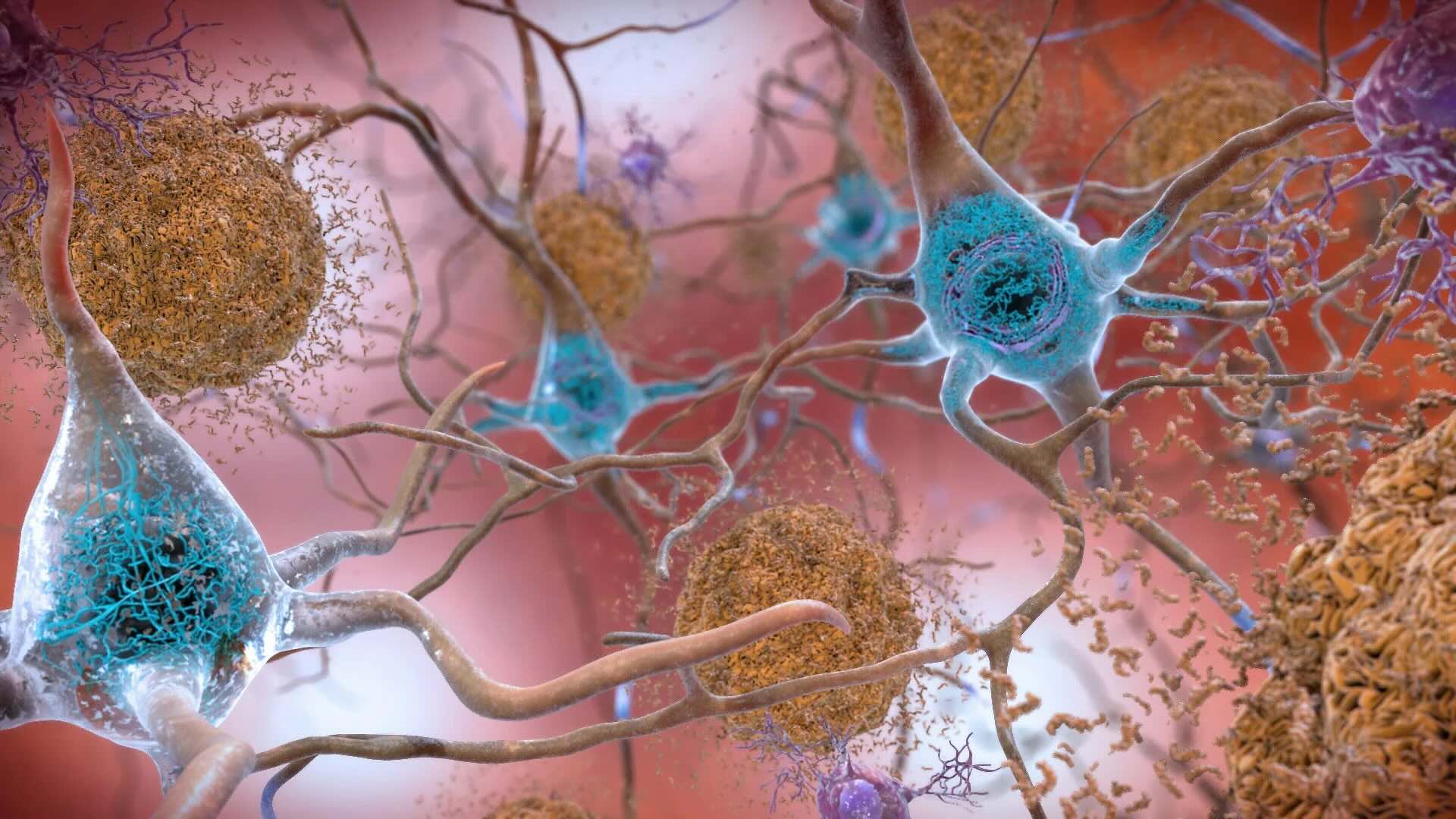
What are amyloids? Amyloids are abnormal protein aggregates that can form in various tissues and organs, leading to diseases. These proteins misfold and clump together, creating fibrous deposits that disrupt normal cellular functions. Why are they important? Amyloids are linked to several serious conditions, including Alzheimer's disease, Parkinson's disease, and type 2 diabetes. Understanding amyloids can help in developing treatments for these diseases. How do they form? Amyloids form when proteins lose their normal shape and stick together. This process can be triggered by genetic mutations, environmental factors, or aging. What can be done? Research is ongoing to find ways to prevent amyloid formation and to develop therapies that can break down existing amyloid deposits.
What Are Amyloids?
Amyloids are protein aggregates that form fibrous deposits in tissues and organs. These deposits can disrupt normal function and are linked to various diseases. Let's dive into some fascinating facts about amyloids.
-
Amyloids are composed of proteins that fold abnormally, creating long, fibrous structures.
-
The term "amyloid" comes from the Latin word "amylum," meaning starch, because early researchers mistakenly thought amyloids were starch-like substances.
-
Amyloids can be found in both humans and animals, affecting a wide range of species.
Diseases Associated with Amyloids
Amyloids are notorious for their role in several serious diseases. Here are some key facts about their involvement in health conditions.
-
Alzheimer's disease is one of the most well-known amyloid-related diseases, characterized by amyloid-beta plaques in the brain.
-
Amyloids are also implicated in Parkinson's disease, where alpha-synuclein proteins form amyloid fibrils.
-
Type 2 diabetes involves amyloid deposits of islet amyloid polypeptide in the pancreas.
-
Amyloidosis is a group of diseases where amyloids accumulate in organs like the heart, kidneys, and liver.
-
Prion diseases, such as Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease, involve amyloid-like prion protein aggregates.
How Amyloids Form
Understanding how amyloids form can help in developing treatments. Here are some insights into their formation process.
-
Amyloids form when proteins misfold and aggregate into insoluble fibrils.
-
These fibrils are stabilized by beta-sheet structures, which are common in amyloid proteins.
-
Environmental factors, such as pH and temperature, can influence amyloid formation.
-
Genetic mutations can increase the likelihood of amyloid formation in certain individuals.
Detection and Diagnosis
Detecting amyloids early can be crucial for managing diseases. Here are some methods used for their detection.
-
Biopsies are often used to detect amyloid deposits in tissues.
-
Imaging techniques like PET scans can visualize amyloid plaques in the brain.
-
Blood tests can sometimes detect biomarkers associated with amyloid diseases.
-
Congo red staining is a common histological method for identifying amyloids in tissue samples.
Amyloids in Research
Amyloids are a hot topic in scientific research. Here are some interesting facts about their study.
-
Researchers use model organisms like mice and yeast to study amyloid formation and toxicity.
-
Cryo-electron microscopy has provided detailed images of amyloid fibrils at the atomic level.
-
Scientists are exploring small molecules and antibodies that can inhibit amyloid formation.
-
Some studies suggest that amyloids might have functional roles in normal biology, not just in disease.
Potential Treatments
Efforts to treat amyloid-related diseases are ongoing. Here are some promising approaches.
-
Immunotherapy aims to use antibodies to target and clear amyloid plaques.
-
Small molecule inhibitors can prevent amyloid proteins from misfolding and aggregating.
-
Gene therapy is being explored to correct genetic mutations that lead to amyloid formation.
-
Lifestyle changes, such as diet and exercise, may help reduce the risk of amyloid-related diseases.
Amyloids Beyond Humans
Amyloids aren't just a human problem. They affect other species too. Here are some examples.
-
Amyloids have been found in the brains of aged dogs, similar to human Alzheimer's disease.
-
Certain fish species develop amyloids in their muscles, affecting their health.
-
Amyloids can form in the silk of spiders, giving it unique mechanical properties.
-
Some bacteria produce amyloid fibers as part of their biofilm structures.
Fun and Surprising Facts
Amyloids have some unexpected and intriguing aspects. Here are a few fun facts.
-
Not all amyloids are harmful; some play beneficial roles in organisms.
-
Researchers are investigating the use of amyloids in nanotechnology and materials science due to their unique properties.
The Final Word on Amyloids
Amyloids are fascinating yet complex proteins with a significant impact on human health. They play roles in diseases like Alzheimer's, Parkinson's, and type 2 diabetes. Understanding amyloids can help in developing treatments for these conditions. Research continues to uncover new aspects of amyloids, offering hope for future medical advancements.
Knowing these 30 facts about amyloids gives you a solid foundation. From their structure to their role in disease, these proteins are more than just microscopic entities. They're key players in some of the most challenging health issues today.
Stay curious and keep learning. The more we know about amyloids, the better equipped we'll be to tackle the diseases they influence. Knowledge is power, especially when it comes to health.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
