Osteosarcoma and Undifferentiated Pleomorphic Sarcoma of Bone are two rare but aggressive bone cancers. These conditions primarily affect children, teenagers, and young adults. Early detection and treatment are crucial for improving survival rates. Treatments often include a combination of surgery, chemotherapy, and sometimes radiation therapy. Advances in medical research have led to more effective therapies, offering hope to patients and their families. Understanding the symptoms, risk factors, and treatment options can empower those affected to make informed decisions. This post will provide 30 essential facts about these bone cancers and their treatments, aiming to educate and support those impacted by these challenging diagnoses.
Key Takeaways:
- Osteosarcoma and undifferentiated pleomorphic sarcoma are rare but aggressive bone cancers that primarily affect teenagers and older adults. Early detection and aggressive treatment can improve survival rates and quality of life for patients.
- Treatment options for these bone cancers include surgery, chemotherapy, and radiation therapy. New therapies like targeted therapy and immunotherapy offer hope for improved outcomes, while support and rehabilitation are vital for recovery and quality of life.
Understanding Osteosarcoma and Undifferentiated Pleomorphic Sarcoma
Osteosarcoma and undifferentiated pleomorphic sarcoma (UPS) of bone are rare but aggressive cancers. They primarily affect bones, often requiring complex treatments. Here are some key facts to help you understand these conditions better.
- Osteosarcoma is the most common type of bone cancer, typically affecting teenagers and young adults.
- Undifferentiated pleomorphic sarcoma of bone is rarer and usually occurs in older adults.
- Both cancers often start in the long bones, like the arms and legs.
- Symptoms include pain, swelling, and sometimes fractures in the affected bone.
Diagnosis and Early Detection
Early detection is crucial for effective treatment. Knowing the signs and diagnostic methods can save lives.
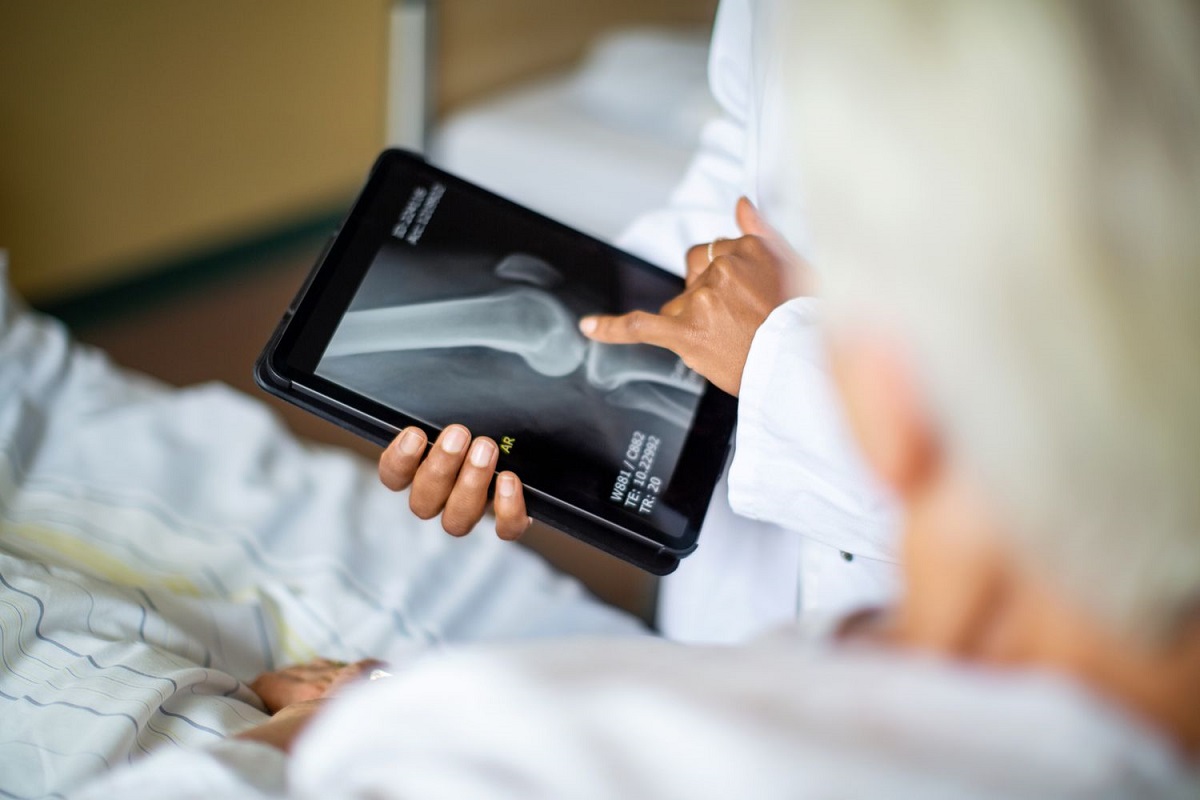
- X-rays are often the first step in diagnosing bone cancers.
- MRI scans provide detailed images of the bone and surrounding tissues.
- CT scans help determine if the cancer has spread to other parts of the body.
- Biopsies are essential for confirming the diagnosis by examining tissue samples under a microscope.
Treatment Options
Treatment for osteosarcoma and UPS of bone involves multiple approaches. Each method aims to remove or destroy cancer cells.
- Surgery is the primary treatment, aiming to remove the tumor completely.
- Limb-sparing surgery tries to save the affected limb while removing the cancer.
- Amputation may be necessary if the tumor is too large or involves critical structures.
- Chemotherapy uses drugs to kill cancer cells and is often used before and after surgery.
- Radiation therapy is less common but can be used if surgery isn't an option.
Chemotherapy Details
Chemotherapy plays a significant role in treating these cancers. It helps shrink tumors and kill remaining cancer cells post-surgery.
- Neoadjuvant chemotherapy is given before surgery to shrink the tumor.
- Adjuvant chemotherapy is administered after surgery to kill any remaining cancer cells.
- Common drugs include doxorubicin, cisplatin, and methotrexate.
- Chemotherapy can cause side effects like nausea, hair loss, and fatigue.
Advances in Treatment
Medical research continually seeks better treatments for osteosarcoma and UPS of bone. New therapies offer hope for improved outcomes.
- Targeted therapy focuses on specific molecules involved in cancer growth.
- Immunotherapy boosts the body's immune system to fight cancer.
- Clinical trials test new treatments and drugs, providing access to cutting-edge therapies.
- Bone grafts and prosthetics improve limb function after surgery.
Support and Rehabilitation
Recovery involves more than just medical treatment. Support and rehabilitation are vital for quality of life.
- Physical therapy helps regain strength and mobility after surgery.
- Occupational therapy assists in adapting to daily activities.
- Support groups provide emotional support and shared experiences.
- Nutritional counseling ensures patients maintain a healthy diet during treatment.
Prognosis and Survival Rates
Understanding the prognosis and survival rates can help patients and families prepare for the journey ahead.
- Survival rates for osteosarcoma have improved with advances in treatment.
- Five-year survival rate for localized osteosarcoma is around 70%.
- Metastatic osteosarcoma has a lower survival rate, around 30%.
- Early detection and aggressive treatment improve outcomes.
- Ongoing research aims to further increase survival rates and improve quality of life for patients.
Final Thoughts on Osteosarcoma and Undifferentiated Pleomorphic Sarcoma Treatment
Understanding osteosarcoma and undifferentiated pleomorphic sarcoma treatment is crucial for patients and their families. These aggressive bone cancers require a combination of surgery, chemotherapy, and sometimes radiation therapy. Early detection significantly improves outcomes. Advances in medical research continue to offer hope, with new treatments and clinical trials providing additional options. Support from healthcare professionals, family, and friends plays a vital role in navigating this challenging journey. Staying informed about the latest developments and maintaining open communication with your medical team can make a significant difference. Remember, each patient's experience is unique, and treatment plans should be tailored to individual needs. Stay hopeful and proactive in seeking the best possible care.
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
