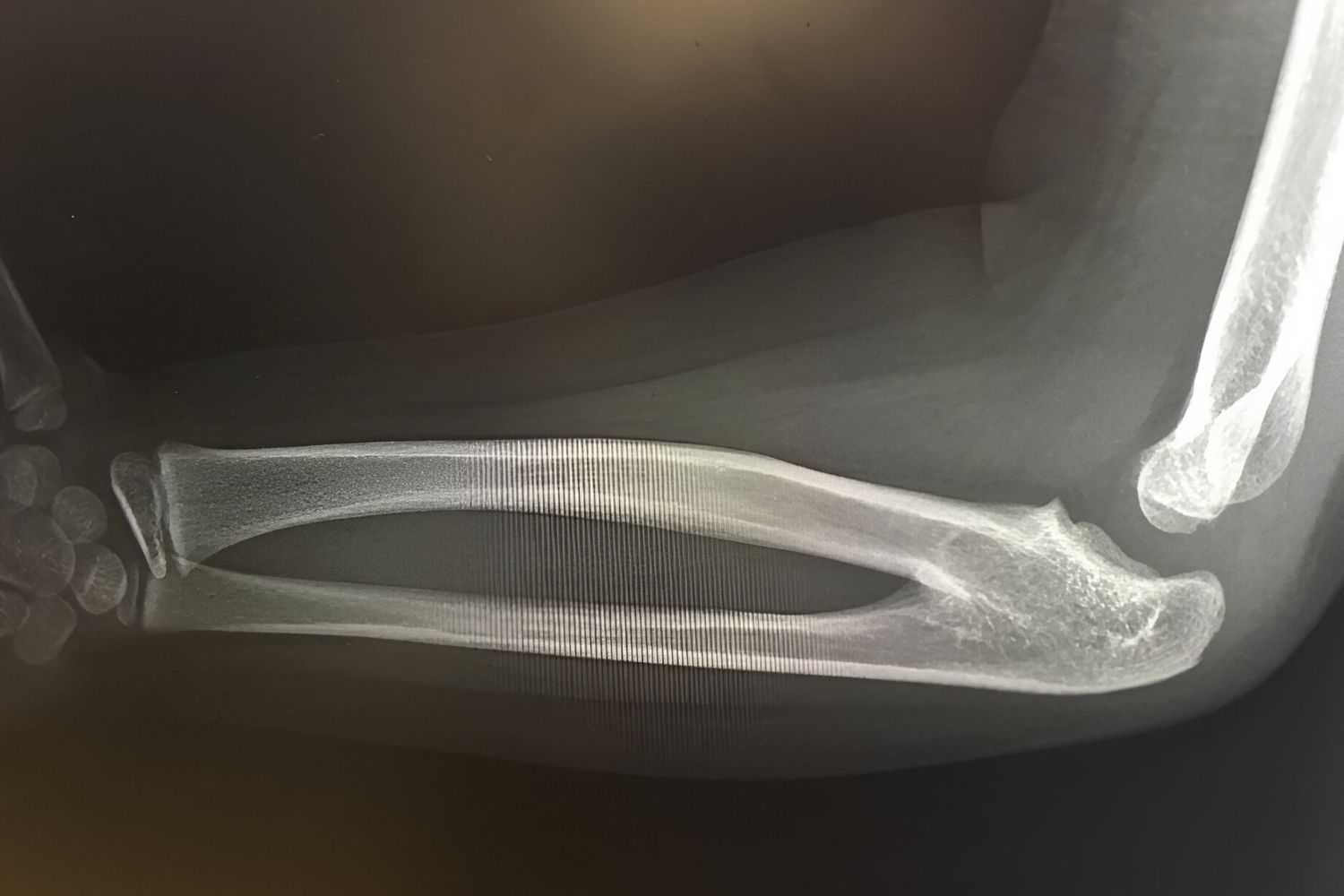
Radio-Ulnar Synostosis Type 1 is a rare condition where the radius and ulna bones in the forearm are fused together. This fusion limits the ability to rotate the forearm, making simple tasks like turning a doorknob or using utensils challenging. The condition can be present at birth or develop later due to trauma or other factors. Symptoms often include limited forearm rotation, pain, and sometimes deformity. Diagnosis typically involves physical exams and imaging tests like X-rays. Treatment options vary from physical therapy to surgery, depending on severity. Understanding this condition can help those affected manage daily activities better.
Key Takeaways:
- Radio-Ulnar Synostosis Type 1 is a rare condition where the forearm bones are fused, limiting rotation. Early detection, physical therapy, and adaptive devices can help manage symptoms and improve quality of life.
- Living with Radio-Ulnar Synostosis Type 1 involves finding support, educating others, and making adjustments for daily activities and career choices. Ongoing research aims to better understand and treat this condition.
What is Radio-Ulnar Synostosis Type 1?
Radio-Ulnar Synostosis Type 1 is a rare congenital condition where the radius and ulna bones in the forearm are fused. This fusion limits the rotation of the forearm, making certain movements difficult or impossible. Here are some intriguing facts about this condition.
-
Congenital Condition: This condition is present at birth, meaning it develops during fetal growth.
-
Genetic Factors: Often, genetic mutations are responsible for this condition. It can be inherited in an autosomal dominant pattern.
-
Bilateral Occurrence: In many cases, both arms are affected, although it can also occur in just one arm.
-
Limited Rotation: The fusion of the radius and ulna restricts the ability to rotate the forearm, affecting daily activities.
-
Diagnosis: X-rays are typically used to diagnose this condition, revealing the fused bones.
-
Early Detection: Pediatricians often detect this condition during routine check-ups in infancy.
Symptoms and Impact
Understanding the symptoms and how they impact daily life can help in managing the condition better.
-
Restricted Movement: The most noticeable symptom is the inability to rotate the forearm.
-
Compensatory Movements: Individuals often develop compensatory movements to perform tasks, like using the shoulder more.
-
Pain: Some people experience pain, especially during activities that require forearm rotation.
-
Functional Limitations: Tasks like turning a doorknob or using utensils can be challenging.
-
Muscle Weakness: Over time, muscle weakness can develop due to limited use of the affected arm.
Treatment Options
While there is no cure, various treatments can help manage the symptoms and improve quality of life.
-
Physical Therapy: Exercises can help maintain muscle strength and improve range of motion.
-
Surgery: In severe cases, surgery may be considered to separate the fused bones, although it carries risks.
-
Adaptive Devices: Special tools and devices can assist with daily activities, making them easier to perform.
-
Pain Management: Medications and other therapies can help manage pain associated with the condition.
-
Occupational Therapy: Therapists can teach new ways to perform tasks, improving independence.
Living with Radio-Ulnar Synostosis Type 1
Adapting to life with this condition involves making adjustments and finding support.
-
Support Groups: Connecting with others who have the condition can provide emotional support and practical advice.
-
Education: Educating family, friends, and teachers about the condition can foster understanding and support.
-
Career Choices: Some career paths may be more suitable than others, depending on the physical demands.
-
Sports and Activities: While some sports may be challenging, many activities can still be enjoyed with modifications.
-
Mental Health: Addressing the emotional impact of the condition is important for overall well-being.
Research and Future Directions
Ongoing research aims to better understand and treat Radio-Ulnar Synostosis Type 1.
-
Genetic Studies: Researchers are studying the genetic mutations that cause this condition to develop better treatments.
-
Innovative Therapies: New therapies, including regenerative medicine, are being explored to improve outcomes.
-
Awareness Campaigns: Raising awareness about this rare condition can lead to better support and resources.
-
Patient Registries: Collecting data from patients worldwide helps researchers identify patterns and potential treatments.
Final Thoughts on Radio-Ulnar Synostosis Type 1
Radio-Ulnar Synostosis Type 1 is a rare condition where the radius and ulna bones in the forearm are fused. This fusion limits the ability to rotate the forearm, making everyday tasks challenging. Early diagnosis and intervention can help manage symptoms and improve quality of life. Treatment options include physical therapy and, in some cases, surgery to separate the fused bones. Understanding the genetic factors and potential complications is crucial for those affected. Support from healthcare professionals and patient communities can make a significant difference. Awareness and education about this condition are essential for better outcomes. If you or someone you know is dealing with Radio-Ulnar Synostosis Type 1, seek medical advice to explore the best treatment options. Stay informed and proactive in managing this condition.
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
