Rothmund–Thomson Syndrome (RTS) is a rare genetic disorder that affects many parts of the body. Characterized by skin rashes, sparse hair, and small stature, RTS can also lead to skeletal abnormalities and an increased risk of cancer. Caused by mutations in the RECQL4 gene, this condition is inherited in an autosomal recessive pattern. Symptoms usually appear in infancy or early childhood, making early diagnosis crucial. Understanding RTS helps in managing its symptoms and improving the quality of life for those affected. In this post, we'll explore 30 intriguing facts about Rothmund–Thomson Syndrome, shedding light on its complexities and the latest research.
Key Takeaways:
- Rothmund–Thomson Syndrome is a rare genetic disorder that affects the skin, bones, and increases the risk of certain cancers. Early detection and management are crucial for individuals with RTS.
- Individuals with RTS may experience skin rashes, skeletal abnormalities, and an increased risk of bone and skin cancers. While there is no cure, treatments can help manage symptoms and improve quality of life.
What is Rothmund–Thomson Syndrome?
Rothmund–Thomson Syndrome (RTS) is a rare genetic disorder that affects multiple parts of the body. It is characterized by skin abnormalities, skeletal issues, and an increased risk of certain cancers. Here are some intriguing facts about this condition:
- RTS is caused by mutations in the RECQL4 gene, which plays a crucial role in DNA repair and maintenance.
- The syndrome is inherited in an autosomal recessive manner, meaning both parents must carry the mutated gene for a child to be affected.
- RTS was first described by August von Rothmund in 1868 and later by Matthew Thomson in 1936.
- The condition is extremely rare, with fewer than 400 cases reported worldwide.
- RTS affects both males and females equally, with no known preference for any particular ethnic group.
Symptoms and Diagnosis
Understanding the symptoms and how RTS is diagnosed can help in early detection and management. Here are some key points:
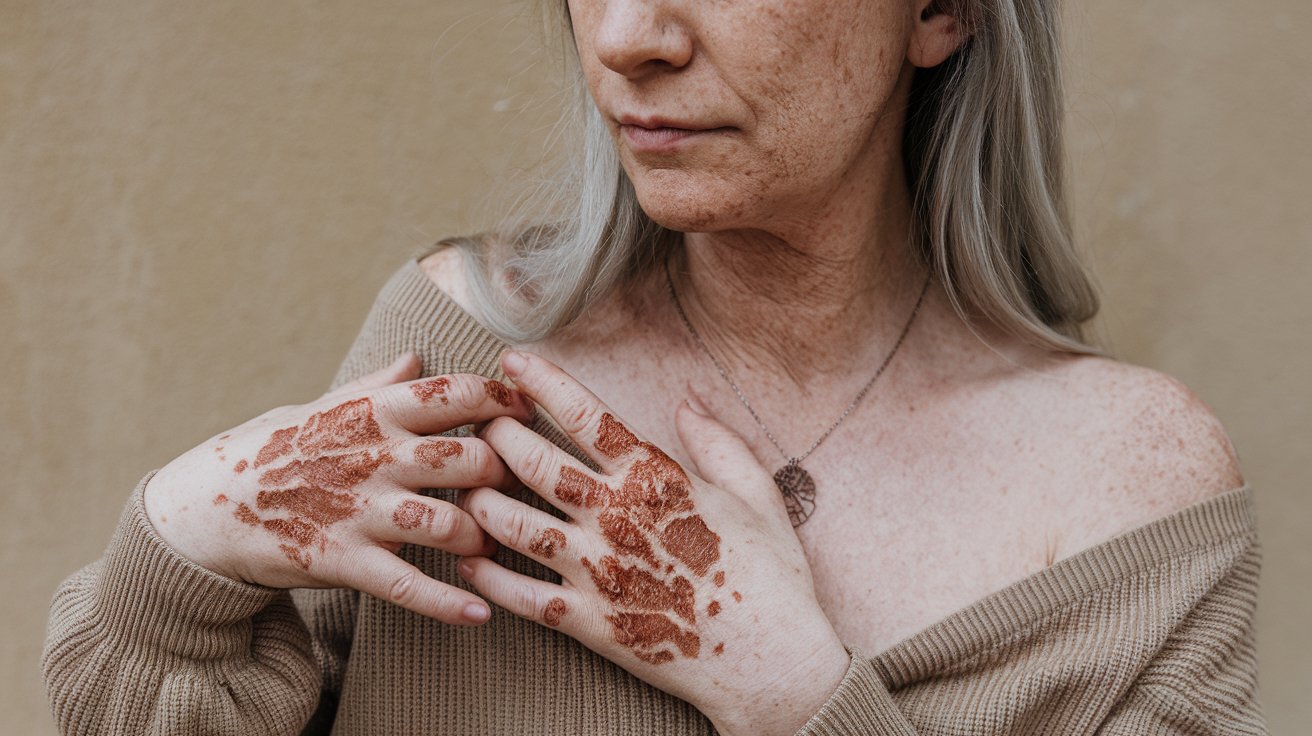
- One of the earliest signs of RTS is a distinctive rash that appears in infancy, usually between 3 to 6 months of age.
- The rash often starts on the cheeks and spreads to other parts of the body, eventually leading to areas of skin atrophy and pigmentation changes.
- Individuals with RTS may have sparse scalp hair, eyebrows, and eyelashes.
- Skeletal abnormalities are common, including short stature, radial ray defects, and osteopenia.
- Dental anomalies such as delayed tooth eruption and missing teeth are frequently observed.
- Eye problems, including cataracts and glaucoma, can occur in RTS patients.
- Gastrointestinal issues like chronic diarrhea and constipation are also reported.
- Diagnosis is typically based on clinical evaluation, family history, and genetic testing to identify RECQL4 mutations.
Complications and Risks
RTS comes with several complications and risks that require careful monitoring. Here are some important facts:
- Individuals with RTS have an increased risk of developing osteosarcoma, a type of bone cancer.
- There is also a heightened risk of skin cancer, particularly squamous cell carcinoma.
- Regular cancer screenings are essential for early detection and treatment.
- RTS patients may experience delayed puberty and fertility issues.
- Immune system abnormalities can make individuals more susceptible to infections.
- Some patients may develop poikiloderma, a condition characterized by skin discoloration, telangiectasia, and atrophy.
- Lifespan can be affected by the severity of complications, but many individuals with RTS live into adulthood.
Treatment and Management
While there is no cure for RTS, various treatments can help manage symptoms and improve quality of life. Here are some approaches:
- Dermatological treatments, including topical creams and sun protection, can help manage skin issues.
- Orthopedic interventions may be necessary for skeletal abnormalities.
- Regular dental check-ups and orthodontic treatments can address dental problems.
- Eye examinations are crucial for early detection and treatment of cataracts and glaucoma.
- Gastrointestinal issues may require dietary modifications and medications.
- Hormone therapy can be considered for delayed puberty and fertility issues.
- Genetic counseling is recommended for families with a history of RTS to understand the risks and implications.
Living with Rothmund–Thomson Syndrome
Living with RTS involves adapting to various challenges and finding ways to thrive. Here are some insights:
- Support groups and counseling can provide emotional support and practical advice for individuals and families.
- Educational accommodations may be necessary to address learning difficulties and physical limitations.
- Advances in medical research continue to improve our understanding of RTS, offering hope for better treatments and outcomes in the future.
Final Thoughts on Rothmund–Thomson Syndrome
Rothmund–Thomson Syndrome (RTS) is a rare genetic disorder that affects many parts of the body. People with RTS often have skin abnormalities, sparse hair, and skeletal issues. They may also face an increased risk of developing certain cancers, particularly osteosarcoma. Early diagnosis and regular medical check-ups are crucial for managing symptoms and reducing complications.
Understanding RTS helps in providing better care and support for those affected. Awareness can lead to more research and improved treatments. If you or someone you know shows signs of RTS, consult a healthcare professional for proper diagnosis and management.
Knowledge about rare conditions like RTS empowers individuals and communities. It fosters empathy and encourages proactive health measures. Stay informed, spread awareness, and support those living with Rothmund–Thomson Syndrome.
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.