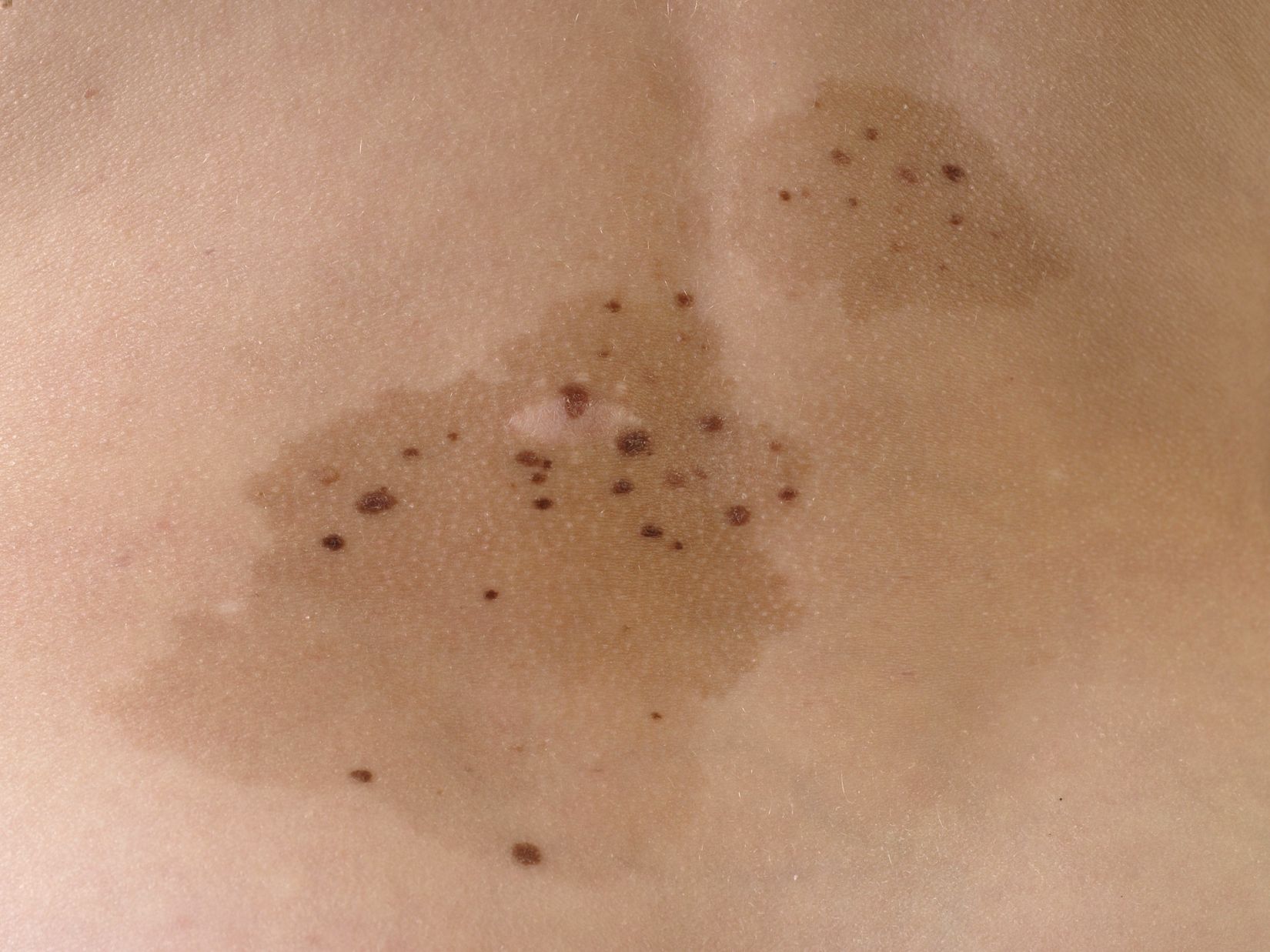
Phacomatosis Pigmentokeratotica is a rare skin disorder that combines features of two conditions: an epidermal nevus and a speckled lentiginous nevus. This condition often presents at birth or early childhood, characterized by dark, pigmented patches and rough, wart-like growths on the skin. Phacomatosis Pigmentokeratotica can sometimes be associated with other abnormalities, including neurological and skeletal issues. Understanding this condition is crucial for early diagnosis and management, ensuring affected individuals receive appropriate care. In this blog post, we will explore 30 intriguing facts about Phacomatosis Pigmentokeratotica, shedding light on its symptoms, causes, and treatment options. Whether you're a medical professional, a student, or simply curious, these facts will provide valuable insights into this unique skin disorder.
Key Takeaways:
- Phacomatosis Pigmentokeratotica is a rare genetic disorder with pigmented and keratotic skin lesions. Early diagnosis and regular monitoring are crucial for managing symptoms and improving quality of life.
- Genetic factors play a significant role in Phacomatosis Pigmentokeratotica. While there is no cure, ongoing research holds promise for better understanding and potential targeted therapies.
What is Phacomatosis Pigmentokeratotica?
Phacomatosis Pigmentokeratotica is a rare genetic disorder characterized by the presence of both pigmented and keratotic skin lesions. These lesions are often present at birth and can vary in size, shape, and color. This condition is part of a group of disorders known as phacomatoses, which involve abnormalities in the skin, eyes, and nervous system.
- Phacomatosis Pigmentokeratotica is a congenital condition, meaning it is present at birth.
- The disorder is extremely rare, with only a few hundred cases reported worldwide.
- It involves the presence of both pigmented (dark) and keratotic (thickened) skin lesions.
- These lesions can appear anywhere on the body but are most commonly found on the trunk and limbs.
- The condition is part of a group of disorders known as phacomatoses, which also include neurofibromatosis and tuberous sclerosis.
Symptoms and Diagnosis
Understanding the symptoms and how Phacomatosis Pigmentokeratotica is diagnosed can help in managing the condition effectively. Early diagnosis is crucial for better outcomes.
- Symptoms often include pigmented nevi (moles) and sebaceous nevi (yellowish, wart-like growths).
- Lesions can vary in size, from a few millimeters to several centimeters.
- The condition can sometimes be associated with neurological abnormalities, such as seizures or developmental delays.
- Diagnosis is typically made based on clinical examination and the appearance of the skin lesions.
- A biopsy may be performed to confirm the diagnosis and rule out other conditions.
Genetic Factors
Genetics play a significant role in the development of Phacomatosis Pigmentokeratotica. Understanding these factors can provide insight into the condition's origins and potential treatments.
- The disorder is believed to result from a genetic mosaicism, where two different cell lines exist within the same individual.
- It is not usually inherited but occurs as a sporadic mutation.
- Genetic testing can sometimes identify the specific mutations involved.
- Research is ongoing to better understand the genetic mechanisms behind the condition.
- Family history is generally not a risk factor due to the sporadic nature of the mutations.
Treatment Options
While there is no cure for Phacomatosis Pigmentokeratotica, various treatments can help manage the symptoms and improve quality of life.
- Treatment often involves the removal of skin lesions, either surgically or through laser therapy.
- Regular monitoring of the lesions is important to check for any changes that might indicate malignancy.
- Neurological symptoms, if present, are managed with medications and supportive therapies.
- Physical therapy may be recommended for individuals with developmental delays or motor difficulties.
- Psychological support can be beneficial for coping with the emotional impact of the condition.
Living with Phacomatosis Pigmentokeratotica
Living with a rare condition like Phacomatosis Pigmentokeratotica can be challenging, but understanding and support can make a significant difference.
- Regular follow-ups with a dermatologist are essential for ongoing management.
- Support groups and online communities can provide valuable resources and emotional support.
- Education about the condition is important for both the affected individuals and their families.
- Adaptive devices and therapies can help manage physical limitations.
- Awareness campaigns can help increase understanding and reduce stigma associated with the condition.
Research and Future Directions
Ongoing research is crucial for improving the understanding and treatment of Phacomatosis Pigmentokeratotica. Future advancements hold promise for better management of the condition.
- Researchers are exploring the genetic basis of the disorder to develop targeted therapies.
- Clinical trials are being conducted to test new treatments and interventions.
- Advances in genetic engineering may offer potential for correcting the underlying mutations in the future.
- Collaboration between researchers, clinicians, and patient advocacy groups is essential for progress.
- Increased awareness and funding for research can accelerate the development of new treatments and improve outcomes for those affected by Phacomatosis Pigmentokeratotica.
Final Thoughts on Phacomatosis Pigmentokeratotica
Phacomatosis Pigmentokeratotica, a rare genetic condition, combines skin pigmentation and wart-like growths. Understanding its symptoms, causes, and treatments can help those affected manage their condition better. Early diagnosis and regular check-ups are crucial for monitoring potential complications, such as neurological issues or skin cancer. While there's no cure, treatments like laser therapy, surgery, and topical medications can improve quality of life. Raising awareness about this condition can lead to better support and resources for patients and their families. If you or someone you know shows signs of Phacomatosis Pigmentokeratotica, consult a healthcare professional for proper diagnosis and management. Knowledge and proactive care make a significant difference in living with this condition. Stay informed, seek support, and remember, you're not alone in this journey.
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
