosis and a multidisciplinary approach can help manage symptoms and improve quality of life.
- Individuals with schizencephaly may experience seizures, motor skill challenges, and cognitive impairments. However, with personalized care, family support, and access to community resources, they can lead fulfilling lives.
What is Schizencephaly?
Schizencephaly is a rare brain malformation characterized by abnormal slits or clefts in the cerebral hemispheres. These clefts can affect brain function and development. Understanding this condition can help in recognizing its impact on individuals and the challenges they face.
-
Rare Condition: Schizencephaly is considered a rare disorder, with only about 1.5 in 100,000 births affected. This rarity makes it a challenge for researchers to gather extensive data.
-
Clefts in the Brain: The defining feature of schizencephaly is the presence of clefts, which can be unilateral (one side) or bilateral (both sides). These clefts can vary in size and depth.
-
Developmental Origin: This condition arises during early fetal brain development, typically between the seventh and twelfth weeks of gestation. It is a result of disrupted neuronal migration.
-
Genetic Factors: While the exact cause is unknown, some cases have been linked to genetic mutations. However, most cases occur sporadically without a clear genetic pattern.
-
Types of Schizencephaly: There are two main types: open-lip and closed-lip. Open-lip schizencephaly involves a gap in the brain tissue, while closed-lip has a closed cleft with a thin layer of tissue covering it.
-
Symptoms Vary: Symptoms can range from mild to severe and may include developmental delays, motor skill challenges, and seizures. The severity often depends on the size and location of the clefts.
-
Seizure Disorders: Many individuals with schizencephaly experience seizures, which can be difficult to control and may require medication or other treatments.
-
Motor Impairments: Motor skills can be significantly affected, leading to difficulties with movement, coordination, and muscle tone.
-
Cognitive Challenges: Some individuals may experience cognitive impairments, affecting learning and intellectual development.
-
Speech and Language: Speech and language development can be delayed or impaired, requiring speech therapy and other interventions.
Diagnosing Schizencephaly
Diagnosing schizencephaly involves a combination of imaging techniques and clinical evaluations. Early diagnosis can help in managing symptoms and planning appropriate interventions.
-
MRI Scans: Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) is the primary tool used to diagnose schizencephaly. It provides detailed images of the brain's structure, revealing the presence and extent of clefts.
-
CT Scans: Computed Tomography (CT) scans can also be used, though they are less detailed than MRIs. They may be used in initial assessments.
-
Prenatal Diagnosis: In some cases, schizencephaly can be detected prenatally through advanced imaging techniques, allowing for early intervention planning.
-
Neurological Evaluations: Comprehensive neurological assessments help determine the impact of the condition on motor skills, cognition, and behavior.
-
Genetic Testing: While not always necessary, genetic testing can be conducted to identify potential genetic mutations associated with the condition.
Treatment and Management
Managing schizencephaly involves a multidisciplinary approach, focusing on alleviating symptoms and improving quality of life.
-
Seizure Management: Antiepileptic medications are commonly prescribed to control seizures. In some cases, surgical interventions may be considered.
-
Physical Therapy: Physical therapy helps improve motor skills, balance, and coordination, enhancing mobility and independence.
-
Occupational Therapy: Occupational therapy focuses on developing daily living skills and improving fine motor abilities.
-
Speech Therapy: Speech and language therapy is crucial for individuals with communication challenges, aiding in language development and articulation.
-
Educational Support: Tailored educational programs and support services can help address cognitive and learning difficulties.
-
Assistive Devices: Some individuals may benefit from assistive devices, such as braces or communication aids, to enhance mobility and communication.
-
Surgical Options: In certain cases, surgery may be considered to address specific issues, such as hydrocephalus or severe clefts.
-
Family Support: Support for families is essential, providing resources, counseling, and guidance to help them navigate the challenges associated with schizencephaly.
-
Regular Monitoring: Ongoing medical evaluations and monitoring are necessary to adjust treatments and interventions as needed.
Living with Schizencephaly
Living with schizencephaly presents unique challenges, but with the right support and interventions, individuals can lead fulfilling lives.
-
Individualized Care: Each person with schizencephaly is unique, requiring personalized care plans tailored to their specific needs and abilities.
-
Community Resources: Access to community resources and support groups can provide valuable connections and assistance for families and individuals.
-
Advocacy and Awareness: Raising awareness about schizencephaly can help promote understanding and support for those affected by the condition.
-
Adaptive Strategies: Developing adaptive strategies and coping mechanisms can empower individuals to overcome obstacles and achieve their goals.
-
Positive Outlook: Encouraging a positive outlook and fostering resilience can make a significant difference in the lives of those with schizencephaly.
-
Research and Advances: Ongoing research and advances in medical science continue to improve our understanding and treatment of schizencephaly.
-
Holistic Approach: A holistic approach to care, addressing physical, emotional, and social aspects, can enhance overall well-being.
-
Family Involvement: Active family involvement in care and decision-making is crucial for successful management and support.
-
Technology Integration: Integrating technology, such as communication devices and apps, can enhance learning and interaction.
-
Celebrating Achievements: Celebrating milestones and achievements, no matter how small, can boost confidence and motivation.
-
Building Independence: Encouraging independence and self-advocacy helps individuals with schizencephaly gain confidence and autonomy.
-
Inclusive Environments: Creating inclusive environments in schools and communities fosters acceptance and understanding.
-
Peer Support: Peer support and friendships can provide emotional support and a sense of belonging.
-
Professional Guidance: Access to professional guidance and expertise ensures that individuals receive the best possible care and support.
-
Long-term Planning: Long-term planning for education, employment, and independent living is essential for future success.
-
Hope and Progress: Despite challenges, hope and progress are possible with the right support, interventions, and determination.
The Final Word on Schizencephaly
Schizencephaly, a rare brain malformation, presents unique challenges and insights into human development. Understanding its causes, symptoms, and treatments is crucial for those affected and their families. Symptoms can vary widely, from mild to severe, impacting motor skills and cognitive abilities. Early diagnosis and intervention can make a significant difference in managing the condition. Therapies like physical, occupational, and speech therapy play a vital role in improving quality of life. Research continues to explore genetic factors and potential treatments, offering hope for future advancements. Support networks and resources are essential for families navigating this journey, providing guidance and community. While challenges exist, knowledge and support empower individuals to lead fulfilling lives. Schizencephaly reminds us of the brain's complexity and the resilience of those living with neurological differences. Stay informed, seek support, and advocate for continued research and awareness.
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
