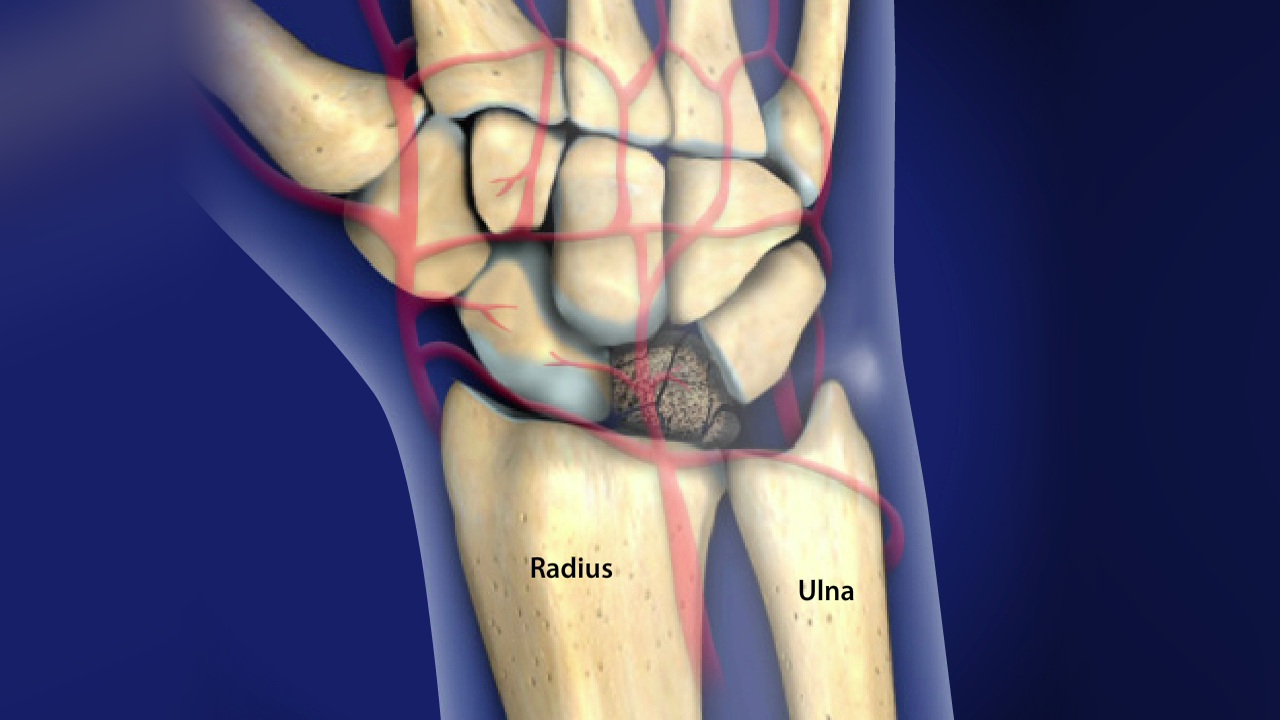
Kienböck's Disease is a rare condition affecting the lunate bone in the wrist, leading to its gradual collapse due to disrupted blood supply. Symptoms often include wrist pain, swelling, and limited motion, making daily tasks challenging. Early diagnosis is crucial for effective treatment, which can range from non-surgical options like splinting to surgical interventions. Risk factors include repetitive wrist trauma and certain anatomical variations. Understanding this disease helps in recognizing symptoms early and seeking appropriate care. This article delves into 40 key facts about Kienböck's Disease, providing a comprehensive overview for those affected and their loved ones.
Key Takeaways:
- Kienböck's Disease is a rare condition that affects the wrist, causing pain, stiffness, and reduced grip strength. Treatment options vary depending on the stage of the disease, and ongoing research aims to improve understanding and develop new treatments.
- If you have Kienböck's Disease, it's important to seek support, modify activities, and manage pain. Ongoing research is exploring genetic factors, advanced imaging, and potential stem cell therapy to improve treatment outcomes.
What is Kienböck's Disease?
Kienböck's Disease, also known as avascular necrosis of the lunate, is a rare condition affecting the wrist. It involves the progressive collapse of one of the small bones in the wrist due to a lack of blood supply. Here are some intriguing facts about this condition.
-
Named After Dr. Robert Kienböck: The disease was first described by Austrian radiologist Dr. Robert Kienböck in 1910.
-
Affects the Lunate Bone: The lunate bone, one of the eight small bones in the wrist, is primarily affected.
-
Rare Condition: It is considered a rare disease, with an estimated incidence of 0.5 to 1 per 100,000 people annually.
-
Common in Adults: Most commonly diagnosed in adults between the ages of 20 and 40.
-
More Common in Men: Men are more frequently affected than women.
Causes and Risk Factors
Understanding what causes Kienböck's Disease can help in identifying those at risk. While the exact cause remains unknown, several factors contribute to its development.
-
Trauma: Previous wrist injuries or fractures can increase the risk.
-
Blood Supply Issues: Problems with blood vessels supplying the lunate bone can lead to the disease.
-
Repetitive Stress: Jobs or activities that involve repetitive wrist movements may contribute.
-
Anatomical Variations: Certain anatomical differences, like a shorter ulna bone, can predispose individuals.
-
Genetic Factors: Family history may play a role, although this is less understood.
Symptoms and Diagnosis
Recognizing the symptoms early can lead to better management. Diagnosis often involves a combination of clinical evaluation and imaging studies.
-
Wrist Pain: Persistent pain in the wrist is a common symptom.
-
Swelling: Swelling around the wrist area may occur.
-
Stiffness: Reduced range of motion and stiffness in the wrist.
-
Weak Grip: Decreased grip strength is often reported.
-
X-rays: Initial imaging usually involves X-rays to identify bone changes.
-
MRI Scans: MRI scans provide detailed images of the bone and surrounding tissues.
-
CT Scans: CT scans can help in assessing the extent of bone collapse.
Stages of Kienböck's Disease
The disease progresses through several stages, each with distinct characteristics and treatment options.
-
Stage I: Early stage with normal X-rays but MRI shows changes in bone marrow.
-
Stage II: X-rays reveal sclerosis (hardening) of the lunate bone.
-
Stage IIIA: Lunate bone begins to collapse but the carpal alignment remains normal.
-
Stage IIIB: Further collapse with carpal misalignment.
-
Stage IV: Advanced stage with arthritis in the wrist joint.
Treatment Options
Treatment varies depending on the stage of the disease and aims to relieve pain and restore function.
-
Non-Surgical Options: Includes rest, splinting, and anti-inflammatory medications.
-
Physical Therapy: Helps in maintaining wrist mobility and strength.
-
Surgical Options: Surgery may be required in advanced stages.
-
Revascularization: Procedures to restore blood supply to the lunate bone.
-
Joint-Leveling Procedures: Adjusting the length of the radius or ulna bone to reduce stress on the lunate.
-
Proximal Row Carpectomy: Removal of the lunate and adjacent bones to relieve pain.
-
Wrist Fusion: Fusing the wrist bones to stabilize the joint.
Living with Kienböck's Disease
Managing daily life with Kienböck's Disease involves adapting activities and seeking support.
-
Activity Modification: Avoiding activities that strain the wrist.
-
Ergonomic Tools: Using tools designed to reduce wrist stress.
-
Pain Management: Techniques like heat, cold therapy, and medications.
-
Support Groups: Connecting with others who have the disease for emotional support.
-
Regular Check-Ups: Ongoing monitoring by a healthcare provider.
Research and Future Directions
Ongoing research aims to better understand and treat Kienböck's Disease.
-
Genetic Studies: Investigating the genetic factors involved.
-
Advanced Imaging: Developing better imaging techniques for early diagnosis.
-
New Treatments: Exploring novel surgical and non-surgical treatments.
-
Stem Cell Therapy: Researching the potential of stem cells to regenerate bone tissue.
-
Patient Registries: Collecting data to improve understanding and treatment outcomes.
-
Clinical Trials: Participating in trials to test new therapies and interventions.
Final Thoughts on Kienböck's Disease
Kienböck's Disease, a rare condition affecting the lunate bone in the wrist, can cause significant pain and limited mobility. Early diagnosis is crucial for effective treatment, which may include immobilization, medication, or surgery. Understanding the symptoms, such as wrist pain and swelling, helps in seeking timely medical advice. While the exact cause remains unclear, factors like trauma and blood supply issues play a role. Awareness and education about this condition can lead to better outcomes for those affected. If you suspect you might have Kienböck's Disease, consult a healthcare professional for proper evaluation and management. Remember, staying informed and proactive is key to maintaining wrist health and overall well-being.
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
