McCune–Albright Syndrome is a rare genetic disorder that affects bones, skin, and several hormone-producing tissues. Caused by mutations in the GNAS gene, this condition often presents itself in early childhood. Symptoms can vary widely but typically include fibrous dysplasia, where normal bone is replaced with fibrous tissue, leading to fractures and deformities. Café-au-lait spots, or light brown skin patches, are another hallmark. Additionally, endocrine problems such as early puberty, thyroid issues, and growth hormone excess can occur. Understanding this syndrome is crucial for early diagnosis and management. Here are 30 facts to help you grasp the complexities of McCune–Albright Syndrome.
Key Takeaways:
- McCune–Albright Syndrome is a rare genetic disorder causing bone, skin, and hormone issues. It's not inherited, can lead to early puberty, and has no cure. Treatment focuses on managing symptoms and improving quality of life.
- Living with McCune–Albright Syndrome can be challenging, impacting physical activities, emotional well-being, and social interactions. Ongoing research aims to better understand the condition and develop new treatments.
What is McCune–Albright Syndrome?
McCune–Albright Syndrome (MAS) is a rare genetic disorder that affects bones, skin, and several hormone-producing tissues. It was first described in the 1930s by Drs. Donovan McCune and Fuller Albright. Here are some intriguing facts about this condition:
-
Genetic Mutation: MAS is caused by a mutation in the GNAS gene, which affects the G-protein signaling pathway.
-
Mosaicism: The mutation occurs after fertilization, leading to a mosaic pattern where only some cells carry the mutation.
-
Not Inherited: MAS is not passed down from parents to children. It occurs spontaneously.
-
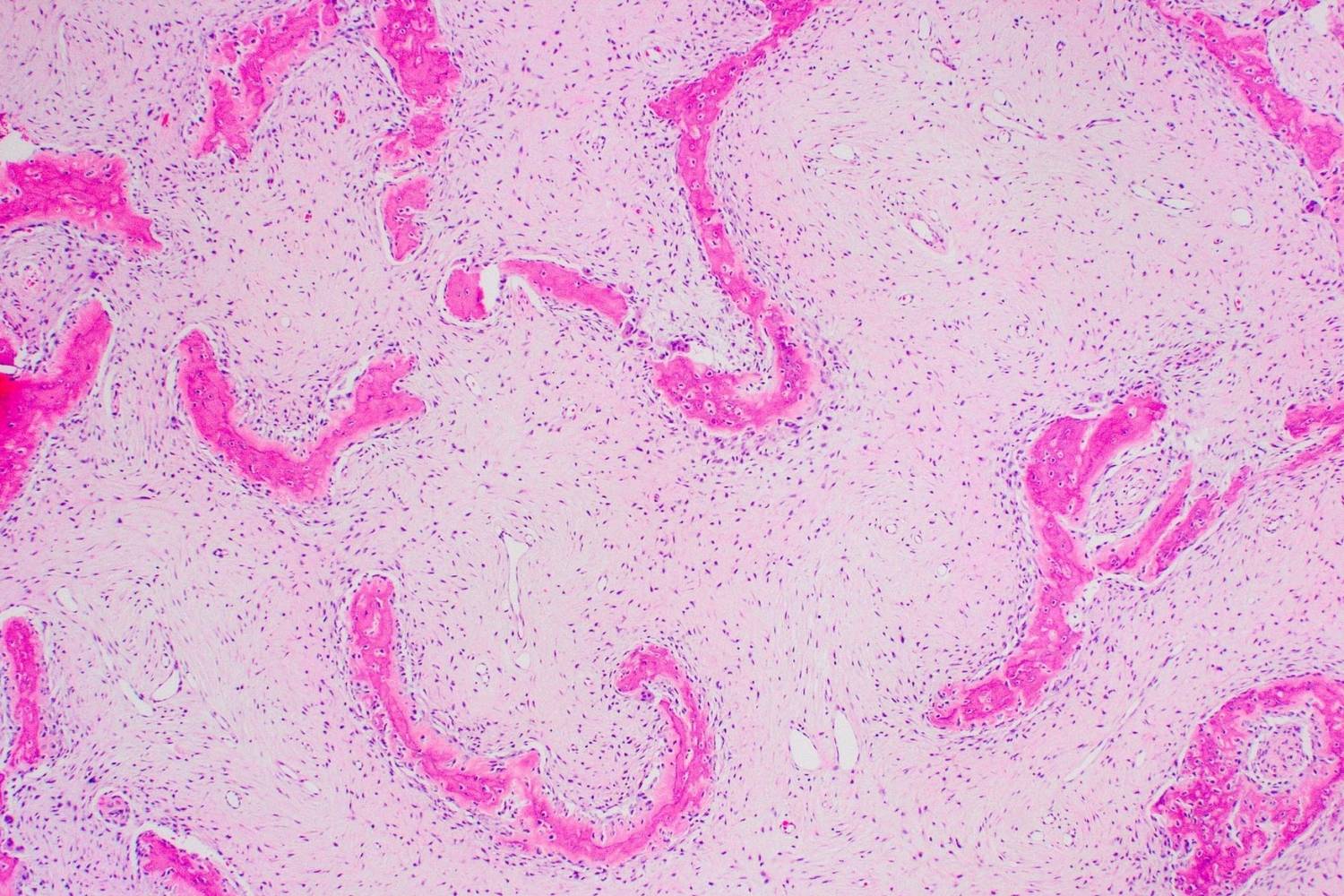
Polyostotic Fibrous Dysplasia: One of the main features is polyostotic fibrous dysplasia, where normal bone is replaced by fibrous tissue.
-
Café-au-lait Spots: Patients often have large, irregularly shaped café-au-lait spots on their skin.
-
Endocrine Problems: MAS can cause various endocrine issues, such as early puberty, hyperthyroidism, and growth hormone excess.
Symptoms and Diagnosis
Understanding the symptoms and how MAS is diagnosed can help in managing the condition effectively. Here are some key points:
-
Early Puberty: Girls with MAS may experience early puberty, sometimes as young as two years old.
-
Thyroid Issues: Hyperthyroidism is common, leading to symptoms like weight loss, rapid heartbeat, and nervousness.
-
Growth Hormone Excess: Some patients may have an excess of growth hormone, causing abnormal growth.
-
Bone Pain: Fibrous dysplasia can cause significant bone pain and fractures.
-
Hormonal Tests: Diagnosis often involves hormonal tests to check for endocrine abnormalities.
-
Imaging Studies: X-rays, CT scans, and MRIs are used to identify fibrous dysplasia in bones.
Treatment Options
While there is no cure for MAS, various treatments can help manage symptoms and improve quality of life. Here are some treatment facts:
-
Bisphosphonates: These drugs can help reduce bone pain and prevent fractures.
-
Hormone Therapy: Hormone therapy can manage endocrine issues like early puberty and hyperthyroidism.
-
Surgery: In some cases, surgery may be needed to correct bone deformities or remove fibrous tissue.
-
Pain Management: Pain management strategies, including medications and physical therapy, are crucial for improving quality of life.
-
Regular Monitoring: Regular monitoring by a team of specialists is essential for managing the various aspects of MAS.
Impact on Daily Life
Living with MAS can be challenging, but understanding its impact can help patients and families cope better. Here are some insights:
-
Physical Limitations: Bone deformities and pain can limit physical activities.
-
Emotional Impact: The condition can lead to emotional and psychological challenges, requiring support and counseling.
-
School and Work: Frequent medical appointments and physical limitations can affect school and work life.
-
Social Interactions: Visible symptoms like café-au-lait spots and early puberty can affect social interactions and self-esteem.
-
Support Groups: Joining support groups can provide emotional support and practical advice for managing MAS.
Research and Future Directions
Ongoing research aims to better understand MAS and develop new treatments. Here are some exciting developments:
-
Gene Therapy: Researchers are exploring gene therapy as a potential treatment for MAS.
-
New Medications: New medications are being tested to manage symptoms more effectively.
-
Clinical Trials: Participating in clinical trials can provide access to cutting-edge treatments.
-
Patient Registries: Patient registries help researchers collect data and identify trends in MAS.
-
International Collaboration: Researchers worldwide are collaborating to find better treatments and ultimately a cure.
Interesting Facts
Here are some additional interesting facts about MAS that you might find intriguing:
-
Rare Condition: MAS is extremely rare, affecting about 1 in 100,000 to 1 in 1,000,000 people.
-
Named After Pioneers: The syndrome is named after Drs. Donovan McCune and Fuller Albright, who first described it.
-
Variable Symptoms: Symptoms can vary widely from person to person, even among those with the same mutation.
Final Thoughts on McCune–Albright Syndrome
McCune–Albright Syndrome (MAS) is a rare genetic disorder that affects bones, skin, and endocrine tissues. Understanding its symptoms, such as fibrous dysplasia, café-au-lait spots, and hormonal imbalances, can help in early diagnosis and management. While there’s no cure, treatments focus on alleviating symptoms and improving quality of life. Advances in medical research offer hope for better therapies in the future. Awareness and education about MAS are crucial for supporting those affected and their families. By staying informed, we can contribute to a more inclusive and understanding community. If you or someone you know shows signs of MAS, consult a healthcare provider for proper evaluation and care. Knowledge empowers us to make informed decisions and advocate for better health outcomes.
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
