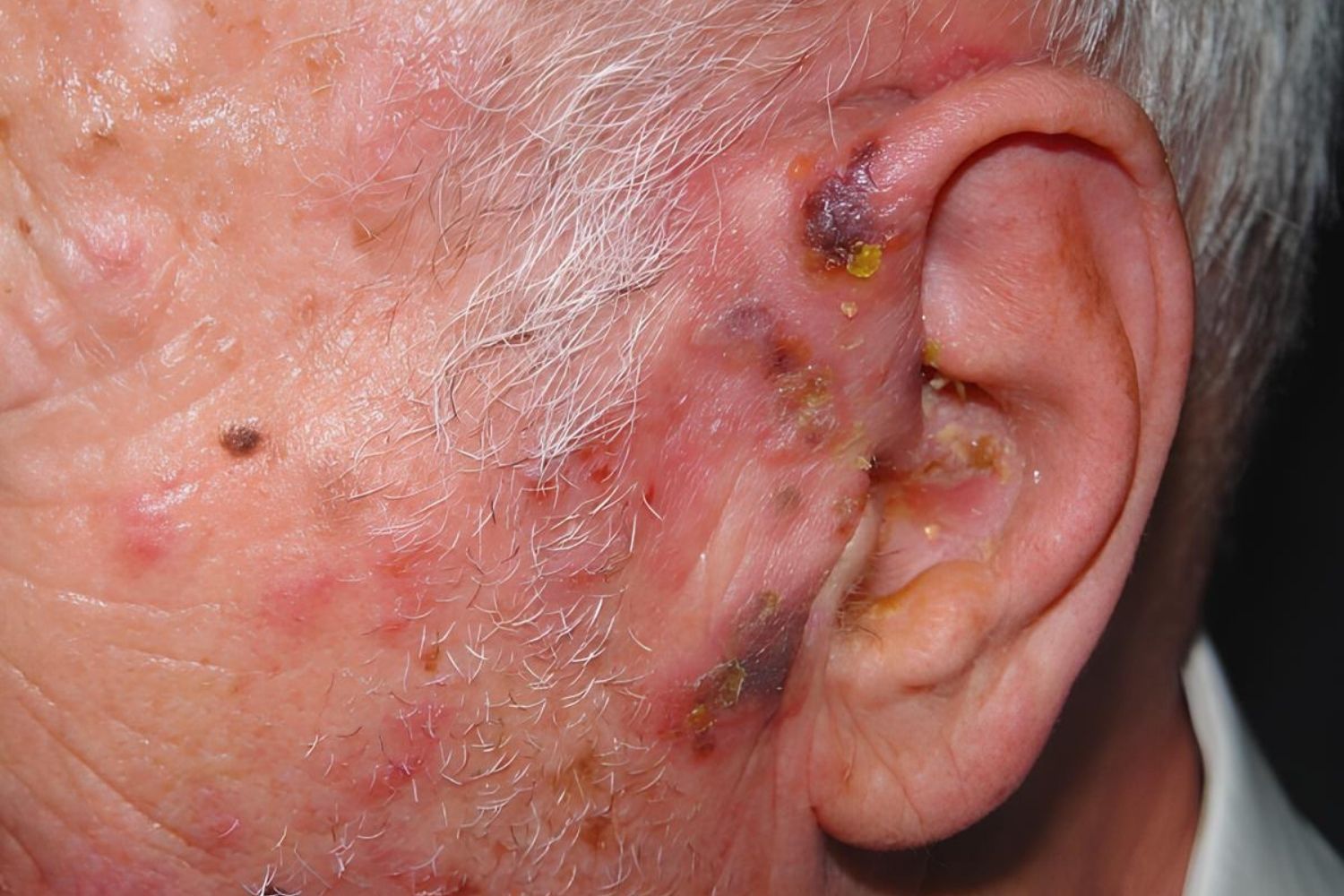
Herpes Zoster Oticus, also known as Ramsay Hunt Syndrome, is a viral infection affecting the ear. This condition occurs when the varicella-zoster virus, the same virus responsible for chickenpox and shingles, reactivates in the facial nerve near the ear. Symptoms can include painful rashes, facial paralysis, and hearing loss. Early diagnosis and treatment are crucial to prevent complications and long-term effects. Understanding the symptoms, causes, and treatments can help manage this condition effectively. In this post, we will explore 40 essential facts about Herpes Zoster Oticus, providing you with a comprehensive overview of this medical condition.
Key Takeaways:
- Herpes Zoster Oticus, caused by the same virus as chickenpox and shingles, can lead to ear pain, facial paralysis, and even hearing loss. Treatment and early diagnosis are crucial for managing this rare condition.
- Understanding risk factors and preventive measures, such as vaccination and maintaining a healthy lifestyle, can help reduce the likelihood of developing Herpes Zoster Oticus. Awareness and ongoing research aim to improve treatments and support for those affected.
What is Herpes Zoster Oticus?
Herpes Zoster Oticus, also known as Ramsay Hunt Syndrome Type II, is a viral infection affecting the ear. It is caused by the varicella-zoster virus, the same virus responsible for chickenpox and shingles. Here are some intriguing facts about this condition.
-
Caused by Varicella-Zoster Virus: This virus remains dormant in the body after a chickenpox infection and can reactivate years later.
-
Affects Facial Nerves: The virus can infect the facial nerve near one of your ears, leading to painful rashes and facial paralysis.
-
Ramsay Hunt Syndrome: Named after neurologist James Ramsay Hunt, who first described the syndrome in 1907.
-
Symptoms Include Ear Pain: Severe ear pain is often the first symptom, followed by a rash.
-
Hearing Loss: Some patients experience hearing loss in the affected ear.
-
Vertigo: Dizziness or vertigo can occur due to the virus affecting the inner ear.
-
Taste Loss: Some individuals lose their sense of taste on the front two-thirds of the tongue.
-
Blisters in the Ear: Painful blisters can appear inside the ear canal and on the outer ear.
How is Herpes Zoster Oticus Diagnosed?
Diagnosis involves a combination of clinical examination and medical history. Here are some key points about the diagnostic process.
-
Physical Examination: Doctors look for characteristic rashes and blisters in and around the ear.
-
Neurological Exam: A neurological exam checks for facial muscle weakness.
-
Hearing Tests: Audiometry tests assess hearing loss.
-
Balance Tests: Balance tests help determine if vertigo is present.
-
Blood Tests: Blood tests can detect antibodies against the varicella-zoster virus.
-
MRI Scans: MRI scans may be used to rule out other causes of facial paralysis.
Treatment Options for Herpes Zoster Oticus
Treatment aims to reduce symptoms and prevent complications. Here are some common treatments.
-
Antiviral Medications: Drugs like acyclovir or valacyclovir can help reduce the severity and duration of the infection.
-
Corticosteroids: Steroids like prednisone can reduce inflammation and swelling.
-
Pain Relievers: Over-the-counter pain relievers or prescription medications can manage pain.
-
Antihistamines: These can help control vertigo and dizziness.
-
Eye Care: If facial paralysis affects blinking, eye drops or ointments can prevent eye damage.
-
Physical Therapy: Exercises can help improve facial muscle strength and coordination.
Complications of Herpes Zoster Oticus
If left untreated, Herpes Zoster Oticus can lead to several complications. Here are some potential issues.
-
Permanent Hearing Loss: Some patients may experience irreversible hearing loss.
-
Chronic Pain: Postherpetic neuralgia can cause long-lasting pain even after the rash heals.
-
Facial Weakness: Permanent facial muscle weakness or paralysis can occur.
-
Eye Damage: Inability to close the eye can lead to corneal damage and vision loss.
-
Secondary Infections: Blisters can become infected with bacteria, leading to further complications.
Prevention and Risk Factors
Understanding risk factors and preventive measures can help reduce the likelihood of developing Herpes Zoster Oticus.
-
Age: Older adults are more susceptible to the virus reactivating.
-
Weakened Immune System: Conditions like HIV/AIDS or cancer can increase risk.
-
Stress: High stress levels can trigger the virus to reactivate.
-
Vaccination: The shingles vaccine can reduce the risk of developing Herpes Zoster Oticus.
-
Healthy Lifestyle: Maintaining a healthy lifestyle can strengthen the immune system.
Interesting Facts About Herpes Zoster Oticus
Here are some lesser-known facts that might surprise you.
-
Not Contagious: The condition itself isn’t contagious, but the virus can spread to someone who hasn’t had chickenpox or the vaccine.
-
Historical Cases: Famous composer Ludwig van Beethoven is believed to have suffered from this condition.
-
Rare Condition: It’s a relatively rare condition, affecting about 5 in 100,000 people annually.
-
Gender Differences: Men and women are equally affected by Herpes Zoster Oticus.
-
Seasonal Trends: Some studies suggest a higher incidence in the spring and summer months.
-
Animal Studies: Research on animals has helped understand the virus’s behavior and potential treatments.
-
Psychological Impact: The condition can lead to anxiety and depression due to its symptoms and complications.
-
Support Groups: Many online and local support groups offer help and advice for those affected.
-
Research Advances: Ongoing research aims to develop better treatments and preventive measures.
-
Awareness Campaigns: Health organizations run campaigns to raise awareness about shingles and related conditions.
Final Thoughts on Herpes Zoster Oticus
Herpes Zoster Oticus, also known as Ramsay Hunt Syndrome, is a condition that can cause significant discomfort and hearing loss. Understanding the symptoms, such as ear pain, facial paralysis, and hearing issues, is crucial for early diagnosis. Prompt treatment with antiviral medications and corticosteroids can help reduce complications and speed up recovery. It's also important to note that vaccination against the varicella-zoster virus can lower the risk of developing this condition. If you or someone you know experiences symptoms, seeking medical advice quickly can make a big difference. Stay informed, take preventive measures, and don't hesitate to consult healthcare professionals for guidance. Knowledge and timely action are key to managing and overcoming Herpes Zoster Oticus effectively.
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
