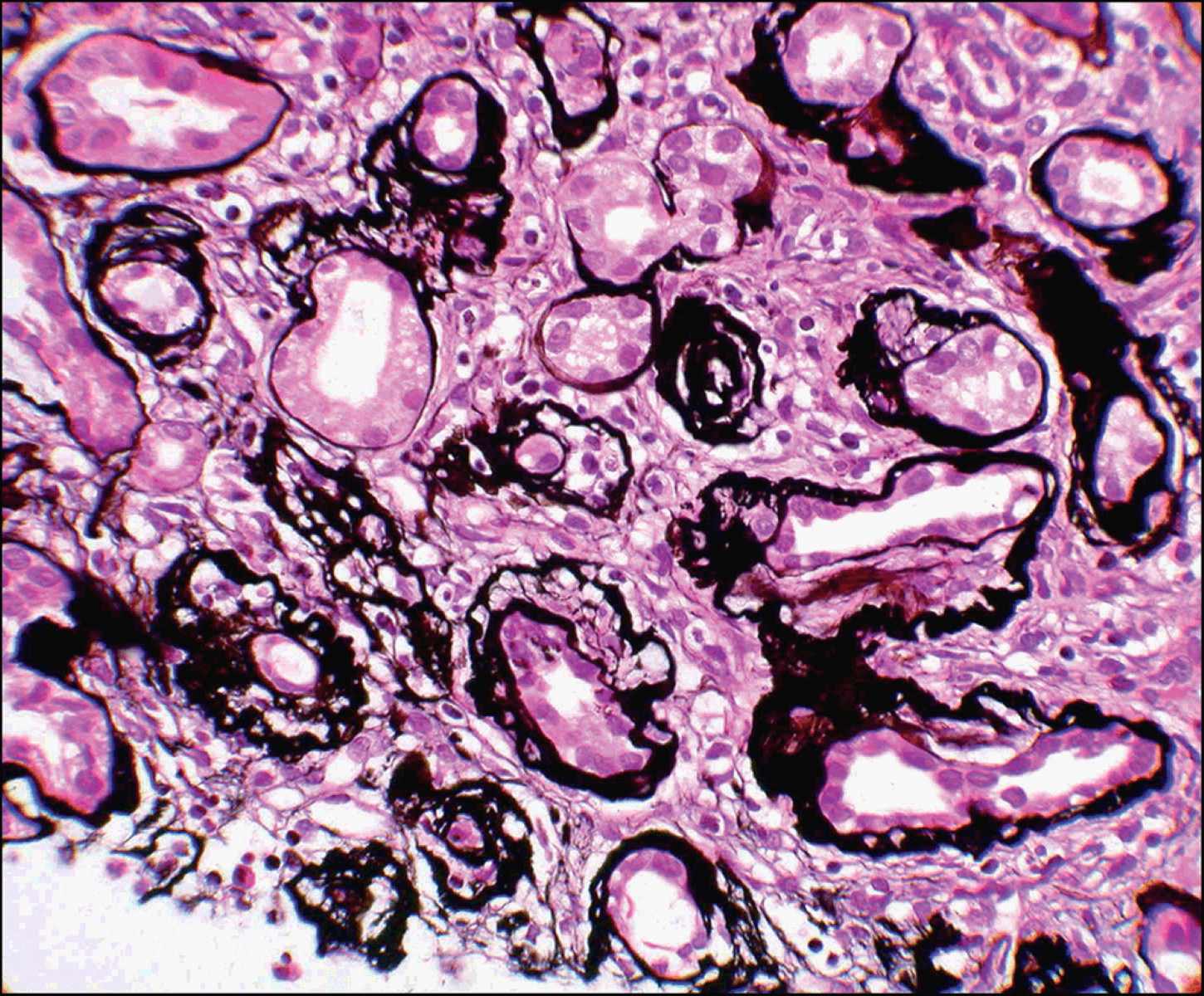
What is Juvenile Nephronophthisis? Juvenile Nephronophthisis is a rare genetic disorder affecting the kidneys, primarily in children and teenagers. This condition leads to progressive kidney failure due to the formation of cysts and fibrosis in the kidney tissue. Symptoms often include excessive thirst, frequent urination, and growth retardation. As the disease progresses, it can lead to end-stage renal disease, requiring dialysis or a kidney transplant. Caused by mutations in specific genes, this disorder is inherited in an autosomal recessive pattern, meaning both parents must carry a copy of the mutated gene. Diagnosing this condition involves genetic testing, ultrasound imaging, and sometimes a kidney biopsy. While there is no cure, early detection and management can help improve quality of life. Understanding Juvenile Nephronophthisis is crucial for families and healthcare providers to ensure timely intervention and support for affected individuals.
Key Takeaways:
- Juvenile Nephronophthisis is a rare genetic kidney disorder affecting children and teenagers, leading to kidney failure. Early diagnosis and genetic research offer hope for better treatments and outcomes.
- Living with Juvenile Nephronophthisis involves regular monitoring, dietary adjustments, and support networks. Public awareness and collaborative research efforts are crucial for improving patient care and outcomes.
Understanding Juvenile Nephronophthisis
Juvenile Nephronophthisis (NPH) is a rare genetic disorder affecting the kidneys, primarily in children and teenagers. This condition leads to kidney failure, often requiring dialysis or transplantation. Let's explore some fascinating facts about this condition.
-
Genetic Roots: Juvenile NPH is inherited in an autosomal recessive manner. This means both parents must carry a copy of the mutated gene for a child to be affected.
-
Ciliopathy Connection: NPH is classified as a ciliopathy, a group of disorders caused by defects in the cilia, tiny hair-like structures on cells. These defects disrupt normal kidney function.
-
Age of Onset: Symptoms typically appear between ages 4 and 15. This timing distinguishes juvenile NPH from infantile and adolescent forms.
-
Common Symptoms: Early signs include excessive thirst and urination, fatigue, and growth retardation. These symptoms often lead to a diagnosis.
-
Kidney Cysts: Small cysts form in the kidneys, leading to scarring and eventual kidney failure. These cysts are a hallmark of the disease.
-
Eye Problems: Some patients experience retinal degeneration, which can lead to vision issues. This is due to the shared genetic pathways affecting both kidneys and eyes.
-
Liver Involvement: In some cases, liver fibrosis occurs alongside kidney issues, complicating the condition further.
-
Diagnosis Challenges: Diagnosing NPH can be tricky due to its rarity and overlapping symptoms with other kidney diseases. Genetic testing is often used for confirmation.
-
No Cure: Currently, there is no cure for NPH. Treatment focuses on managing symptoms and delaying kidney failure.
-
Dialysis and Transplantation: As kidney function declines, dialysis or a kidney transplant becomes necessary to sustain life.
Genetic Insights and Research
Research into the genetic underpinnings of NPH is ongoing, offering hope for better treatments and understanding of the disease.
-
Gene Mutations: Mutations in several genes, including NPHP1, NPHP3, and NPHP4, are linked to NPH. These genes play roles in cilia function.
-
Genetic Testing: Advances in genetic testing have improved diagnosis accuracy, allowing for earlier intervention.
-
Research Models: Animal models, like mice, are used to study NPH, providing insights into disease mechanisms and potential therapies.
-
Potential Therapies: Researchers are exploring gene therapy and other innovative treatments to address the root causes of NPH.
-
Family Planning: Genetic counseling is recommended for families with a history of NPH to understand risks and options.
Living with Juvenile Nephronophthisis
Managing life with NPH involves a combination of medical care, lifestyle adjustments, and support systems.
-
Regular Monitoring: Patients require frequent check-ups to monitor kidney function and manage complications.
-
Dietary Adjustments: A kidney-friendly diet, low in salt and protein, can help manage symptoms and slow disease progression.
-
Hydration Importance: Staying well-hydrated is crucial, as the kidneys struggle to concentrate urine.
-
Support Networks: Connecting with support groups and communities can provide emotional and practical support for patients and families.
-
Education and Advocacy: Raising awareness about NPH can lead to better resources and support for those affected.
The Broader Impact of NPH
Understanding NPH extends beyond individual patients, influencing medical research and public health.
-
Rare Disease Awareness: NPH highlights the challenges faced by those with rare diseases, emphasizing the need for research and resources.
-
Interdisciplinary Research: Studying NPH involves collaboration across genetics, nephrology, and other fields, advancing knowledge in multiple areas.
-
Healthcare Costs: Managing NPH can be expensive, impacting families and healthcare systems.
-
Policy Implications: Advocacy for rare diseases can lead to policy changes that improve access to care and funding for research.
-
Global Perspective: NPH affects individuals worldwide, requiring international collaboration for research and treatment advancements.
Future Directions in NPH Research
The future of NPH research holds promise for new discoveries and improved patient outcomes.
-
Biomarker Development: Identifying biomarkers could lead to earlier diagnosis and targeted treatments.
-
Personalized Medicine: Tailoring treatments to individual genetic profiles may improve effectiveness and reduce side effects.
-
Stem Cell Research: Exploring stem cell therapies offers potential for regenerating damaged kidney tissue.
-
Public Awareness Campaigns: Increasing public knowledge about NPH can drive support for research and funding.
-
Collaborative Efforts: Partnerships between researchers, clinicians, and patient advocacy groups are crucial for advancing NPH research.
Challenges and Opportunities in NPH Management
Managing NPH presents unique challenges but also opportunities for innovation and improvement.
-
Early Intervention: Identifying and treating NPH early can delay kidney failure and improve quality of life.
-
Technological Advances: New technologies in genetic testing and imaging enhance diagnosis and monitoring.
-
Patient Empowerment: Educating patients about their condition empowers them to take an active role in their care.
-
Healthcare Access: Ensuring access to specialized care and treatments is vital for managing NPH effectively.
-
Research Funding: Securing funding for NPH research is essential for developing new treatments and understanding the disease better.
Community and Support for NPH Patients
Support networks play a crucial role in the lives of those affected by NPH, offering resources and connection.
-
Online Communities: Virtual support groups provide a platform for sharing experiences and advice.
-
Patient Advocacy Organizations: These groups work to raise awareness, fund research, and support patients and families.
-
Educational Resources: Providing information about NPH helps patients and families navigate the challenges of the disease.
-
Family Support: Families play a key role in managing NPH, offering emotional and practical support.
-
Hope for the Future: Advances in research and treatment offer hope for improved outcomes and quality of life for those with NPH.
Final Thoughts on Juvenile Nephronophthisis
Juvenile Nephronophthisis is a rare yet significant kidney disorder affecting children and teens. Understanding its symptoms, like excessive thirst and frequent urination, can lead to early diagnosis and better management. Genetic testing plays a crucial role in identifying this condition, as it often runs in families. While there's no cure, treatments focus on managing symptoms and slowing disease progression. Regular check-ups with healthcare professionals are vital for monitoring kidney function and overall health. Awareness and education about this disorder can help families and communities support affected individuals. By staying informed and proactive, those dealing with juvenile nephronophthisis can improve their quality of life and navigate the challenges it presents. Remember, knowledge is power, and being informed can make a world of difference for those facing this condition.
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
