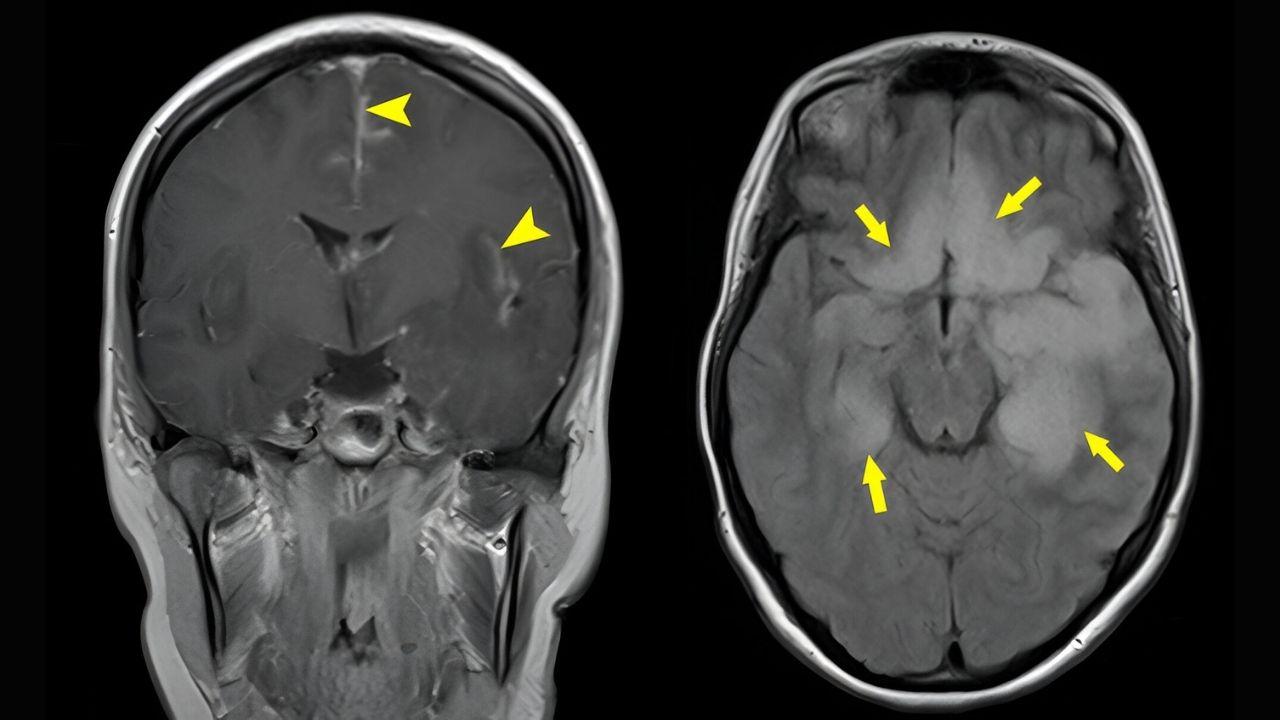
Herpes Simplex Encephalitis (HSE) is a rare but serious brain infection caused by the herpes simplex virus. Affecting around 2 in every million people annually, it can lead to severe neurological damage if not treated promptly. Symptoms often include fever, headache, confusion, seizures, and changes in personality or behavior. Early diagnosis and treatment with antiviral medications are crucial for improving outcomes. Understanding HSE is vital for recognizing its signs and seeking timely medical help. This article will provide 40 essential facts about HSE, covering its causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment, and prevention, to help you stay informed and prepared.
Key Takeaways:
- Herpes Simplex Encephalitis is a rare but serious brain condition caused by the herpes virus, leading to neurological damage and long-term effects.
- Good hygiene, avoiding close contact with active HSV infections, and maintaining a healthy immune system can help reduce the risk of Herpes Simplex Encephalitis.
What is Herpes Simplex Encephalitis?
Herpes Simplex Encephalitis (HSE) is a rare but serious condition caused by the herpes simplex virus (HSV). It affects the brain, leading to inflammation and potentially severe neurological damage. Here are some key facts about this condition:
-
Herpes Simplex Virus: HSE is primarily caused by HSV-1, the same virus responsible for cold sores.
-
Rare Occurrence: HSE is rare, with an estimated incidence of 1 in 250,000 to 500,000 individuals per year.
-
Age Groups: It can affect any age group but is most common in children and older adults.
-
Symptoms: Early symptoms include fever, headache, confusion, and seizures.
-
Diagnosis: Diagnosis often involves MRI scans, EEGs, and lumbar punctures to detect HSV DNA in cerebrospinal fluid.
How Does Herpes Simplex Encephalitis Spread?
Understanding how HSE spreads can help in prevention and early detection. Here are some important points:
-
HSV Transmission: HSV-1 is typically spread through oral contact, such as kissing or sharing utensils.
-
Latency: The virus can remain dormant in the body and reactivate later, potentially leading to HSE.
-
Direct Brain Infection: HSE occurs when HSV travels to the brain, often through the olfactory nerve.
-
Immune System Role: A weakened immune system can increase the risk of HSV reactivation and HSE.
-
Genetic Factors: Certain genetic mutations may predispose individuals to HSE.
Treatment Options for Herpes Simplex Encephalitis
Timely treatment is crucial for improving outcomes in HSE patients. Here are the main treatment strategies:
-
Antiviral Therapy: Acyclovir is the primary antiviral medication used to treat HSE.
-
Early Intervention: Starting antiviral treatment early can significantly reduce mortality and morbidity.
-
Supportive Care: Patients may require supportive care, including hydration, fever management, and seizure control.
-
Rehabilitation: Post-recovery rehabilitation may be necessary to address neurological deficits.
-
Monitoring: Regular follow-up is essential to monitor for potential relapses or complications.
Complications and Long-term Effects
HSE can lead to various complications and long-term effects. Here are some of the potential issues:
-
Neurological Damage: Severe cases can result in permanent brain damage.
-
Cognitive Impairment: Survivors may experience memory loss, difficulty concentrating, and other cognitive issues.
-
Behavioral Changes: Some patients may exhibit changes in behavior, such as increased irritability or depression.
-
Seizures: Persistent seizures can occur even after the initial infection is treated.
-
Mortality Rate: Without treatment, HSE has a high mortality rate, estimated at 70%.
Preventive Measures
While HSE cannot always be prevented, certain measures can reduce the risk. Here are some preventive strategies:
-
Good Hygiene: Practicing good hygiene, such as regular handwashing, can reduce the spread of HSV.
-
Avoiding Contact: Avoiding close contact with individuals who have active HSV infections can lower risk.
-
Immune System Health: Maintaining a healthy immune system through proper diet, exercise, and sleep can help prevent HSV reactivation.
-
Vaccination Research: Ongoing research aims to develop vaccines against HSV, which could potentially prevent HSE.
-
Public Awareness: Increasing public awareness about HSE and its symptoms can lead to earlier diagnosis and treatment.
Research and Future Directions
Research continues to improve our understanding and treatment of HSE. Here are some current and future research directions:
-
Genetic Studies: Research into genetic factors that predispose individuals to HSE is ongoing.
-
New Antivirals: Development of new antiviral medications aims to improve treatment outcomes.
-
Immunotherapy: Investigating the role of immunotherapy in treating HSE is a current research focus.
-
Neuroprotective Agents: Research into neuroprotective agents seeks to minimize brain damage caused by HSE.
-
Clinical Trials: Ongoing clinical trials are testing new treatments and interventions for HSE.
Impact on Quality of Life
HSE can significantly impact a patient's quality of life. Here are some ways it can affect individuals:
-
Daily Functioning: Cognitive and behavioral changes can affect daily functioning and independence.
-
Employment: Neurological deficits may impact a person's ability to work.
-
Social Relationships: Changes in behavior and cognition can strain social relationships.
-
Mental Health: Survivors may experience anxiety, depression, and other mental health issues.
-
Support Systems: Strong support systems, including family and healthcare providers, are crucial for recovery.
Case Studies and Real-life Examples
Real-life examples and case studies can provide valuable insights into HSE. Here are some notable cases:
-
Famous Cases: Some well-documented cases of HSE have raised public awareness about the condition.
-
Survivor Stories: Stories of HSE survivors highlight the challenges and triumphs of living with the condition.
-
Medical Literature: Case studies in medical literature provide detailed accounts of HSE diagnosis and treatment.
-
Educational Resources: Educational resources and support groups can help patients and families navigate life with HSE.
-
Advocacy: Advocacy efforts aim to increase funding for HSE research and support for affected individuals.
Final Thoughts on Herpes Simplex Encephalitis
Herpes Simplex Encephalitis (HSE) is a serious condition that requires immediate medical attention. Understanding the symptoms, causes, and treatment options can make a significant difference in outcomes. Early diagnosis and prompt antiviral therapy are crucial for reducing the risk of long-term complications.
HSE can affect anyone, but certain groups, like newborns and immunocompromised individuals, are at higher risk. Awareness and education about this condition can help in early detection and treatment.
If you or someone you know shows signs of encephalitis, such as severe headache, fever, confusion, or seizures, seek medical help right away. Knowledge is power, and being informed about HSE can save lives. Stay vigilant, stay informed, and prioritize health.
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
