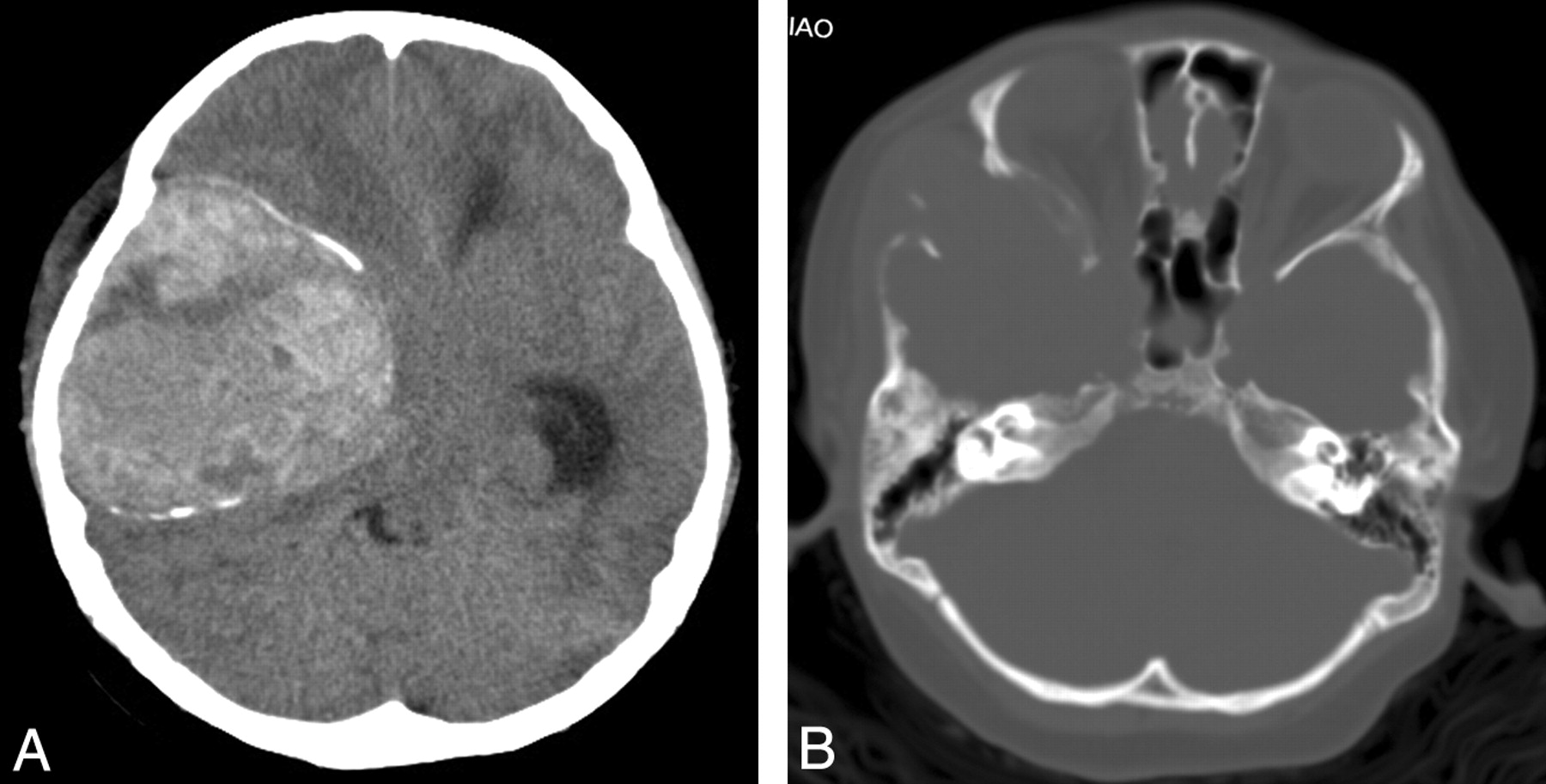
Hemangiopericytoma is a rare type of tumor that originates from pericytes, the cells surrounding blood vessels. These tumors can appear anywhere in the body but are most commonly found in the legs, pelvis, and retroperitoneum. Hemangiopericytomas can be benign or malignant, and their behavior can be unpredictable. Symptoms often depend on the tumor's location and size, ranging from pain and swelling to more severe complications if it presses on vital organs. Early detection and treatment are crucial for better outcomes. This article will provide 40 intriguing facts about hemangiopericytoma, shedding light on its characteristics, diagnosis, and treatment options.
Key Takeaways:
- Hemangiopericytoma is a rare tumor that can occur anywhere in the body, causing varied symptoms. Early detection and complete surgical removal significantly improve the prognosis, while ongoing research aims to develop more effective treatments.
- Managing life with hemangiopericytoma involves addressing physical and emotional challenges. Support groups, physical therapy, and regular monitoring are crucial for patients and their families.
What is Hemangiopericytoma?
Hemangiopericytoma is a rare type of tumor that originates from pericytes, the cells surrounding blood vessels. These tumors can occur anywhere in the body but are most commonly found in the legs, pelvis, and retroperitoneum.
- Hemangiopericytomas were first described by Dr. Arthur Purdy Stout and Dr. Margaret Murray in 1942.
- These tumors are known for their unpredictable behavior, ranging from benign to highly malignant.
- Hemangiopericytomas can affect individuals of any age but are most commonly diagnosed in adults between 30 and 50 years old.
- The exact cause of hemangiopericytomas remains unknown, though genetic mutations are suspected to play a role.
- Symptoms vary depending on the tumor's location, often including pain, swelling, and functional impairment.
Diagnosis and Detection
Identifying hemangiopericytomas can be challenging due to their rarity and varied presentation. Medical professionals use several diagnostic tools to confirm their presence.
- Imaging studies like MRI and CT scans are crucial for detecting hemangiopericytomas and assessing their size and location.
- A biopsy is often necessary to confirm the diagnosis, where a tissue sample is examined under a microscope.
- Hemangiopericytomas can sometimes be mistaken for other types of soft tissue tumors, making accurate diagnosis essential.
- Immunohistochemistry, a lab technique that uses antibodies to detect specific proteins in cells, helps differentiate hemangiopericytomas from other tumors.
- Genetic testing may reveal mutations in the NAB2-STAT6 gene fusion, commonly associated with hemangiopericytomas.
Treatment Options
Treating hemangiopericytomas involves a combination of surgical and non-surgical approaches. The choice of treatment depends on the tumor's size, location, and malignancy.
- Surgery is the primary treatment for hemangiopericytomas, aiming to remove the tumor entirely.
- Radiation therapy may be used post-surgery to eliminate any remaining cancer cells and reduce the risk of recurrence.
- Chemotherapy is less commonly used but may be considered for aggressive or metastatic hemangiopericytomas.
- Targeted therapy, which uses drugs to target specific cancer cells, is an emerging treatment option for hemangiopericytomas.
- Clinical trials are ongoing to explore new and more effective treatments for this rare tumor.
Prognosis and Survival Rates
The prognosis for individuals with hemangiopericytomas varies widely based on several factors, including the tumor's location, size, and malignancy.
- Early detection and complete surgical removal of the tumor significantly improve the prognosis.
- The five-year survival rate for localized hemangiopericytomas is approximately 70-80%.
- Tumors that have metastasized or are inoperable have a poorer prognosis, with a five-year survival rate of around 30-40%.
- Regular follow-up and monitoring are essential for detecting any recurrence or metastasis.
- Advances in medical research and treatment options continue to improve the outlook for individuals with hemangiopericytomas.
Hemangiopericytoma in Different Body Parts
Hemangiopericytomas can develop in various parts of the body, each presenting unique challenges and symptoms.
- In the brain, hemangiopericytomas can cause headaches, seizures, and neurological deficits.
- Spinal hemangiopericytomas may lead to back pain, weakness, and sensory changes.
- Tumors in the lungs can result in coughing, shortness of breath, and chest pain.
- Abdominal hemangiopericytomas might cause abdominal pain, bloating, and changes in bowel habits.
- Hemangiopericytomas in the extremities often present as a painless mass, but can cause discomfort if they compress nerves or blood vessels.
Research and Future Directions
Ongoing research aims to better understand hemangiopericytomas and develop more effective treatments.
- Scientists are investigating the genetic and molecular mechanisms underlying hemangiopericytomas to identify potential therapeutic targets.
- Research into the tumor microenvironment may reveal new strategies to inhibit tumor growth and spread.
- Advances in imaging technology are improving the accuracy of hemangiopericytoma diagnosis and monitoring.
- Collaboration between researchers, clinicians, and patients is essential for advancing hemangiopericytoma research.
- Patient registries and biobanks are valuable resources for studying hemangiopericytomas and developing personalized treatment approaches.
Living with Hemangiopericytoma
Managing life with hemangiopericytoma involves addressing both physical and emotional challenges.
- Support groups and counseling can help patients and their families cope with the diagnosis and treatment process.
- Physical therapy may be beneficial for individuals recovering from surgery or experiencing functional impairments.
- Nutritional support and a healthy lifestyle can improve overall well-being and aid in recovery.
- Pain management strategies, including medications and alternative therapies, are important for maintaining quality of life.
- Regular follow-up appointments and monitoring are crucial for detecting any recurrence or complications.
Rare and Unique Cases
Some hemangiopericytomas present unique challenges due to their unusual locations or behaviors.
- Pediatric hemangiopericytomas are extremely rare, requiring specialized care and treatment.
- Hemangiopericytomas of the liver are uncommon and can mimic other liver tumors, complicating diagnosis.
- Tumors that recur multiple times or metastasize to distant organs pose significant treatment challenges.
- Hemangiopericytomas in the orbit (eye socket) can affect vision and eye movement, necessitating careful management.
- Rarely, hemangiopericytomas may produce hormones or other substances that cause systemic symptoms, adding complexity to their treatment.
Final Thoughts on Hemangiopericytoma
Hemangiopericytoma, a rare vascular tumor, often leaves people with more questions than answers. Understanding its origins, symptoms, and treatment options can make a huge difference. Early detection and proper medical care are crucial for managing this condition.
Patients should always consult with healthcare professionals for personalized advice. Staying informed about the latest research and treatment advancements can offer hope and better outcomes.
Remember, knowledge is power. By learning more about hemangiopericytoma, you’re better equipped to handle its challenges. Keep asking questions, stay curious, and never hesitate to seek support from medical experts and support groups.
In the end, awareness and education are your best tools in navigating the complexities of this rare tumor. Stay proactive, and you’ll be better prepared to face whatever comes your way.
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
