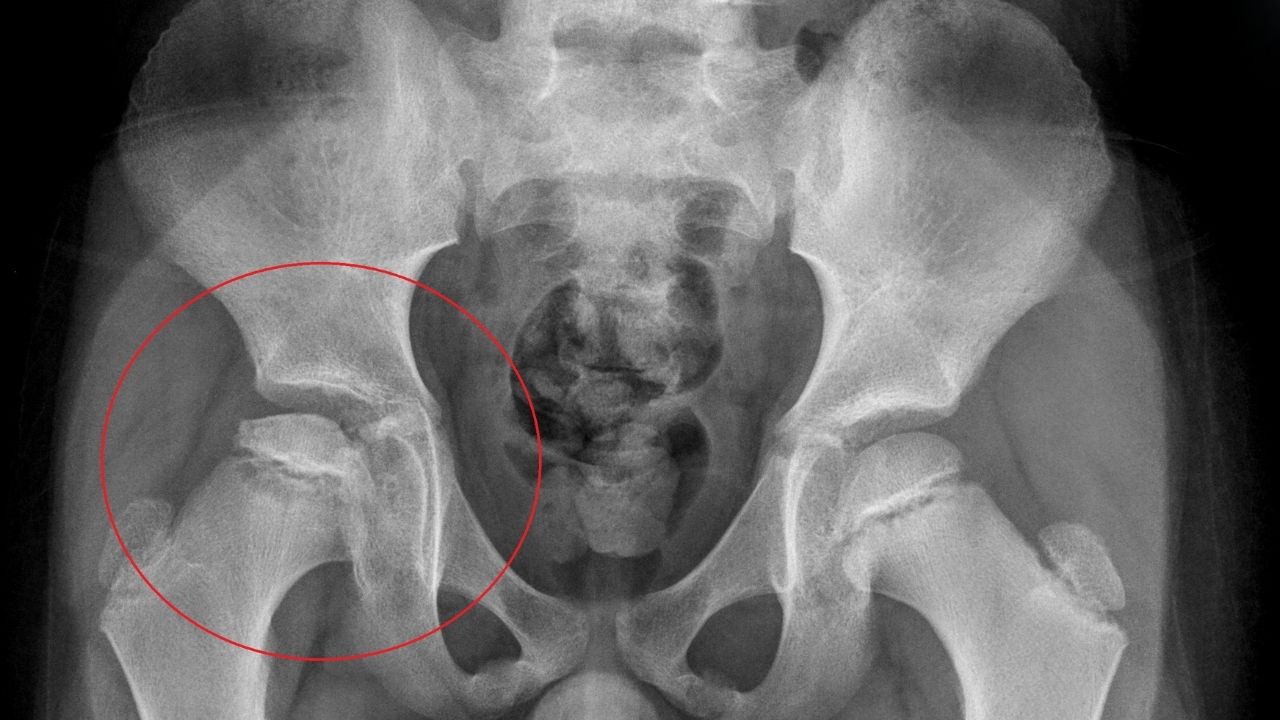
Perthes Syndrome might sound like a complex medical term, but understanding it can be straightforward. This condition affects the hip joint in children, causing pain and limping. Perthes Syndrome occurs when blood supply to the rounded head of the femur (thighbone) is temporarily disrupted, leading to bone death. Over time, the body naturally repairs the damage, but the process can take several years. Early diagnosis and treatment are crucial to ensure the hip heals properly and functions well. In this blog post, we'll share 30 essential facts about Perthes Syndrome to help you grasp its causes, symptoms, treatments, and long-term effects.
Key Takeaways:
- Perthes Syndrome affects children's hip joints, causing pain, limping, and limited movement. Early diagnosis and treatment can lead to better outcomes, allowing kids to lead active lives with proper management.
- Children with Perthes Syndrome may need monitoring, physical therapy, and sometimes surgery. With support from family, friends, and healthcare professionals, many kids can still enjoy sports and lead fulfilling lives.
What is Perthes Syndrome?
Perthes Syndrome, also known as Legg-Calvé-Perthes disease, affects the hip joint in children. It occurs when blood supply to the femoral head (the ball part of the hip joint) is temporarily disrupted. This leads to bone death and can cause long-term issues if not treated properly.
- Rare Condition: Perthes Syndrome affects about 1 in 10,000 children worldwide.
- Age Range: Most commonly diagnosed in children between 4 and 8 years old.
- Gender Bias: Boys are four times more likely to develop Perthes Syndrome than girls.
- Unilateral Impact: Typically affects only one hip, though it can affect both in rare cases.
- Unknown Cause: The exact cause remains unknown, though it may involve genetic and environmental factors.
Symptoms of Perthes Syndrome
Recognizing the symptoms early can lead to better outcomes. Here are some common signs to watch for.
- Limping: A noticeable limp is often the first symptom.
- Hip Pain: Pain in the hip, groin, or thigh is common.
- Limited Range of Motion: Difficulty moving the hip joint freely.
- Knee Pain: Sometimes, the pain is felt in the knee instead of the hip.
- Muscle Wasting: Thigh muscles may appear smaller on the affected side.
Diagnosis and Tests
Diagnosing Perthes Syndrome involves several steps. Early diagnosis is crucial for effective treatment.
- Physical Examination: Doctors will check for limping, pain, and range of motion.
- X-rays: Initial imaging tests to look at the hip joint.
- MRI Scans: Provide detailed images of the bone and soft tissues.
- Bone Scans: Help assess blood flow to the femoral head.
- Blood Tests: Rule out other conditions that could cause similar symptoms.
Treatment Options
Treatment varies depending on the severity and stage of the disease. Here are some common approaches.
- Observation: Mild cases may only require regular monitoring.
- Physical Therapy: Helps maintain hip mobility and muscle strength.
- Anti-inflammatory Medications: Reduce pain and inflammation.
- Bracing: Keeps the femoral head in the hip socket.
- Surgery: In severe cases, surgical intervention may be necessary.
Long-term Outlook
The long-term outlook for children with Perthes Syndrome can vary. Early treatment often leads to better outcomes.
- Bone Regrowth: The femoral head can regenerate over time.
- Hip Deformity: Some children may develop a misshapen femoral head.
- Arthritis Risk: Increased risk of developing arthritis in the affected hip later in life.
- Activity Restrictions: High-impact activities may be limited to protect the hip.
- Regular Follow-ups: Ongoing medical check-ups are essential for monitoring progress.
Living with Perthes Syndrome
Living with Perthes Syndrome can be challenging, but many children lead normal, active lives with proper management.
- Support Groups: Connecting with others who have the condition can provide emotional support.
- Education: Informing teachers and caregivers about the condition helps in managing daily activities.
- Adaptive Sports: Many children can participate in sports with some modifications.
- Healthy Diet: A balanced diet supports overall health and bone strength.
- Positive Attitude: Encouraging a positive outlook can make a significant difference in coping with the condition.
Final Thoughts on Perthes Syndrome
Perthes Syndrome, a condition affecting the hip joint in children, can be challenging for families. Early diagnosis and treatment are crucial for managing symptoms and improving outcomes. Regular check-ups, physical therapy, and sometimes surgery help kids lead active lives. Understanding the condition's stages and symptoms empowers parents to seek timely medical advice. Support groups and resources offer valuable information and emotional support. Staying informed and proactive makes a significant difference in a child's journey with Perthes Syndrome. Remember, every child's experience is unique, and personalized care plans are essential. Keep communication open with healthcare providers to ensure the best possible care. By staying vigilant and informed, families can navigate Perthes Syndrome more effectively, providing their children with the best chance for a healthy, active future.
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
