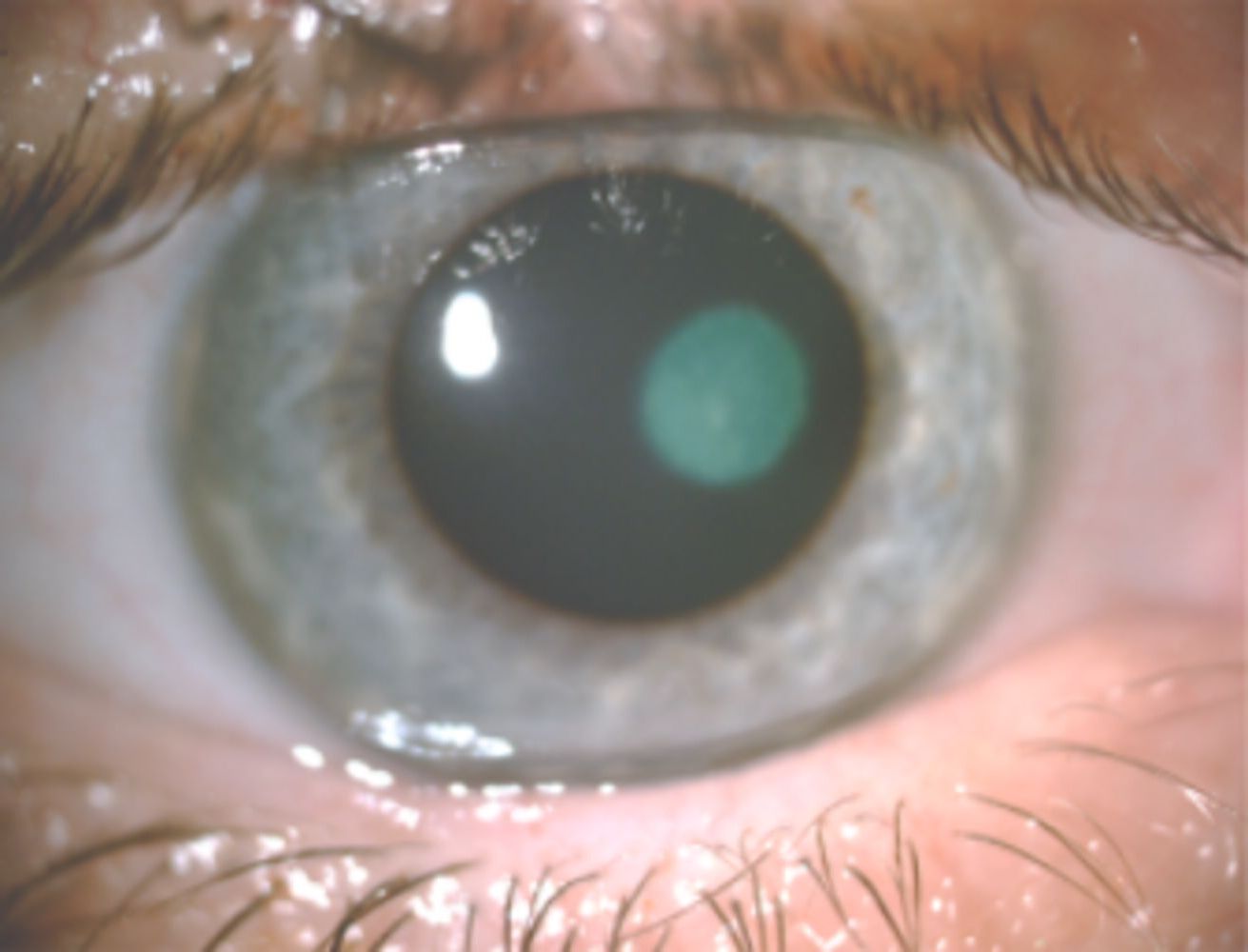
Herpetic keratitis is a serious eye infection caused by the herpes simplex virus (HSV). This condition can lead to vision loss if not treated promptly. Herpetic keratitis affects the cornea, the clear front part of the eye, causing pain, redness, and blurred vision. It's important to know that HSV can remain dormant in the body and reactivate, leading to recurrent infections. Herpetic keratitis is often mistaken for other eye conditions, making accurate diagnosis crucial. Treatments include antiviral medications and, in severe cases, surgery. Understanding the symptoms and risks associated with herpetic keratitis can help in seeking timely medical attention and preventing complications.
Key Takeaways:
- Herpetic keratitis is an eye infection caused by the herpes simplex virus, leading to pain, redness, and vision problems. It can recur and affect anyone, but good hygiene and regular check-ups are important for prevention and early management.
- Avoiding contact with infected individuals, maintaining good hygiene, and wearing sunglasses for UV protection can help prevent herpetic keratitis. Regular eye examinations are crucial for early detection and management.
What is Herpetic Keratitis?
Herpetic keratitis is an eye infection caused by the herpes simplex virus (HSV). This condition affects the cornea, the clear front part of the eye, leading to pain, redness, and vision problems. Here are some fascinating facts about herpetic keratitis.
- Herpes Simplex Virus: Herpetic keratitis is primarily caused by HSV-1, the same virus responsible for cold sores.
- Transmission: The virus can spread through direct contact with an infected person’s saliva or skin.
- Dormant Virus: HSV can remain dormant in the body and reactivate later, causing recurrent infections.
- Symptoms: Common symptoms include eye pain, redness, tearing, blurred vision, and sensitivity to light.
- Diagnosis: Doctors often diagnose herpetic keratitis through a slit-lamp examination and sometimes a viral culture or PCR test.
- Types: There are two main types: epithelial keratitis, affecting the outer layer of the cornea, and stromal keratitis, affecting deeper layers.
- Epithelial Keratitis: This type is more common and usually less severe, often presenting with dendritic ulcers.
- Stromal Keratitis: This type can lead to more serious complications, including scarring and vision loss.
- Treatment: Antiviral medications like acyclovir or ganciclovir are commonly used to treat herpetic keratitis.
- Steroid Use: In some cases, corticosteroids may be prescribed to reduce inflammation, but they must be used cautiously.
- Recurrence: Herpetic keratitis can recur, with some patients experiencing multiple episodes over their lifetime.
- Prevention: Avoiding contact with infected individuals and maintaining good hygiene can help prevent the spread of HSV.
- Complications: Potential complications include corneal scarring, secondary bacterial infections, and glaucoma.
- Vision Loss: Severe cases can lead to permanent vision loss if not treated promptly.
- Corneal Transplant: In extreme cases, a corneal transplant may be necessary to restore vision.
- Immune Response: The body’s immune response to HSV can contribute to corneal damage.
- Age Factor: Herpetic keratitis can affect individuals of any age but is more common in adults.
- Gender: Both men and women are equally susceptible to herpetic keratitis.
- Global Prevalence: Herpetic keratitis is a global issue, affecting millions of people worldwide.
- Reactivation Triggers: Stress, illness, and UV light exposure can trigger reactivation of the virus.
- Cold Sores Connection: Individuals with a history of cold sores are at higher risk of developing herpetic keratitis.
- Contact Lenses: Wearing contact lenses can increase the risk of complications if infected with HSV.
- Eye Trauma: Previous eye injuries can make the cornea more susceptible to HSV infection.
- Immune System: A weakened immune system can increase the risk of herpetic keratitis.
- Seasonal Variation: Some studies suggest that herpetic keratitis may be more common in certain seasons.
- Genetic Factors: Genetic predisposition may play a role in susceptibility to HSV infections.
- Public Health: Herpetic keratitis is a significant public health concern due to its potential for causing vision impairment.
- Research: Ongoing research aims to develop better treatments and vaccines for HSV.
- Awareness: Increased awareness and education about herpetic keratitis can help reduce its incidence.
- Support Groups: Support groups and online communities can provide valuable information and support for those affected.
- Eye Protection: Wearing sunglasses can help protect the eyes from UV light, reducing the risk of reactivation.
- Regular Check-ups: Regular eye examinations are crucial for early detection and management of herpetic keratitis.
- Antiviral Resistance: Some strains of HSV may develop resistance to antiviral medications, complicating treatment.
- Alternative Therapies: Researchers are exploring alternative therapies, including natural remedies and new drug formulations.
- Vaccination: While there is no vaccine for HSV, research is ongoing to develop one.
- Psychological Impact: Chronic herpetic keratitis can have a significant psychological impact on patients.
- Healthcare Costs: The condition can lead to substantial healthcare costs due to frequent doctor visits and treatments.
- Work and School: Herpetic keratitis can affect a person’s ability to work or attend school due to vision problems.
- Quality of Life: Managing herpetic keratitis can be challenging, impacting overall quality of life.
- Future Outlook: Advances in medical research hold promise for better management and potential cures for herpetic keratitis.
Final Thoughts on Herpetic Keratitis
Herpetic keratitis, caused by the herpes simplex virus, is a significant eye condition. It can lead to serious complications if not treated promptly. Symptoms like eye pain, redness, and blurred vision should never be ignored. Early diagnosis and treatment are crucial for preventing long-term damage. Antiviral medications often help manage the condition, but regular follow-ups with an eye specialist are essential.
Understanding the risk factors, such as a weakened immune system or previous herpes infections, can help in taking preventive measures. Practicing good hygiene and avoiding contact with infected individuals also play a key role in prevention.
Stay informed and proactive about eye health. If you experience any symptoms, seek medical advice immediately. Your vision is precious, and taking steps to protect it from conditions like herpetic keratitis is vital.
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
