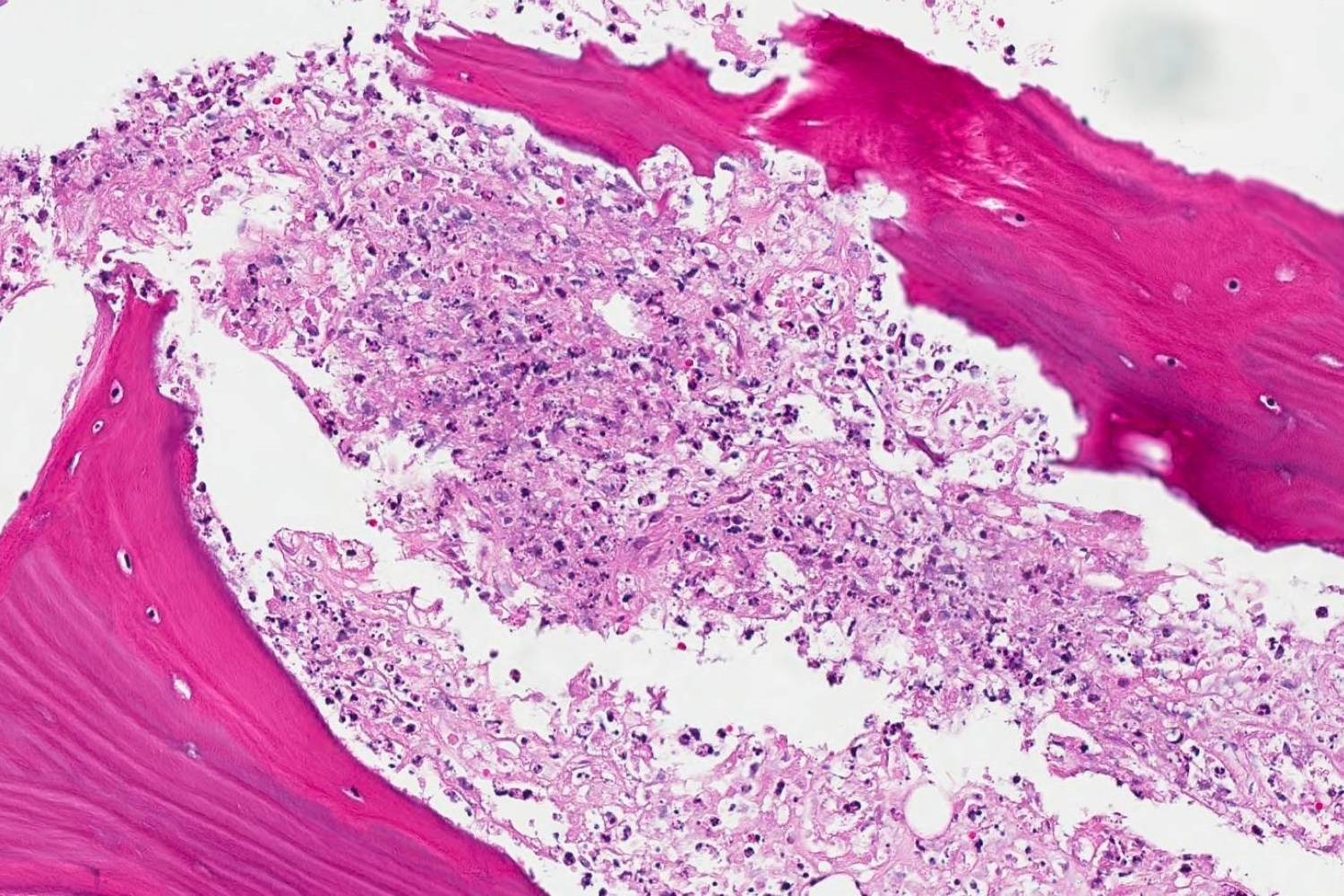
Brodie abscess might sound like a complicated medical term, but it’s simpler than you think. Named after Sir Benjamin Brodie, this condition involves a type of bone infection. Brodie abscess usually affects the long bones, like those in your legs or arms. It’s often seen in children and young adults. The infection causes a cavity in the bone, filled with pus. Symptoms can include pain, swelling, and sometimes fever. Diagnosing it often requires X-rays or MRI scans. Treatment usually involves antibiotics, and sometimes surgery. Understanding Brodie abscess can help you recognize symptoms early and seek proper care.
Key Takeaways:
- Brodie abscess is a rare bone infection primarily affecting children and young adults. Prompt treatment and good hygiene can help prevent this condition, which is named after a British surgeon.
- Recognizing localized pain, swelling, and tenderness are key to diagnosing Brodie abscess. Treatment involves antibiotics, surgical drainage, and long-term therapy, with good prognosis when managed properly.
Understanding Brodie Abscess
Brodie abscess is a rare type of bone infection. Named after British surgeon Sir Benjamin Collins Brodie, it primarily affects children and young adults. Here are some intriguing facts about this medical condition.
-
Named After Sir Benjamin Collins Brodie: The condition was first described by Sir Benjamin Collins Brodie in 1832.
-
Common in Long Bones: It typically occurs in the long bones of the body, such as the tibia and femur.
-
Subacute Osteomyelitis: Brodie abscess is a form of subacute osteomyelitis, meaning it develops more slowly than acute osteomyelitis.
-
Affects Children and Young Adults: Most cases are found in children and young adults, particularly those aged 2 to 15 years.
-
Rare in Adults: While it can occur in adults, it is much less common.
Symptoms and Diagnosis
Recognizing the symptoms and diagnosing Brodie abscess can be challenging. Here are some key points to help understand this aspect.
-
Localized Pain: The most common symptom is localized pain, often worse at night.
-
Swelling and Tenderness: Swelling and tenderness over the affected bone are also common.
-
No Systemic Symptoms: Unlike acute osteomyelitis, Brodie abscess usually does not cause fever or other systemic symptoms.
-
X-rays for Diagnosis: X-rays can show a well-defined lytic lesion, often with a sclerotic border.
-
MRI and CT Scans: MRI and CT scans provide more detailed images and can help in the diagnosis.
Causes and Risk Factors
Understanding what causes Brodie abscess and the risk factors involved can help in prevention and early detection.
-
Bacterial Infection: The abscess is usually caused by a bacterial infection, most commonly Staphylococcus aureus.
-
Trauma: Trauma to the bone can increase the risk of developing a Brodie abscess.
-
Weakened Immune System: Individuals with a weakened immune system are at higher risk.
-
Previous Infections: A history of previous bone infections can be a risk factor.
-
Poor Blood Supply: Areas of bone with poor blood supply are more susceptible.
Treatment Options
Treating Brodie abscess involves a combination of medical and sometimes surgical interventions.
-
Antibiotics: The primary treatment is antibiotics to fight the bacterial infection.
-
Surgical Drainage: In some cases, surgical drainage of the abscess is necessary.
-
Bone Grafting: Bone grafting may be required if there is significant bone loss.
-
Long-term Antibiotics: Long-term antibiotic therapy may be needed to ensure the infection is completely eradicated.
-
Follow-up Care: Regular follow-up care is essential to monitor for recurrence.
Complications and Prognosis
While treatable, Brodie abscess can lead to complications if not managed properly.
-
Chronic Infection: If not treated, the infection can become chronic.
-
Bone Deformity: Chronic infection can lead to bone deformity and growth disturbances in children.
-
Sepsis: Although rare, the infection can spread and lead to sepsis.
-
Joint Involvement: The infection can spread to nearby joints, causing septic arthritis.
-
Good Prognosis with Treatment: With proper treatment, the prognosis is generally good.
Historical Cases and Research
Historical cases and ongoing research provide valuable insights into Brodie abscess.
-
First Described in 1832: Sir Benjamin Collins Brodie first described the condition in 1832.
-
Early Treatments: Early treatments included surgical drainage and the use of poultices.
-
Modern Research: Modern research focuses on improving diagnostic techniques and treatment options.
-
Case Studies: Numerous case studies have been published, providing insights into the condition.
-
Advancements in Imaging: Advances in imaging technology have improved the ability to diagnose and treat Brodie abscess.
Prevention and Awareness
Prevention and awareness are key to reducing the incidence of Brodie abscess.
-
Prompt Treatment of Infections: Prompt treatment of bone infections can prevent the development of Brodie abscess.
-
Good Hygiene: Good hygiene practices can reduce the risk of infections.
-
Protective Gear: Using protective gear during sports and activities can prevent bone injuries.
-
Regular Check-ups: Regular medical check-ups can help in early detection.
-
Awareness Campaigns: Awareness campaigns can educate the public about the condition.
Interesting Facts
Here are some additional interesting facts about Brodie abscess.
-
Named After a Surgeon: It is one of the few medical conditions named after a surgeon.
-
Rare Condition: It is considered a rare condition, with only a few cases reported each year.
-
Historical Treatments: Historical treatments included the use of leeches and poultices.
-
Modern Advances: Modern advances in medicine have significantly improved the treatment and prognosis.
-
Educational Value: Studying Brodie abscess provides valuable insights into bone infections and their management.
Final Thoughts on Brodie Abscess
Brodie abscess, a type of subacute osteomyelitis, often presents a diagnostic challenge due to its subtle symptoms and slow progression. Recognizing the signs early, such as localized pain and swelling, can lead to timely intervention and better outcomes. Treatment typically involves antibiotics and sometimes surgical drainage, depending on the severity. Understanding the risk factors, like a history of trauma or weakened immune system, can help in prevention and early detection. Regular follow-ups and imaging studies are crucial to ensure the infection is fully resolved. Staying informed and vigilant can make a significant difference in managing this condition effectively. Remember, if you suspect a Brodie abscess, consult a healthcare professional promptly for proper diagnosis and treatment. Knowledge and awareness are your best tools in combating this rare but serious infection. Stay proactive about your health!
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
