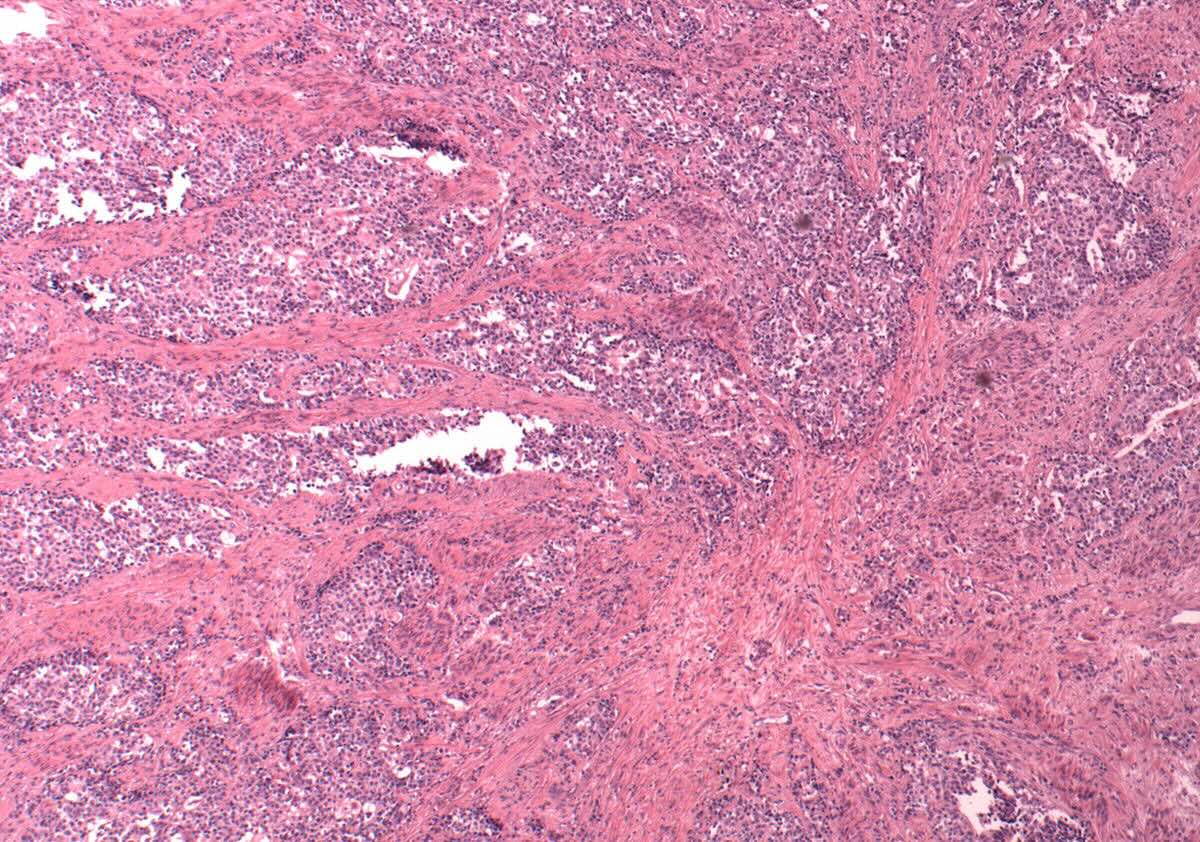
Mixed Müllerian Tumor, also known as carcinosarcoma, is a rare and aggressive form of cancer that primarily affects the female reproductive organs, particularly the uterus. This tumor is unique because it contains both carcinomatous (epithelial) and sarcomatous (mesenchymal) components. Understanding Mixed Müllerian Tumor is crucial for early detection and treatment. These tumors often present symptoms similar to other gynecological conditions, making diagnosis challenging. Common signs include abnormal vaginal bleeding, pelvic pain, and a noticeable mass. Risk factors include advanced age, obesity, and a history of pelvic radiation. Treatment typically involves surgery, chemotherapy, and radiation therapy. Early diagnosis and comprehensive treatment plans can improve outcomes for those affected by this complex cancer.
Key Takeaways:
- Mixed Müllerian Tumor (MMT) is a rare and aggressive cancer found in the female reproductive system, often in postmenopausal women. Early detection and understanding symptoms are crucial for effective treatment.
- Treatment for MMT involves surgery, chemotherapy, and radiation therapy. Support groups, counseling, and palliative care are available to help patients and their families cope with the challenges of living with MMT.
What is a Mixed Müllerian Tumor?
Mixed Müllerian Tumor (MMT), also known as carcinosarcoma, is a rare and aggressive form of cancer. It typically arises in the uterus but can also occur in other parts of the female reproductive system. Understanding this condition is crucial for early detection and treatment.
- MMTs are composed of both carcinoma (cancer of epithelial tissue) and sarcoma (cancer of connective tissue).
- They are most commonly found in postmenopausal women.
- The exact cause of MMTs remains unknown, but genetic mutations and hormonal imbalances are suspected contributors.
- Symptoms often include abnormal vaginal bleeding, pelvic pain, and a noticeable mass in the pelvic area.
- Diagnosis typically involves imaging tests like ultrasounds and MRIs, followed by a biopsy to confirm the presence of cancerous cells.
Risk Factors and Causes
Several factors can increase the likelihood of developing MMTs. While the exact cause is still under investigation, certain risk factors have been identified.
- Age is a significant risk factor, with most cases occurring in women over 60.
- A history of pelvic radiation therapy can increase the risk of developing MMTs.
- Obesity is another risk factor, as excess body fat can lead to hormonal imbalances.
- Women with a history of breast cancer or ovarian cancer may have a higher risk.
- Genetic predispositions, such as mutations in the BRCA1 and BRCA2 genes, can also play a role.
Symptoms and Diagnosis
Recognizing the symptoms early can lead to more effective treatment. Diagnosis involves several steps to ensure accuracy.
- Early symptoms can be subtle, often mistaken for less severe conditions.
- Persistent pelvic pain is a common symptom that should not be ignored.
- Unexplained weight loss and fatigue can also be indicators of MMT.
- A pelvic exam can sometimes reveal abnormalities that warrant further investigation.
- Blood tests, including CA-125 levels, can help in the diagnosis process.
Treatment Options
Treatment for MMTs often involves a combination of surgery, chemotherapy, and radiation therapy. The approach depends on the stage and spread of the tumor.
- Surgery is usually the first line of treatment, aiming to remove as much of the tumor as possible.
- Chemotherapy is often used post-surgery to target any remaining cancer cells.
- Radiation therapy can help shrink tumors and alleviate symptoms.
- Hormone therapy may be considered, especially if the tumor is hormone receptor-positive.
- Clinical trials offer access to new and experimental treatments that might be more effective.
Prognosis and Survival Rates
The prognosis for MMTs varies depending on several factors, including the stage at diagnosis and the patient's overall health.
- Early-stage MMTs have a better prognosis compared to advanced stages.
- The five-year survival rate for early-stage MMTs can be as high as 50%.
- Advanced-stage MMTs have a significantly lower survival rate, often below 20%.
- Regular follow-up care is crucial for monitoring recurrence and managing side effects.
- New treatments and ongoing research are continually improving survival rates and quality of life for patients.
Living with Mixed Müllerian Tumor
Living with MMT can be challenging, but support and resources are available to help patients and their families cope.
- Support groups provide emotional and practical support from others who understand the experience.
- Counseling and mental health services can help manage the emotional toll of a cancer diagnosis.
- Nutritional support and physical therapy can improve overall well-being and recovery.
- Palliative care focuses on relieving symptoms and improving quality of life, especially in advanced stages.
- Staying informed and involved in treatment decisions can empower patients and improve outcomes.
Final Thoughts on Mixed Müllerian Tumors
Mixed Müllerian Tumors, also known as carcinosarcomas, are rare but aggressive cancers. They often affect the uterus, ovaries, and fallopian tubes. Early detection is crucial for better outcomes. Symptoms can include abnormal bleeding, pelvic pain, and bloating. Treatment usually involves surgery, chemotherapy, and sometimes radiation. Research is ongoing to find more effective treatments and improve survival rates.
Understanding the risk factors, such as age and previous radiation therapy, can help in early diagnosis. Regular check-ups and being aware of changes in your body are essential. If you experience any unusual symptoms, consult a healthcare provider promptly.
Staying informed about this condition can make a significant difference. Knowledge empowers you to take proactive steps for your health. Keep up with the latest research and advancements in treatment options. Your health is your most valuable asset.
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
