Cranio osteoarthropathy might sound like a mouthful, but it's a condition worth understanding. This rare disorder affects bones and joints, leading to symptoms like clubbing of fingers and toes, joint pain, and skin changes. Primary hypertrophic osteoarthropathy is often inherited, while secondary forms can be linked to other diseases like lung cancer or heart conditions. Knowing the facts about cranio osteoarthropathy can help in recognizing symptoms early and seeking appropriate treatment. Whether you're a student, a curious mind, or someone affected by this condition, these 30 facts will shed light on its causes, symptoms, and treatments. Buckle up for an informative ride!
Key Takeaways:
- Cranio Osteoarthropathy is a rare condition causing bone and joint changes, skin thickening, and nail clubbing. It can be genetic or secondary to lung, heart, gastrointestinal, or liver diseases.
- Symptoms include swollen joints, chronic pain, fatigue, fever, and weight loss. Diagnosis involves X-rays, bone scans, blood tests, genetic testing, and CT scans. Treatment options include medications, physical therapy, surgery, lifestyle changes, and addressing underlying conditions.
What is Cranio Osteoarthropathy?
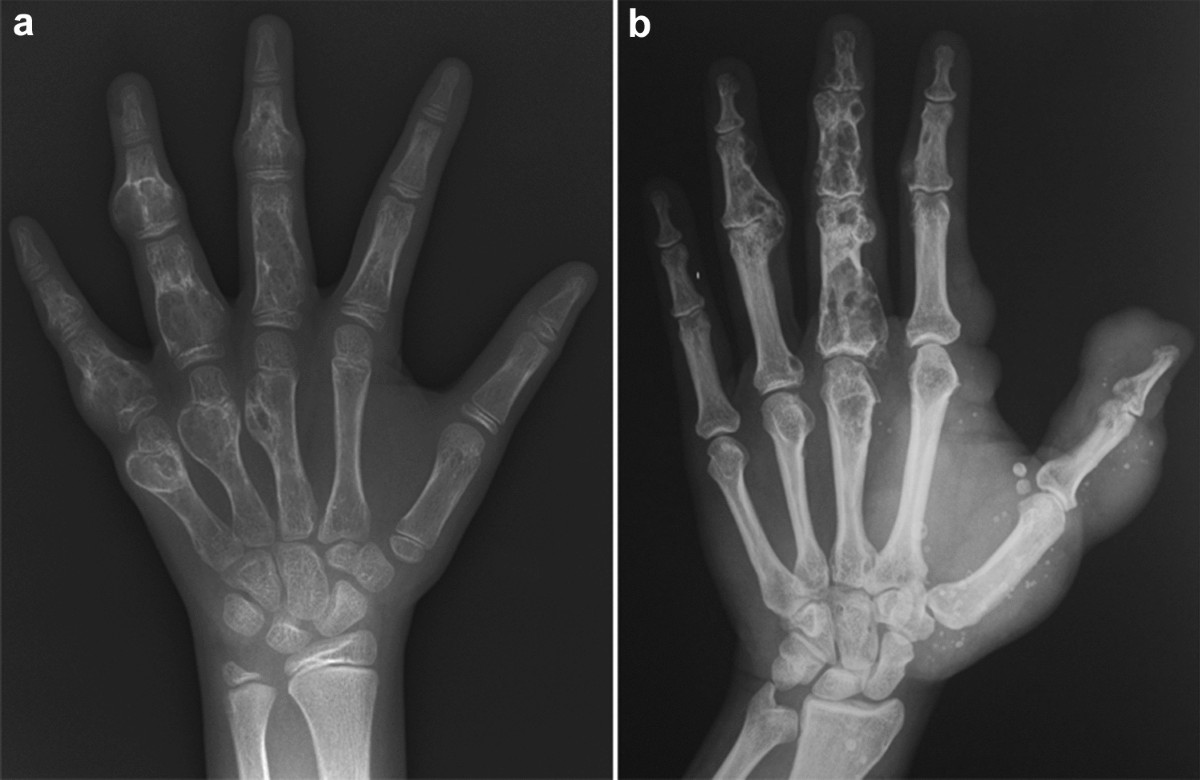
Cranio Osteoarthropathy, also known as hypertrophic osteoarthropathy, is a medical condition that affects bones and joints. It often involves the skin and soft tissues too. This condition can be primary or secondary, depending on its cause.
-
Rare Condition: Cranio Osteoarthropathy is a rare disease, affecting only a small percentage of the population.
-
Bone Changes: It causes abnormal bone growth, particularly in the long bones of the arms and legs.
-
Joint Pain: Patients often experience joint pain and swelling, making movement difficult.
-
Skin Thickening: The skin over the affected bones can become thick and coarse.
-
Nail Changes: Clubbing of the fingers and toes is common, where nails become rounded and bulbous.
Causes of Cranio Osteoarthropathy
Understanding the causes can help in diagnosing and managing the condition better. It can be primary (genetic) or secondary (due to another disease).
-
Genetic Factors: Primary cranio osteoarthropathy is often inherited and linked to genetic mutations.
-
Lung Diseases: Secondary cranio osteoarthropathy is frequently associated with lung diseases like lung cancer or chronic infections.
-
Heart Conditions: Some heart diseases can also lead to secondary cranio osteoarthropathy.
-
Gastrointestinal Issues: Conditions like Crohn's disease or ulcerative colitis may contribute to its development.
-
Liver Diseases: Liver cirrhosis is another potential cause of secondary cranio osteoarthropathy.
Symptoms to Watch For
Recognizing symptoms early can lead to better management and treatment outcomes. Symptoms can vary but often include the following.
-
Swollen Joints: Persistent swelling in joints, especially in the knees and ankles.
-
Pain: Chronic pain in the affected areas, which can be severe.
-
Fatigue: General fatigue and weakness are common among patients.
-
Fever: Low-grade fever may accompany other symptoms.
-
Weight Loss: Unintentional weight loss can occur, especially in secondary cases.
Diagnosis Methods
Accurate diagnosis is crucial for effective treatment. Various methods are used to diagnose cranio osteoarthropathy.
-
X-Rays: X-rays can reveal abnormal bone growth and joint changes.
-
Bone Scans: These scans help in detecting bone abnormalities early.
-
Blood Tests: Blood tests can identify underlying conditions contributing to the disease.
-
Genetic Testing: For primary cases, genetic testing can confirm the diagnosis.
-
CT Scans: CT scans provide detailed images of bones and joints, aiding in diagnosis.
Treatment Options
While there is no cure, several treatments can help manage symptoms and improve quality of life.
-
Medications: Pain relievers and anti-inflammatory drugs are commonly prescribed.
-
Physical Therapy: Physical therapy can help maintain joint function and reduce pain.
-
Surgery: In severe cases, surgery may be necessary to correct bone deformities.
-
Lifestyle Changes: Diet and exercise can play a role in managing symptoms.
-
Treating Underlying Conditions: Addressing the root cause, like lung or heart disease, can alleviate symptoms.
Living with Cranio Osteoarthropathy
Living with this condition requires adjustments and ongoing care. Here are some tips for managing daily life.
-
Regular Check-Ups: Frequent medical check-ups are essential for monitoring the condition.
-
Support Groups: Joining support groups can provide emotional support and practical advice.
-
Healthy Diet: A balanced diet rich in nutrients can help maintain overall health.
-
Exercise: Gentle exercises like swimming or yoga can improve joint flexibility.
-
Mental Health: Managing stress and mental health is crucial for overall well-being.
Final Thoughts on Cranio Osteoarthropathy
Cranio osteoarthropathy, though rare, offers a fascinating glimpse into the complexity of human health. Understanding its symptoms, causes, and treatments can help those affected manage their condition better. Early diagnosis remains crucial for effective treatment and improved quality of life.
Doctors often rely on a combination of medical history, physical exams, and imaging tests to diagnose this condition. Treatment usually involves addressing the underlying cause, which can range from lung diseases to genetic factors. Medications, physical therapy, and sometimes surgery can provide relief.
Staying informed about cranio osteoarthropathy can empower patients and their families. Knowledge is power, especially when dealing with rare medical conditions. If you or someone you know shows symptoms, consult a healthcare professional for a thorough evaluation. Awareness and timely intervention can make a significant difference.
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
