Scapholunate Advanced Collapse (SLAC) is a wrist condition that can cause significant pain and dysfunction. But what exactly is SLAC? In simple terms, it's a type of arthritis that develops due to untreated or poorly healed injuries between the scaphoid and lunate bones in the wrist. Over time, this leads to joint instability and cartilage wear, resulting in chronic pain and limited movement. Why should you care about SLAC? If left untreated, it can severely impact daily activities like gripping, lifting, or even typing. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options can help manage this condition effectively. Ready to learn more? Let's dive into 30 essential facts about SLAC that will give you a comprehensive understanding of this wrist ailment.
Key Takeaways:
- Scapholunate Advanced Collapse (SLAC) is a common form of wrist arthritis caused by untreated ligament injuries. It progresses through four stages, leading to severe pain and limited wrist movement.
- Trauma, repetitive stress, age, and previous wrist injuries are key factors contributing to SLAC. Recognizing symptoms early and seeking accurate diagnosis are crucial for effective management and treatment.
What is Scapholunate Advanced Collapse?
Scapholunate Advanced Collapse (SLAC) is a type of wrist arthritis that occurs due to untreated or poorly treated scapholunate ligament injuries. This condition can lead to severe pain and limited wrist movement. Here are some interesting facts about SLAC.
-
SLAC is the most common form of wrist arthritis. It often results from chronic scapholunate ligament injuries.
-
The scapholunate ligament connects the scaphoid and lunate bones. These bones are part of the eight small bones in the wrist.
-
SLAC progresses through four stages. Each stage shows increasing severity of arthritis and joint damage.
-
Stage 1 involves the scapholunate joint. This is the initial stage where the ligament injury begins to affect the joint.
-
Stage 2 affects the radioscaphoid joint. This stage shows more significant wear and tear on the wrist.
-
Stage 3 involves the capitolunate joint. By this stage, the arthritis has spread to more areas of the wrist.
-
Stage 4 is the most severe. It involves pancarpal arthritis, affecting nearly all wrist joints.
Causes and Risk Factors
Understanding what leads to SLAC can help in prevention and early diagnosis. Here are some key causes and risk factors.
-
Trauma is a leading cause. Injuries like falls or direct blows can damage the scapholunate ligament.
-
Repetitive stress can contribute. Activities that put constant strain on the wrist increase the risk.
-
Age is a significant factor. SLAC is more common in older adults due to wear and tear over time.
-
Previous wrist injuries increase risk. Those with a history of wrist fractures or sprains are more susceptible.
-
Occupational hazards play a role. Jobs requiring heavy manual labor or repetitive wrist movements can lead to SLAC.
Symptoms of SLAC
Recognizing the symptoms early can lead to better management and treatment. Here are some common signs.
-
Wrist pain is the most common symptom. The pain often worsens with activity and improves with rest.
-
Swelling around the wrist. This can be a sign of inflammation due to arthritis.
-
Limited range of motion. Difficulty in moving the wrist can indicate advanced stages of SLAC.
-
Weakness in the wrist. This can make it hard to grip objects or perform daily tasks.
-
Clicking or popping sounds. These noises can occur when moving the wrist.
Diagnosis and Imaging
Accurate diagnosis is crucial for effective treatment. Here are some methods used to diagnose SLAC.
-
Physical examination is the first step. Doctors check for tenderness, swelling, and range of motion.
-
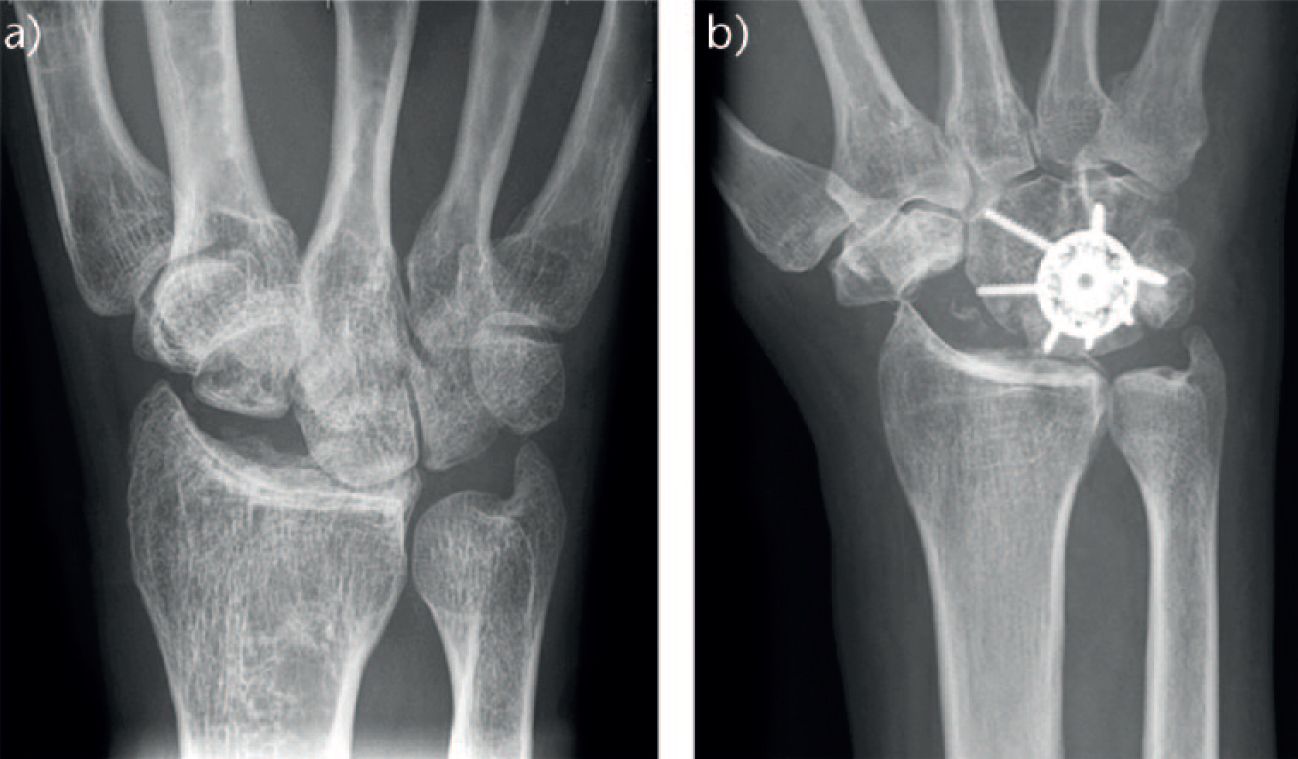
X-rays are commonly used. They help visualize the extent of arthritis and joint damage.
-
MRI scans provide detailed images. These scans can show soft tissue damage and early stages of SLAC.
-
CT scans offer a 3D view. They are useful for assessing the severity of bone and joint damage.
-
Arthroscopy is a minimally invasive procedure. It allows doctors to look inside the joint and confirm the diagnosis.
Treatment Options
Various treatments can help manage SLAC and improve quality of life. Here are some common options.
-
Non-surgical treatments include medications. Pain relievers and anti-inflammatory drugs can reduce symptoms.
-
Physical therapy can be beneficial. Exercises help improve strength and flexibility in the wrist.
-
Wrist splints provide support. They can help immobilize the wrist and reduce pain.
-
Corticosteroid injections offer temporary relief. These injections reduce inflammation and pain.
-
Surgical options are available for severe cases. Procedures like partial wrist fusion or proximal row carpectomy can help.
Living with SLAC
Managing SLAC involves lifestyle changes and ongoing care. Here are some tips for living with this condition.
-
Regular exercise is important. Low-impact activities like swimming can help maintain wrist mobility.
-
Avoid activities that strain the wrist. This includes heavy lifting or repetitive motions.
-
Use ergonomic tools and devices. These can reduce stress on the wrist during daily activities.
Final Thoughts on Scapholunate Advanced Collapse
Scapholunate Advanced Collapse (SLAC) is a serious wrist condition that affects many people. Understanding SLAC helps in recognizing symptoms early and seeking appropriate treatment. This condition often results from untreated scapholunate ligament injuries, leading to arthritis and wrist pain. Early diagnosis and intervention can prevent severe complications. Treatments range from non-surgical options like splinting and medication to surgical procedures for advanced cases. Knowing the facts about SLAC empowers patients to make informed decisions about their health. If you suspect you have symptoms of SLAC, consult a healthcare professional for a proper diagnosis and treatment plan. Taking proactive steps can significantly improve quality of life and wrist function. Stay informed, stay proactive, and prioritize your wrist health.
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
