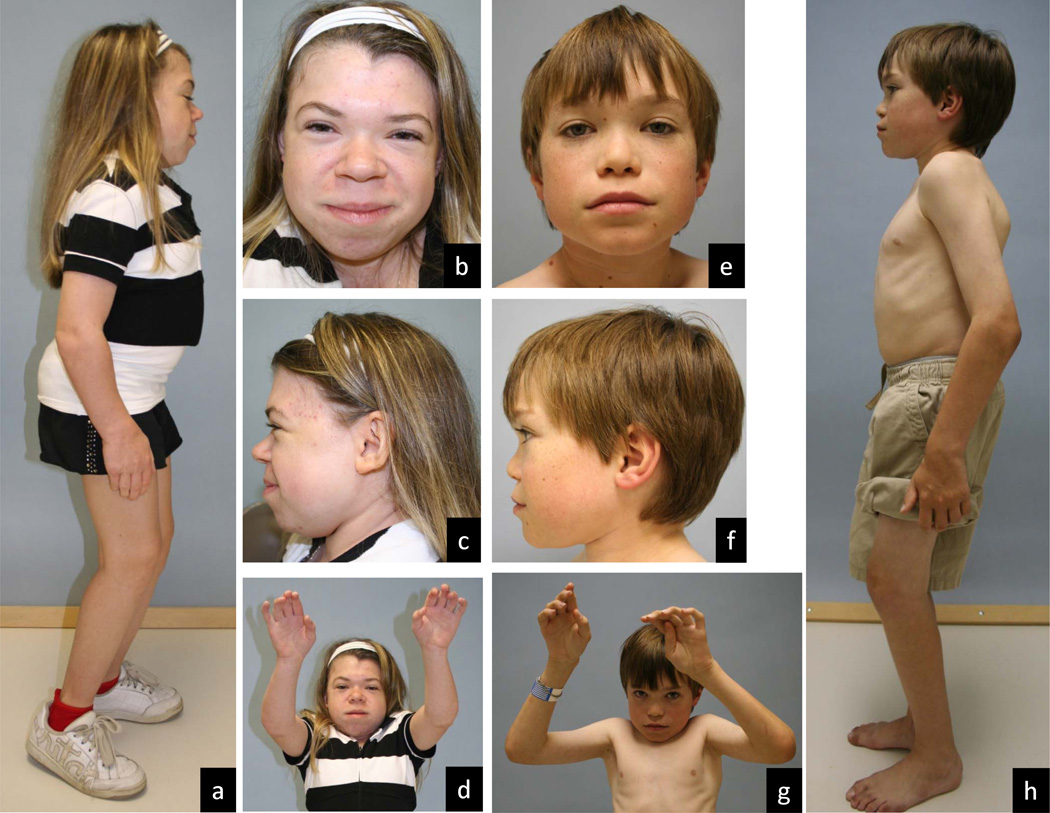
Mucolipidosis Type 3 is a rare genetic disorder that affects the body's ability to break down certain fats and sugars. This condition, also known as pseudo-Hurler polydystrophy, typically presents symptoms in early childhood. Symptoms can include joint stiffness, heart valve abnormalities, and distinctive facial features. Unlike some other lysosomal storage disorders, Mucolipidosis Type 3 does not usually affect the brain, allowing for normal cognitive development. Diagnosis often involves genetic testing and enzyme assays. Treatment focuses on managing symptoms and improving quality of life, as there is currently no cure. Understanding this condition is crucial for early intervention and better management.
Key Takeaways:
- Mucolipidosis Type 3 is a rare genetic disorder causing joint stiffness, growth delays, and heart issues. Diagnosis involves genetic testing and enzyme assays. Treatment focuses on symptom management and regular monitoring.
- Living with Mucolipidosis Type 3 requires educational and social support, physical and occupational therapy, and adaptive devices for mobility. Nutritional support, pain management, and mental health care are crucial for a fulfilling life.
Understanding Mucolipidosis Type 3
Mucolipidosis Type 3 (ML III) is a rare genetic disorder that affects the body's ability to break down certain fats and sugars. This condition can lead to various symptoms and complications. Here are some key facts to help you understand ML III better.
-
Genetic Origin: ML III is caused by mutations in the GNPTAB gene, which is responsible for producing an enzyme crucial for breaking down certain molecules in the body.
-
Inheritance Pattern: This disorder follows an autosomal recessive inheritance pattern, meaning a child must inherit two copies of the mutated gene, one from each parent, to develop the condition.
-
Enzyme Deficiency: Individuals with ML III have a deficiency in the enzyme N-acetylglucosamine-1-phosphotransferase, leading to the accumulation of certain substances in cells.
-
Symptoms Onset: Symptoms typically appear in early childhood, although the severity and progression can vary widely among individuals.
-
Common Symptoms: Joint stiffness, coarse facial features, and skeletal abnormalities are common symptoms of ML III.
-
Growth Delays: Children with ML III often experience growth delays and may have short stature compared to their peers.
-
Cardiac Issues: Heart valve abnormalities and other cardiac issues are common in individuals with ML III.
-
Respiratory Problems: Respiratory complications, including frequent infections and breathing difficulties, can occur.
Diagnosis and Testing
Diagnosing ML III involves a combination of clinical evaluation, genetic testing, and other diagnostic procedures. Here are some important facts about the diagnosis process.
-
Clinical Evaluation: Doctors often start with a thorough clinical evaluation, looking for characteristic symptoms and signs of ML III.
-
Genetic Testing: Genetic testing can confirm the diagnosis by identifying mutations in the GNPTAB gene.
-
Enzyme Assays: Enzyme assays measure the activity of N-acetylglucosamine-1-phosphotransferase to help diagnose ML III.
-
Imaging Studies: X-rays and other imaging studies can reveal skeletal abnormalities associated with ML III.
-
Prenatal Testing: Prenatal testing is available for families with a known history of ML III to determine if the fetus is affected.
Treatment and Management
While there is no cure for ML III, various treatments and management strategies can help alleviate symptoms and improve quality of life. Here are some key facts about treatment options.
-
Symptomatic Treatment: Treatment focuses on managing symptoms, such as pain relief for joint stiffness and physical therapy to improve mobility.
-
Surgical Interventions: Some individuals may require surgical interventions to address skeletal abnormalities or cardiac issues.
-
Respiratory Support: Respiratory support, including the use of ventilators or other breathing aids, may be necessary for those with severe respiratory problems.
-
Regular Monitoring: Regular monitoring by a team of specialists is crucial to manage the various complications associated with ML III.
-
Bone Health: Maintaining bone health through diet, supplements, and medications can help manage skeletal issues.
-
Cardiac Care: Regular cardiac evaluations and appropriate treatments are essential for managing heart-related complications.
-
Genetic Counseling: Genetic counseling can provide valuable information and support for families affected by ML III.
Living with Mucolipidosis Type 3
Living with ML III presents unique challenges, but with proper care and support, individuals can lead fulfilling lives. Here are some facts about daily life with ML III.
-
Educational Support: Children with ML III may require special educational support to address learning difficulties and developmental delays.
-
Physical Therapy: Regular physical therapy can help improve mobility and reduce joint stiffness.
-
Occupational Therapy: Occupational therapy can assist with daily activities and improve quality of life.
-
Social Support: Building a strong support network of family, friends, and healthcare professionals is crucial for emotional well-being.
-
Adaptive Devices: Adaptive devices, such as braces or wheelchairs, can enhance mobility and independence.
-
Nutritional Support: A balanced diet and nutritional support can help manage growth delays and maintain overall health.
-
Pain Management: Effective pain management strategies are essential for improving comfort and quality of life.
-
Mental Health: Addressing mental health needs through counseling or therapy can help individuals and families cope with the challenges of ML III.
-
Community Resources: Connecting with community resources and support groups can provide valuable information and emotional support.
-
Research and Advocacy: Staying informed about ongoing research and advocacy efforts can offer hope for future treatments and advancements in the understanding of ML III.
Final Thoughts on Mucolipidosis Type 3
Mucolipidosis Type 3, a rare genetic disorder, affects many aspects of a person's health. Understanding its symptoms, causes, and treatments can help those affected manage their condition better. Early diagnosis and intervention are crucial for improving quality of life. Genetic counseling can provide valuable insights for families dealing with this disorder. While there's no cure yet, ongoing research offers hope for future treatments. Support groups and resources can also play a significant role in coping with the challenges of Mucolipidosis Type 3. Staying informed and connected with healthcare professionals ensures that patients receive the best care possible. By spreading awareness, we can foster a supportive community for those impacted by this condition. Remember, knowledge is power, and staying educated about Mucolipidosis Type 3 can make a big difference in the lives of patients and their families.
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
