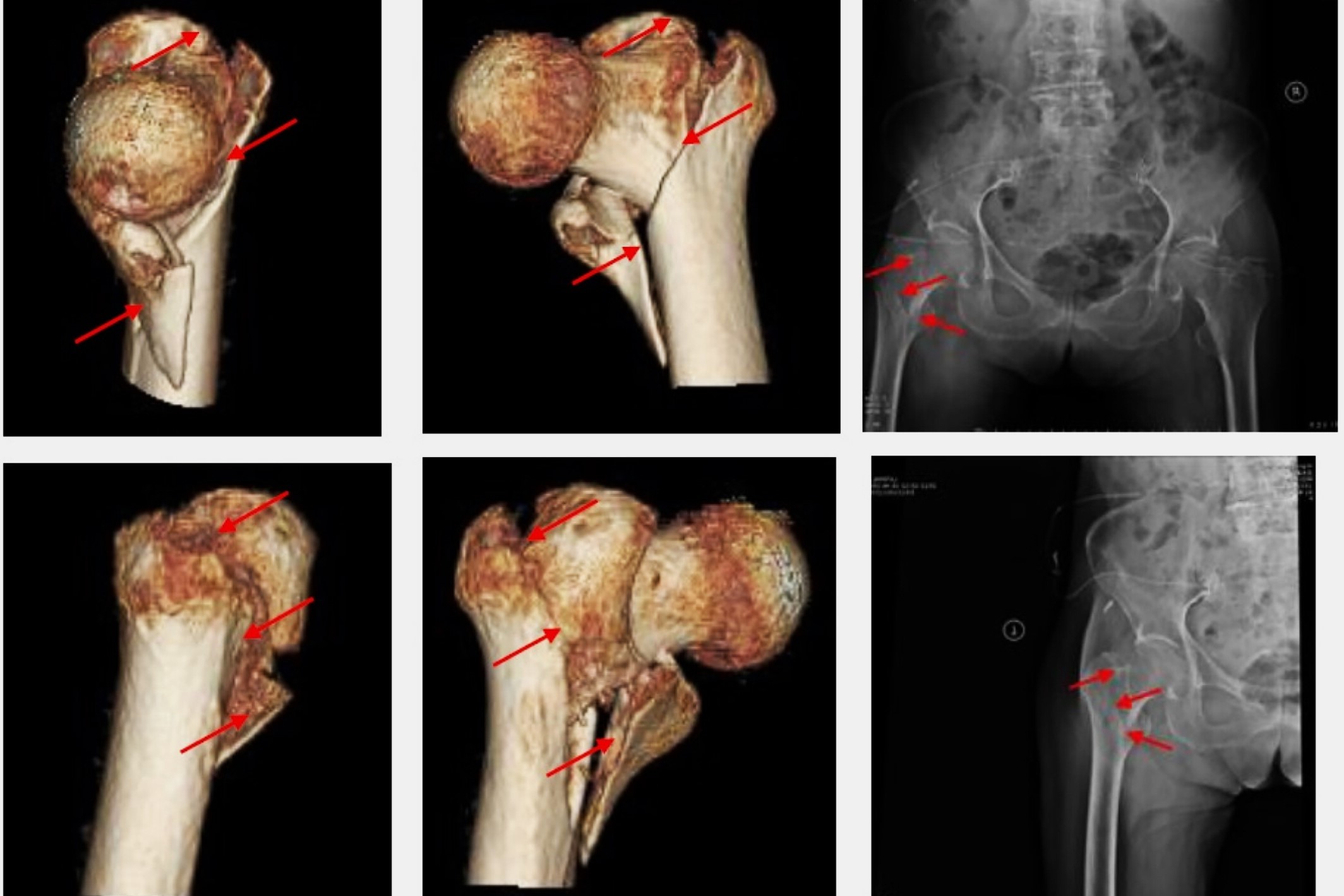
What is the Evans-Jensen Classification? This system categorizes different types of fractures based on their location and severity. Why is it important? Knowing the classification helps doctors decide the best treatment for each type of fracture. Who uses it? Orthopedic surgeons, radiologists, and medical students rely on this system. When was it developed? The Evans-Jensen Classification was introduced in the mid-20th century. Where is it applied? Hospitals and clinics worldwide use this system to improve patient care. How does it work? It divides fractures into specific categories, making diagnosis and treatment more straightforward. Want to learn more? Keep reading to uncover 30 fascinating facts about the Evans-Jensen Classification!
Key Takeaways:
- The Evans-Jensen Classification helps doctors identify and treat different types of bone tumors, whether they are non-cancerous (benign) or cancerous (malignant). This system uses imaging tests and biopsies to make accurate diagnoses.
- Treatment options for bone tumors include surgery, chemotherapy, radiation therapy, targeted therapy, and physical therapy. Early detection and treatment can significantly improve the prognosis for patients with bone tumors.
What is the Evans-Jensen Classification?
The Evans-Jensen Classification is a system used to categorize various types of bone tumors. Developed by Dr. Evans and Dr. Jensen, this classification helps medical professionals diagnose and treat bone tumors more effectively. Let's dive into some interesting facts about this classification system.
-
The Evans-Jensen Classification was first introduced in the 1970s. It has since become a cornerstone in orthopedic oncology.
-
This system categorizes bone tumors into benign and malignant types. This distinction is crucial for determining the appropriate treatment plan.
-
Benign tumors are generally non-cancerous. They are less aggressive and have a lower risk of spreading to other parts of the body.
-
Malignant tumors are cancerous. They are more aggressive and can spread to other tissues and organs.
-
The classification system uses radiographic imaging to help identify the type of tumor. X-rays, MRIs, and CT scans are commonly used.
Benign Bone Tumors in the Evans-Jensen Classification
Benign bone tumors are less worrisome but still require medical attention. Here are some key facts about benign tumors in this classification.
-
Osteochondroma is the most common benign bone tumor. It usually affects children and adolescents.
-
Enchondroma is another type of benign tumor. It often occurs in the small bones of the hands and feet.
-
Giant cell tumor is a benign but locally aggressive tumor. It can cause significant bone destruction if not treated.
-
Osteoid osteoma is a small, painful tumor. It often affects the long bones of the legs.
-
Fibrous dysplasia is a benign condition where normal bone is replaced with fibrous tissue. It can weaken the affected bone.
Malignant Bone Tumors in the Evans-Jensen Classification
Malignant bone tumors are more serious and require aggressive treatment. Here are some important facts about malignant tumors in this classification.
-
Osteosarcoma is the most common malignant bone tumor. It usually affects teenagers and young adults.
-
Ewing's sarcoma is another type of malignant tumor. It often occurs in the bones of the pelvis, thigh, and upper arm.
-
Chondrosarcoma is a cancer that forms in cartilage cells. It typically affects adults over the age of 40.
-
Malignant fibrous histiocytoma is a rare type of cancer. It can occur in both bone and soft tissue.
-
Multiple myeloma is a cancer of the plasma cells in the bone marrow. It often affects older adults.
Diagnostic Techniques in the Evans-Jensen Classification
Accurate diagnosis is crucial for effective treatment. Here are some facts about the diagnostic techniques used in this classification.
-
X-rays are often the first imaging test used. They can reveal the location and size of the tumor.
-
MRI scans provide detailed images of soft tissues and bone marrow. They are useful for assessing the extent of the tumor.
-
CT scans offer detailed cross-sectional images of the body. They can help identify the tumor's exact location and size.
-
Bone scans use a small amount of radioactive material to detect bone abnormalities. They are useful for identifying areas of increased bone activity.
-
Biopsies involve taking a small sample of the tumor tissue. This sample is then examined under a microscope to determine the type of tumor.
Treatment Options Based on the Evans-Jensen Classification
Treatment varies depending on whether the tumor is benign or malignant. Here are some facts about the treatment options.
-
Surgery is often the primary treatment for both benign and malignant tumors. It involves removing the tumor and some surrounding healthy tissue.
-
Chemotherapy uses drugs to kill cancer cells. It is often used for malignant tumors like osteosarcoma and Ewing's sarcoma.
-
Radiation therapy uses high-energy rays to kill cancer cells. It is sometimes used in combination with surgery and chemotherapy.
-
Targeted therapy involves drugs that specifically target cancer cells. It is a newer treatment option for certain types of bone cancer.
-
Physical therapy is often recommended after surgery. It helps patients regain strength and mobility.
Prognosis and Survival Rates in the Evans-Jensen Classification
The prognosis for bone tumors varies widely. Here are some facts about survival rates and factors that influence prognosis.
-
The five-year survival rate for osteosarcoma is around 70% if the cancer has not spread.
-
Ewing's sarcoma has a five-year survival rate of about 70% for localized tumors. This rate drops if the cancer has spread.
-
Chondrosarcoma has a better prognosis for low-grade tumors. High-grade tumors have a lower survival rate.
-
Early detection and treatment significantly improve the prognosis for most bone tumors.
-
Ongoing research aims to develop new treatments and improve survival rates for bone cancer patients.
Final Thoughts on Evans-Jensen Classification
Understanding the Evans-Jensen Classification can be a game-changer for anyone diving into the world of medical diagnostics. This system, which categorizes tumors based on their histological features, helps doctors make more accurate diagnoses and tailor treatment plans. Knowing these 30 facts not only broadens your knowledge but also highlights the importance of this classification in modern medicine. From its origins to its applications, the Evans-Jensen Classification remains a cornerstone in the field. Whether you're a medical student, a professional, or just curious, these insights offer a clear picture of why this system matters. Keep these facts handy; they might just come in useful someday.
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
