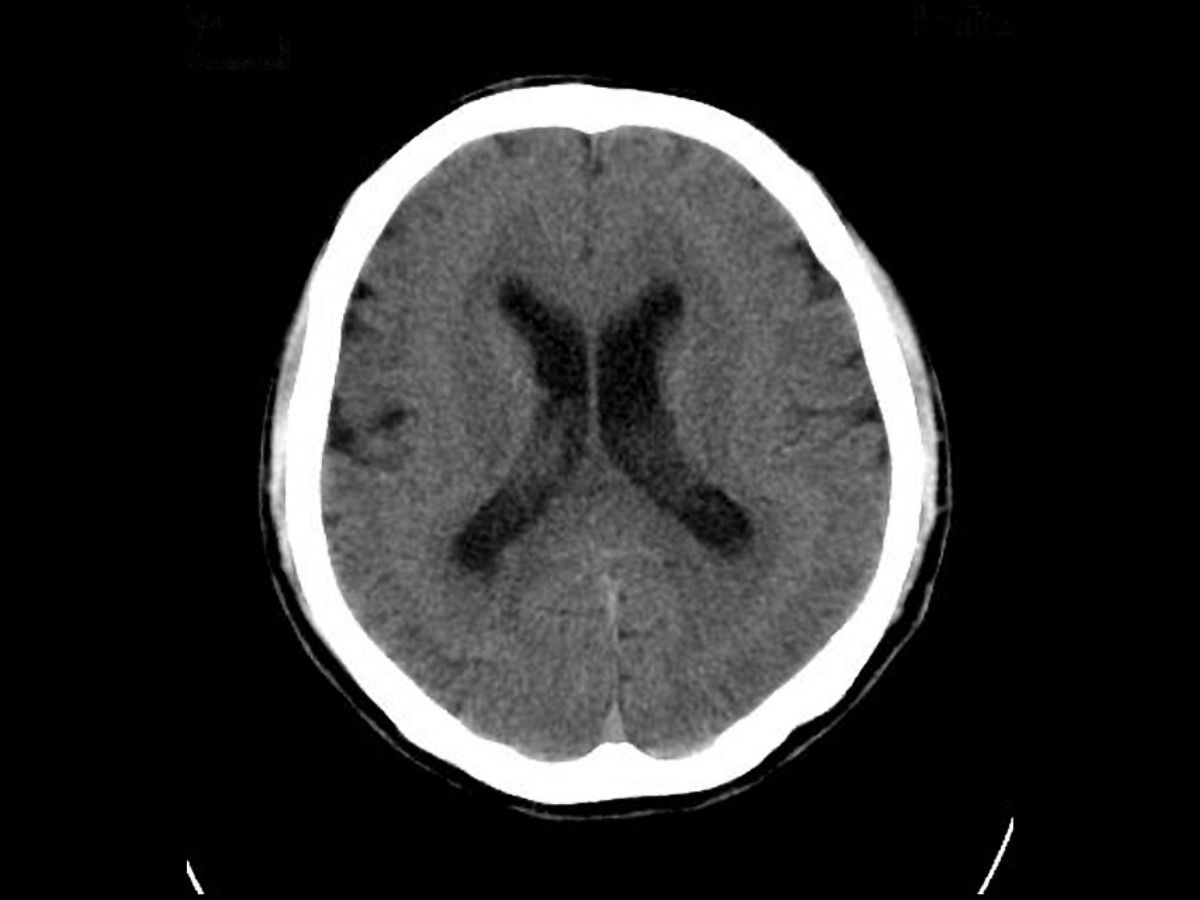
Familial Band Heterotopia is a rare genetic disorder that affects brain development. This condition, also known as double cortex syndrome, primarily impacts females due to its X-linked dominant inheritance pattern. Symptoms can range from mild to severe, including seizures, developmental delays, and intellectual disabilities. The disorder occurs when neurons fail to migrate properly during brain development, leading to a "double cortex" appearance on brain scans. Diagnosis typically involves MRI imaging and genetic testing. While there is no cure, treatments focus on managing symptoms, particularly seizures. Understanding this condition can help families and healthcare providers better support affected individuals.
Key Takeaways:
- Familial Band Heterotopia (FBH) is a rare genetic disorder affecting brain development, causing seizures and cognitive impairments. It is inherited in an X-linked dominant pattern and has no cure, but supportive therapies can improve quality of life.
- Understanding the genetic basis of FBH is crucial for diagnosis and potential treatments. Males are more severely affected, while females typically exhibit milder symptoms. Genetic testing and counseling are important for families affected by FBH.
What is Familial Band Heterotopia?
Familial Band Heterotopia (FBH) is a rare genetic disorder affecting brain development. It involves abnormal migration of neurons during fetal development, leading to bands of gray matter in unusual locations within the brain. This condition can cause various neurological symptoms and cognitive impairments.
-
FBH is a genetic disorder: It is inherited in an X-linked dominant pattern, meaning the gene responsible is located on the X chromosome.
-
Affects females more than males: Males with the mutation often have more severe symptoms or may not survive, while females typically exhibit milder symptoms.
-
Caused by mutations in the DCX gene: The DCX gene provides instructions for making a protein crucial for neuron migration during brain development.
-
Symptoms vary widely: Some individuals may have mild learning disabilities, while others experience severe epilepsy and intellectual disabilities.
-
Epilepsy is common: Many people with FBH suffer from seizures, which can be difficult to control with medication.
-
Cognitive impairments: These can range from mild learning difficulties to severe intellectual disabilities.
-
MRI scans reveal abnormal brain structure: MRI imaging shows bands of gray matter in unusual locations, which is a hallmark of FBH.
-
Diagnosis often occurs in childhood: Symptoms usually become apparent in early childhood, leading to further investigation and diagnosis.
-
No cure currently exists: Treatment focuses on managing symptoms, particularly epilepsy and cognitive impairments.
-
Supportive therapies are crucial: Speech therapy, occupational therapy, and special education can help improve quality of life.
Genetic Aspects of Familial Band Heterotopia
Understanding the genetic basis of FBH is essential for diagnosis and potential future treatments. Here are some key genetic facts about the disorder.
-
X-linked dominant inheritance: This means that a single copy of the mutated gene on the X chromosome can cause the disorder.
-
Males are more severely affected: Since males have only one X chromosome, a mutation in the DCX gene can lead to more severe symptoms or even be lethal.
-
Females have two X chromosomes: This can result in a milder presentation of the disorder due to the presence of one normal copy of the gene.
-
Genetic testing can confirm diagnosis: Identifying mutations in the DCX gene through genetic testing can confirm a diagnosis of FBH.
-
Family history is important: A family history of similar symptoms can suggest the presence of FBH and prompt genetic testing.
-
Carrier testing is available: Women with a family history of FBH can undergo carrier testing to determine their risk of passing the mutation to their children.
-
Prenatal testing is possible: For families with a known mutation, prenatal testing can determine if a fetus has inherited the mutation.
-
Genetic counseling is recommended: Families affected by FBH should seek genetic counseling to understand the risks and implications of the disorder.
Symptoms and Management of Familial Band Heterotopia
Managing FBH involves addressing the various symptoms and improving the quality of life for affected individuals. Here are some important facts about symptoms and management.
-
Seizures are a major concern: Epilepsy is a common symptom, and managing seizures is a primary focus of treatment.
-
Antiepileptic drugs are used: Medications like valproate, lamotrigine, and levetiracetam can help control seizures.
-
Regular monitoring is necessary: Individuals with FBH require regular follow-up with a neurologist to manage symptoms effectively.
-
Cognitive and developmental support: Special education programs and therapies can help address learning and developmental challenges.
-
Behavioral issues may arise: Some individuals may exhibit behavioral problems, requiring behavioral therapy and support.
-
Physical therapy can help: Physical therapy may be beneficial for those with motor impairments or coordination issues.
-
Speech therapy is often needed: Speech and language therapy can assist with communication difficulties.
-
Individualized education plans (IEPs): Schools can develop IEPs to provide tailored educational support for children with FBH.
-
Support groups are valuable: Connecting with other families affected by FBH can provide emotional support and practical advice.
-
Research is ongoing: Scientists are continually studying FBH to better understand the disorder and develop potential treatments.
-
Early intervention is key: Early diagnosis and intervention can improve outcomes for children with FBH.
-
Multidisciplinary approach: Effective management of FBH often involves a team of healthcare professionals, including neurologists, geneticists, therapists, and educators.
Final Thoughts on Familial Band Heterotopia
Familial Band Heterotopia (FBH) is a rare genetic disorder affecting brain development. It often leads to seizures, developmental delays, and cognitive challenges. Understanding FBH helps in early diagnosis and better management of symptoms. Genetic testing plays a crucial role in identifying this condition, allowing families to make informed decisions about treatment and care.
Living with FBH requires a strong support system, including medical professionals, therapists, and family members. Staying informed about the latest research and treatment options can improve quality of life for those affected. Awareness and education about FBH are essential for reducing stigma and providing better support for individuals and families.
By sharing knowledge and experiences, we can foster a more inclusive and understanding community for those living with Familial Band Heterotopia. Let's continue to support research and advocacy efforts to improve the lives of those affected by this condition.
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
