Renal caliceal diverticuli might sound like a mouthful, but understanding it can be simpler than you think. These small pouches form in the kidney's calyces, often going unnoticed until they cause problems. Deafness, on the other hand, affects millions worldwide, impacting communication and daily life. What if these two seemingly unrelated conditions had more in common than meets the eye? In this blog post, we'll dive into 25 intriguing facts about renal caliceal diverticuli and deafness. From their causes and symptoms to surprising connections, you'll gain a clearer picture of these medical conditions. Ready to learn more? Let's get started!
Key Takeaways:
- Renal caliceal diverticuli are small pouches in the kidney that can cause pain if infected or obstructed. They are often found accidentally during imaging tests and may require surgical treatment.
- Deafness can be present at birth or develop later in life due to genetic factors, infections, or exposure to loud noises. Treatments like hearing aids and cochlear implants can help manage deafness.
What is Renal Caliceal Diverticuli?
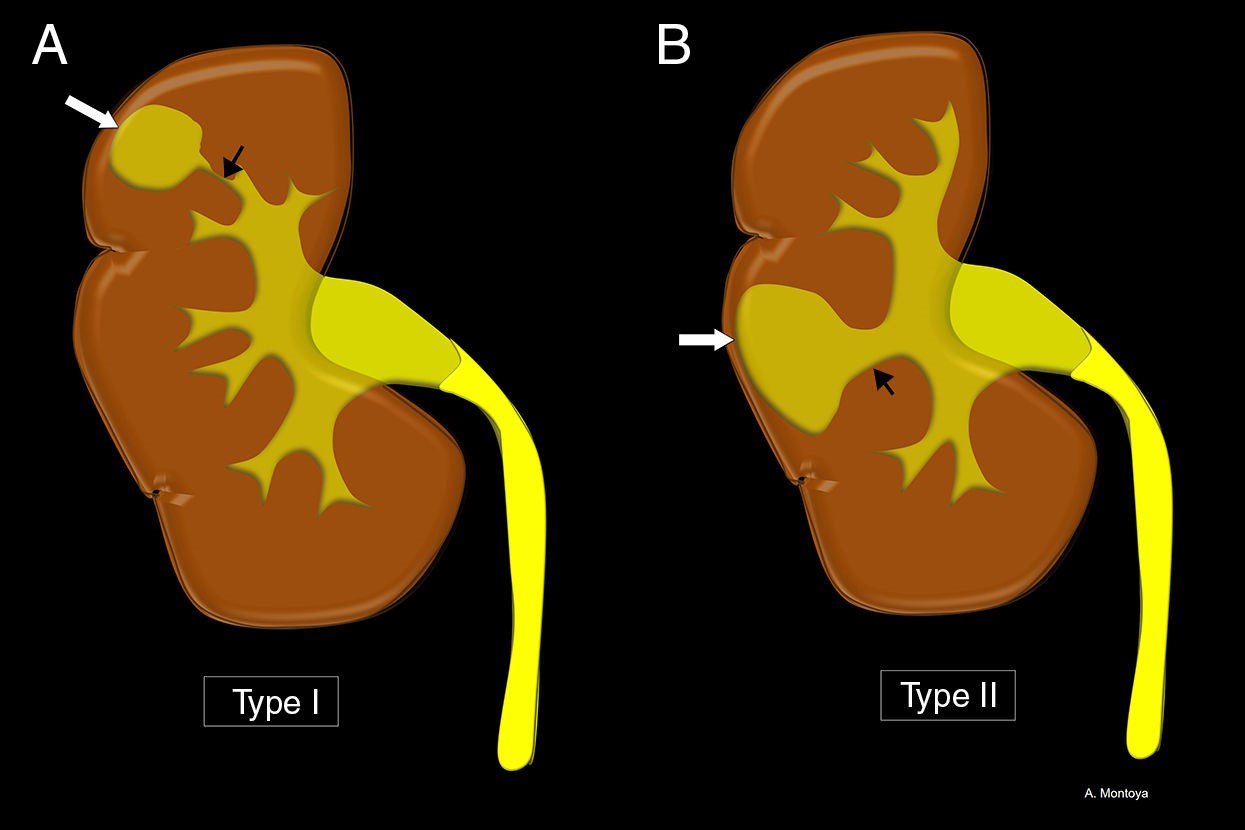
Renal caliceal diverticuli are small, pouch-like structures that form in the kidney's calyces. These pockets can collect urine and sometimes lead to complications.
- Renal caliceal diverticuli are often discovered incidentally during imaging tests for other conditions.
- These diverticuli can be congenital, meaning present from birth, or acquired due to infections or trauma.
- They are usually asymptomatic but can cause pain if they become infected or obstructed.
- Diagnosis is typically made using ultrasound, CT scans, or intravenous pyelography.
- Treatment options range from observation to surgical intervention, depending on symptoms and complications.
Understanding Deafness
Deafness refers to the partial or complete inability to hear. It can affect one or both ears and can occur at any age.
- Deafness can be congenital, meaning present at birth, or acquired later in life.
- Common causes include genetic factors, infections, exposure to loud noises, and aging.
- There are different types of deafness: conductive, sensorineural, and mixed.
- Conductive deafness occurs when sound waves cannot reach the inner ear due to blockages or damage.
- Sensorineural deafness results from damage to the inner ear or auditory nerve.
- Mixed deafness is a combination of conductive and sensorineural hearing loss.
- Hearing aids and cochlear implants are common treatments for managing deafness.
The Connection Between Renal Caliceal Diverticuli and Deafness
While renal caliceal diverticuli and deafness are distinct conditions, there are some interesting overlaps in their occurrence and management.
- Both conditions can be congenital, highlighting the role of genetics in their development.
- Imaging techniques like CT scans and ultrasounds are crucial for diagnosing both conditions.
- Surgical interventions may be necessary for severe cases of either condition.
- Both conditions can significantly impact quality of life, requiring ongoing medical management.
- Early diagnosis and intervention can improve outcomes for both renal caliceal diverticuli and deafness.
Interesting Facts About Renal Caliceal Diverticuli
Renal caliceal diverticuli, though not widely known, have some fascinating aspects worth noting.
- These diverticuli can sometimes mimic kidney stones on imaging tests.
- They are more common in adults than in children.
- In rare cases, renal caliceal diverticuli can lead to the formation of kidney stones within the diverticulum.
- Some patients may experience recurrent urinary tract infections due to these diverticuli.
- Minimally invasive techniques like endoscopic surgery are often used to treat symptomatic diverticuli.
Fascinating Facts About Deafness
Deafness, a condition affecting millions worldwide, has a rich history and many intriguing aspects.
- The first known hearing aid dates back to the 17th century and was a simple ear trumpet.
- Sign language, a vital communication tool for the deaf community, has been used for centuries.
- Famous individuals like Ludwig van Beethoven and Helen Keller overcame deafness to achieve remarkable success in their fields.
Final Thoughts on Renal Caliceal Diverticuli Deafness
Renal caliceal diverticuli and deafness might seem unrelated, but understanding them can be crucial. Renal caliceal diverticuli are small pouches in the kidney that can cause pain or infection. Regular check-ups and imaging tests help in early detection and management. Deafness, on the other hand, affects hearing and can be congenital or acquired. Early intervention, hearing aids, and sign language can significantly improve quality of life for those affected.
Both conditions highlight the importance of early diagnosis and treatment. While renal caliceal diverticuli require medical attention to prevent complications, deafness benefits from supportive therapies and technologies. Awareness and education about these conditions can lead to better health outcomes and improved quality of life. Stay informed, consult healthcare professionals, and take proactive steps for your well-being.
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
