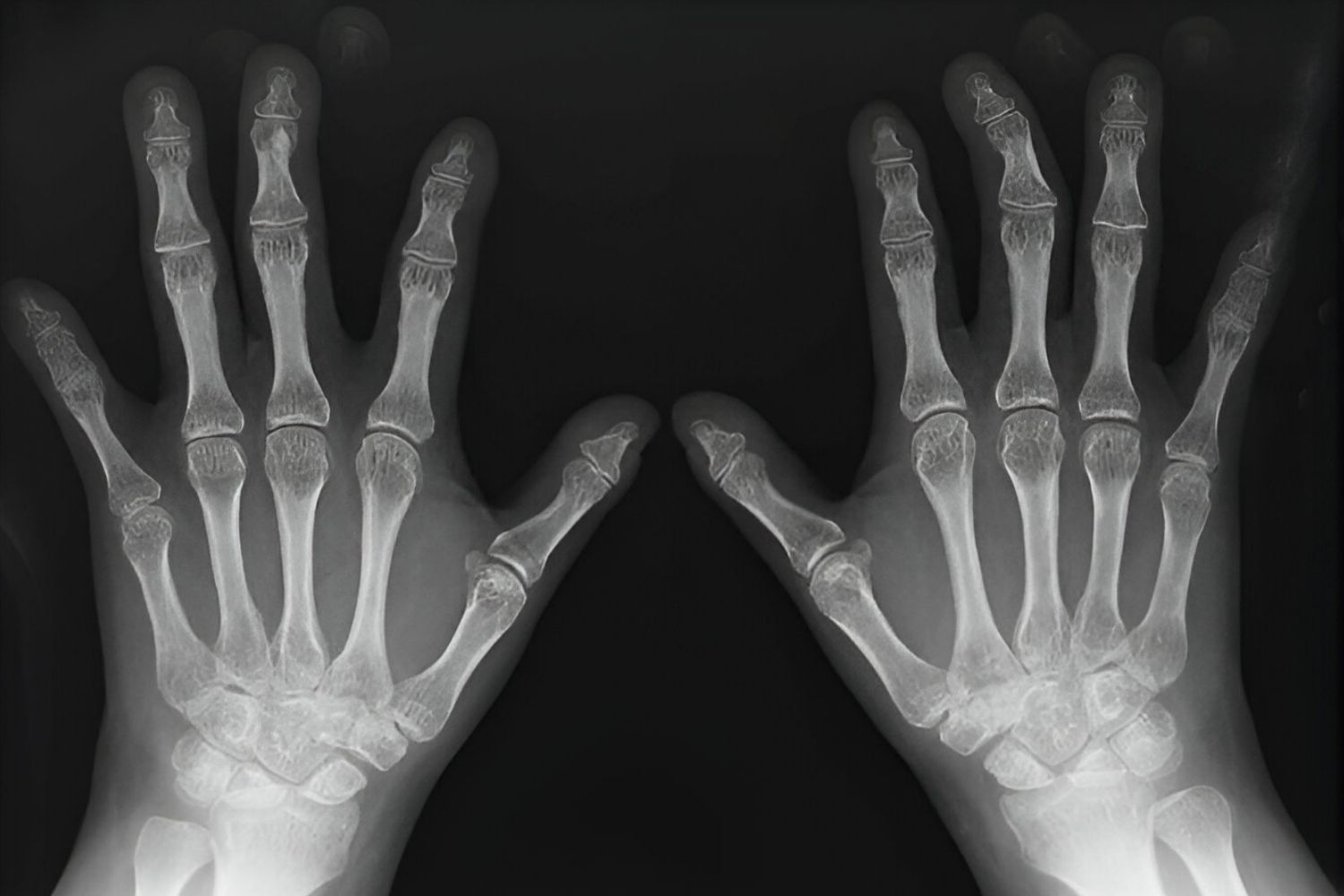
Spondyloperipheral dysplasia is a rare genetic disorder that affects bone growth, leading to short stature and other skeletal abnormalities. Caused by mutations in the COL2A1 gene, this condition impacts the development of collagen, a crucial protein for bone and cartilage formation. Individuals with spondyloperipheral dysplasia often experience joint pain, spinal issues, and distinctive facial features. Diagnosing this disorder typically involves genetic testing and imaging studies to assess bone structure. While there is no cure, treatments focus on managing symptoms and improving quality of life. Understanding this condition is essential for those affected and their families, offering insights into potential challenges and care strategies.
Key Takeaways:
- Spondyloperipheral Dysplasia (SPD) is a rare genetic disorder affecting bone growth, causing short stature, spinal deformities, and joint pain. Early diagnosis and a supportive team of specialists are crucial for managing the condition.
- Living with SPD presents unique challenges, but with proper support and management, individuals can lead fulfilling lives. Adaptive devices, maintaining a healthy weight, regular exercise, emotional support, and educational accommodations are important for daily life.
What is Spondyloperipheral Dysplasia?
Spondyloperipheral Dysplasia (SPD) is a rare genetic disorder affecting bone growth. It primarily impacts the spine and the ends of long bones, leading to various skeletal abnormalities. Understanding SPD can help in managing the condition better.
- SPD is caused by mutations in the COL2A1 gene, which is crucial for collagen production.
- Collagen is a protein that provides structure and strength to connective tissues, including bones and cartilage.
- SPD is inherited in an autosomal dominant pattern, meaning one copy of the altered gene is enough to cause the disorder.
- Symptoms often appear in early childhood, though the severity can vary widely among individuals.
- Common signs include short stature, spinal deformities, and joint pain.
Symptoms and Diagnosis
Recognizing the symptoms early can lead to a timely diagnosis and better management of SPD. Here are some key facts about the symptoms and how SPD is diagnosed.
- Short stature is one of the most noticeable symptoms, often becoming apparent in early childhood.
- Individuals with SPD may have a disproportionately short trunk compared to their limbs.
- Spinal abnormalities, such as scoliosis or kyphosis, are common in SPD patients.
- Joint pain and stiffness, particularly in the hips and knees, can occur due to abnormal bone growth.
- Radiographic imaging, such as X-rays, is essential for diagnosing SPD, revealing characteristic bone abnormalities.
- Genetic testing can confirm the diagnosis by identifying mutations in the COL2A1 gene.
Treatment and Management
While there is no cure for SPD, various treatments can help manage symptoms and improve quality of life. Here are some important facts about treatment options.
- Physical therapy can help maintain mobility and reduce joint pain.
- Orthopedic surgery may be necessary to correct severe spinal deformities or joint issues.
- Pain management strategies, including medications and lifestyle changes, can alleviate discomfort.
- Regular monitoring by a team of specialists, including geneticists, orthopedists, and physical therapists, is crucial.
- Early intervention can prevent complications and improve long-term outcomes.
Living with Spondyloperipheral Dysplasia
Living with SPD presents unique challenges, but with proper support and management, individuals can lead fulfilling lives. Here are some facts about daily life with SPD.
- Adaptive devices, such as braces or custom footwear, can aid mobility and reduce pain.
- Maintaining a healthy weight is important to minimize stress on the joints.
- Regular exercise, tailored to individual capabilities, can improve overall health and well-being.
- Emotional support from family, friends, and support groups can help individuals cope with the challenges of SPD.
- Educational accommodations may be necessary for children with SPD to ensure they succeed in school.
Research and Future Directions
Ongoing research aims to better understand SPD and develop new treatments. Here are some exciting developments in the field.
- Researchers are exploring gene therapy as a potential treatment for SPD, aiming to correct the underlying genetic mutation.
- Advances in imaging technology are improving the ability to diagnose SPD earlier and more accurately.
- Studies on the role of collagen in bone development may lead to new therapeutic approaches.
- Patient registries and collaborative research efforts are helping to gather more data on SPD, which could lead to better treatments and outcomes.
Final Thoughts on Spondyloperipheral Dysplasia
Spondyloperipheral Dysplasia, a rare genetic disorder, affects bone growth and development. Understanding its symptoms, causes, and treatments can help those affected lead better lives. Genetic mutations in the COL2A1 gene play a significant role in this condition. Early diagnosis and intervention are crucial for managing symptoms and improving quality of life. While there's no cure, treatments like physical therapy, orthopedic interventions, and regular monitoring can make a big difference. Raising awareness about this rare disorder can lead to better support and resources for patients and their families. Remember, knowledge is power. The more we learn about Spondyloperipheral Dysplasia, the better equipped we are to support those living with it. Stay informed, stay supportive, and let's work together to make a difference.
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
