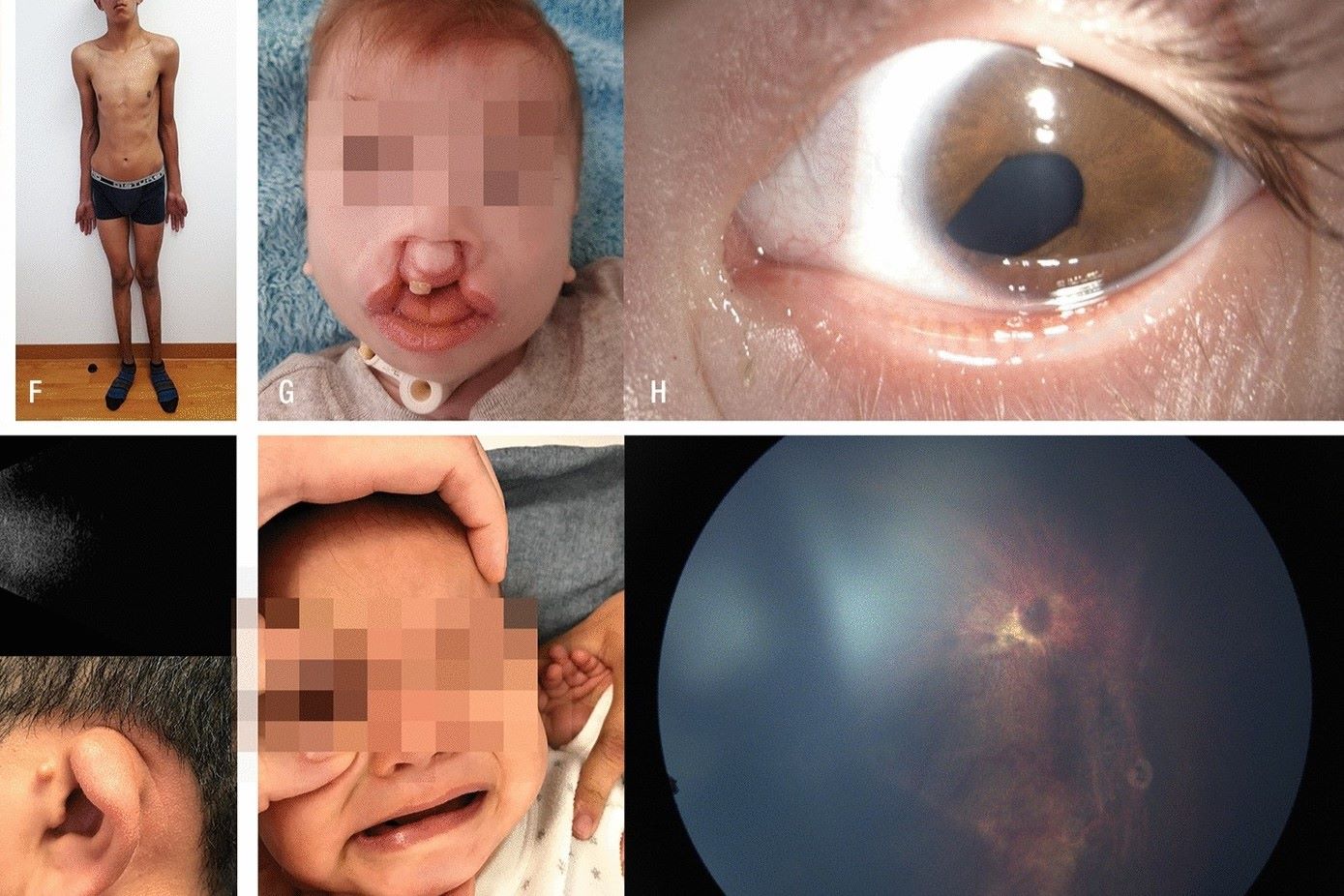
Hypertelorism and Tetralogy of Fallot might sound like complex medical terms, but understanding them can be straightforward. Hypertelorism refers to an abnormally increased distance between two body parts, often the eyes. This condition can be a standalone trait or part of a syndrome. On the other hand, Tetralogy of Fallot is a congenital heart defect that affects normal blood flow through the heart. It includes four heart abnormalities: a ventricular septal defect, pulmonary stenosis, right ventricular hypertrophy, and an overriding aorta. Both conditions can impact a person's health and appearance, but early diagnosis and treatment can improve outcomes. Let's dive into 30 intriguing facts about these medical conditions to better understand their causes, symptoms, and treatments.
Key Takeaways:
- Hypertelorism and Tetralogy of Fallot are unique medical conditions that can impact a person's appearance and heart function. Early diagnosis and multidisciplinary care are crucial for improving outcomes and quality of life.
- Genetic factors play a significant role in the development of both hypertelorism and Tetralogy of Fallot. Ongoing research and support networks are essential for better understanding and managing these conditions.
Understanding Hypertelorism
Hypertelorism is a medical condition characterized by an abnormally increased distance between two body parts, typically the eyes. This condition can be a standalone feature or part of a syndrome.
- Hypertelorism is often diagnosed through physical examination and imaging techniques like X-rays or MRI scans.
- The condition can be present at birth or develop later due to other medical issues.
- Hypertelorism can affect vision and facial symmetry, impacting a person's appearance and self-esteem.
- Surgical intervention is sometimes necessary to correct severe cases, especially if it affects vision or other functions.
- Genetic factors play a significant role in the development of hypertelorism, often linked to syndromes like Apert or Crouzon.
- Mild cases may not require treatment, but regular monitoring is essential to manage any potential complications.
- Hypertelorism can be associated with other craniofacial abnormalities, necessitating a multidisciplinary approach to treatment.
- Early diagnosis and intervention can significantly improve outcomes for individuals with hypertelorism.
- Support groups and counseling can help individuals and families cope with the emotional and psychological aspects of the condition.
- Research is ongoing to better understand the genetic and environmental factors contributing to hypertelorism.
Exploring Tetralogy of Fallot
Tetralogy of Fallot (TOF) is a congenital heart defect that involves four anatomical abnormalities of the heart. This condition affects normal blood flow through the heart.
- Tetralogy of Fallot includes four defects: ventricular septal defect, pulmonary stenosis, right ventricular hypertrophy, and an overriding aorta.
- TOF is one of the most common congenital heart defects, affecting about 1 in 2,500 newborns.
- Cyanosis, or a bluish tint to the skin, is a hallmark symptom due to reduced oxygen levels in the blood.
- Surgical repair is the primary treatment for TOF, usually performed within the first year of life.
- Children with TOF often require lifelong follow-up care to monitor heart function and manage any complications.
- Genetic factors can contribute to the development of TOF, with some cases linked to chromosomal abnormalities like Down syndrome.
- Advancements in surgical techniques have significantly improved survival rates and quality of life for individuals with TOF.
- Exercise restrictions may be necessary for some individuals with TOF to prevent undue strain on the heart.
- Prenatal diagnosis of TOF is possible through fetal echocardiography, allowing for early planning and intervention.
- Support networks and specialized care centers play a crucial role in managing the long-term health of individuals with TOF.
Hypertelorism and Tetralogy of Fallot: A Rare Connection
While hypertelorism and Tetralogy of Fallot are distinct conditions, they can sometimes co-occur, particularly in certain genetic syndromes.
- Certain syndromes, like Noonan syndrome, can present with both hypertelorism and Tetralogy of Fallot.
- Genetic testing can help identify syndromes that include both conditions, aiding in comprehensive diagnosis and treatment planning.
- Multidisciplinary care is essential for managing patients with both hypertelorism and TOF, involving cardiologists, geneticists, and craniofacial specialists.
- Early intervention can improve outcomes for individuals with both conditions, addressing both cardiac and craniofacial issues.
- Family history plays a significant role in the occurrence of these conditions, highlighting the importance of genetic counseling.
- Research into the genetic links between hypertelorism and TOF is ongoing, aiming to uncover shared pathways and potential treatments.
- Awareness and education about these conditions can help in early detection and management, improving quality of life.
- Technological advancements in imaging and surgical techniques continue to enhance the care and outcomes for individuals with these conditions.
- Patient advocacy groups provide valuable resources and support for families dealing with hypertelorism and TOF.
- Ongoing studies aim to better understand the long-term outcomes and quality of life for individuals with these conditions, guiding future care practices.
Final Thoughts on Hypertelorism and Tetralogy of Fallot
Hypertelorism and Tetralogy of Fallot, though rare, have significant impacts on those affected. Understanding these conditions helps in recognizing their symptoms and seeking timely medical intervention. Hypertelorism, characterized by widely spaced eyes, can be a standalone condition or part of a syndrome. Tetralogy of Fallot, a complex heart defect, requires early diagnosis and surgical correction for better outcomes.
Awareness and education about these conditions are crucial. They empower families and individuals to seek appropriate care and support. Medical advancements continue to improve the quality of life for those with these conditions. By staying informed and advocating for research, we can contribute to better treatment options and support systems.
Remember, knowledge is power. The more we learn about these conditions, the better equipped we are to support those affected and foster a more inclusive society.
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
