Myopathy Tubular Aggregates might sound like a mouthful, but understanding it can be simpler than you think. This rare muscle disorder involves the presence of abnormal tube-like structures in muscle cells, leading to muscle weakness and fatigue. What causes Myopathy Tubular Aggregates? The exact cause remains unclear, but genetic mutations and certain medications are often linked. Symptoms can vary widely, from mild muscle cramps to severe weakness. Diagnosing this condition typically involves muscle biopsies and genetic testing. Treatments focus on managing symptoms, as no cure currently exists. Ready to learn more? Let's dive into 30 intriguing facts about this unique condition.
Key Takeaways:
- Myopathy Tubular Aggregates (MTA) is a rare muscle disorder caused by abnormal structures in muscle fibers, leading to weakness, cramps, and fatigue. Genetic factors play a crucial role, and while there's no cure, treatments can help manage symptoms.
- Living with MTA involves adapting daily activities, using adaptive devices, and seeking support for physical and mental health. Research is ongoing to better understand the condition and develop new treatments.
What is Myopathy Tubular Aggregates?
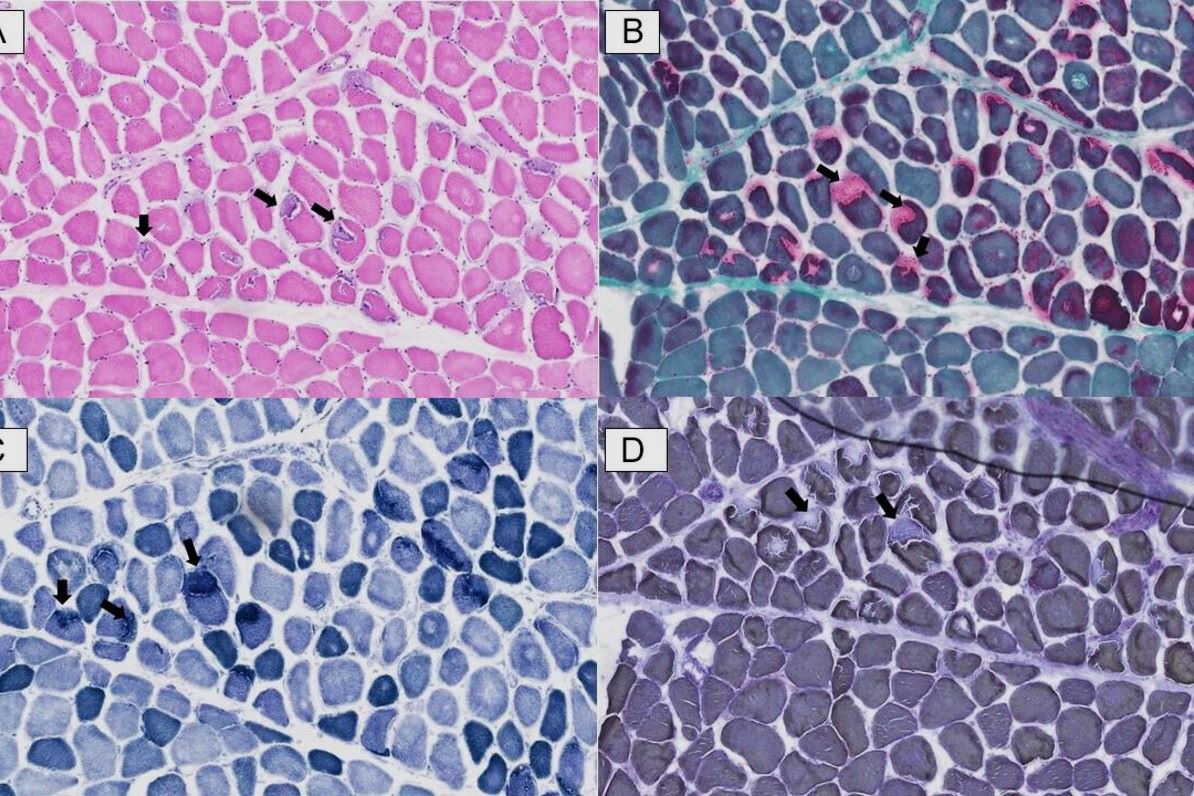
Myopathy Tubular Aggregates (MTA) is a rare muscle disorder characterized by the presence of tubular aggregates in muscle fibers. These aggregates are abnormal structures that can affect muscle function. Let's dive into some fascinating facts about this condition.
- MTA is a rare disease: It affects only a small number of people worldwide, making it a rare condition.
- Tubular aggregates are abnormal structures: These are cylindrical structures found within muscle fibers, disrupting normal muscle function.
- Genetic mutations play a role: Mutations in specific genes, such as STIM1 and ORAI1, are linked to MTA.
- Symptoms vary widely: Individuals with MTA can experience muscle weakness, cramps, and fatigue.
- Onset can be at any age: MTA can develop in childhood or adulthood, with symptoms appearing at different stages of life.
Symptoms and Diagnosis
Understanding the symptoms and how MTA is diagnosed can help in managing the condition effectively.
- Muscle weakness is common: Many individuals with MTA experience progressive muscle weakness.
- Cramps and pain: Muscle cramps and pain are frequent symptoms, often triggered by physical activity.
- Fatigue: Chronic fatigue is a common complaint among those with MTA.
- Electromyography (EMG) is used for diagnosis: EMG tests can help detect abnormalities in muscle function.
- Muscle biopsy confirms the diagnosis: A muscle biopsy revealing tubular aggregates is definitive for diagnosing MTA.
Genetic Factors
Genetics play a crucial role in the development of MTA. Let's explore some genetic aspects of this condition.
- STIM1 gene mutation: Mutations in the STIM1 gene are a known cause of MTA.
- ORAI1 gene mutation: Changes in the ORAI1 gene can also lead to the development of MTA.
- Inherited in an autosomal dominant manner: MTA can be passed down from one generation to the next in an autosomal dominant pattern.
- De novo mutations: Some cases of MTA result from new mutations that occur spontaneously.
- Genetic testing is available: Genetic tests can identify mutations in the STIM1 and ORAI1 genes, aiding in diagnosis.
Treatment and Management
While there is no cure for MTA, various treatments and management strategies can help alleviate symptoms.
- Physical therapy: Regular physical therapy can improve muscle strength and function.
- Pain management: Medications and other therapies can help manage muscle pain and cramps.
- Fatigue management: Strategies to manage fatigue include rest, pacing activities, and energy conservation techniques.
- Genetic counseling: Families affected by MTA can benefit from genetic counseling to understand the risks and implications.
- Support groups: Joining support groups can provide emotional support and practical advice for managing MTA.
Research and Future Directions
Ongoing research aims to better understand MTA and develop new treatments.
- Animal models: Researchers use animal models to study the genetic and molecular mechanisms of MTA.
- Gene therapy: Experimental gene therapies are being explored as potential treatments for MTA.
- Clinical trials: Clinical trials are essential for testing new treatments and therapies.
- Biomarker discovery: Identifying biomarkers can help in early diagnosis and monitoring disease progression.
- Patient registries: Patient registries collect data on individuals with MTA, aiding research and improving care.
Living with Myopathy Tubular Aggregates
Living with MTA requires adapting to the challenges it presents. Here are some facts about daily life with this condition.
- Adaptive devices: Tools and devices can assist with daily activities and improve quality of life.
- Exercise modifications: Tailored exercise programs can help maintain muscle function without overexertion.
- Nutritional support: Proper nutrition can support overall health and muscle function.
- Mental health support: Counseling and mental health services can help cope with the emotional impact of MTA.
- Education and awareness: Raising awareness about MTA can lead to better understanding and support for those affected.
Final Thoughts on Myopathy Tubular Aggregates
Myopathy Tubular Aggregates, a rare muscle disorder, affects muscle function and strength. Understanding its symptoms, causes, and treatment options can help those affected manage their condition better. Symptoms often include muscle weakness, cramps, and fatigue. Causes range from genetic mutations to environmental factors. While there's no cure, treatments like physical therapy, medications, and lifestyle changes can improve quality of life.
Staying informed and seeking support from healthcare professionals and support groups can make a significant difference. Knowledge empowers patients and their families to navigate the challenges of this condition. Remember, early diagnosis and intervention are key to managing symptoms effectively. Keep learning, stay proactive, and don't hesitate to reach out for help when needed.
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
