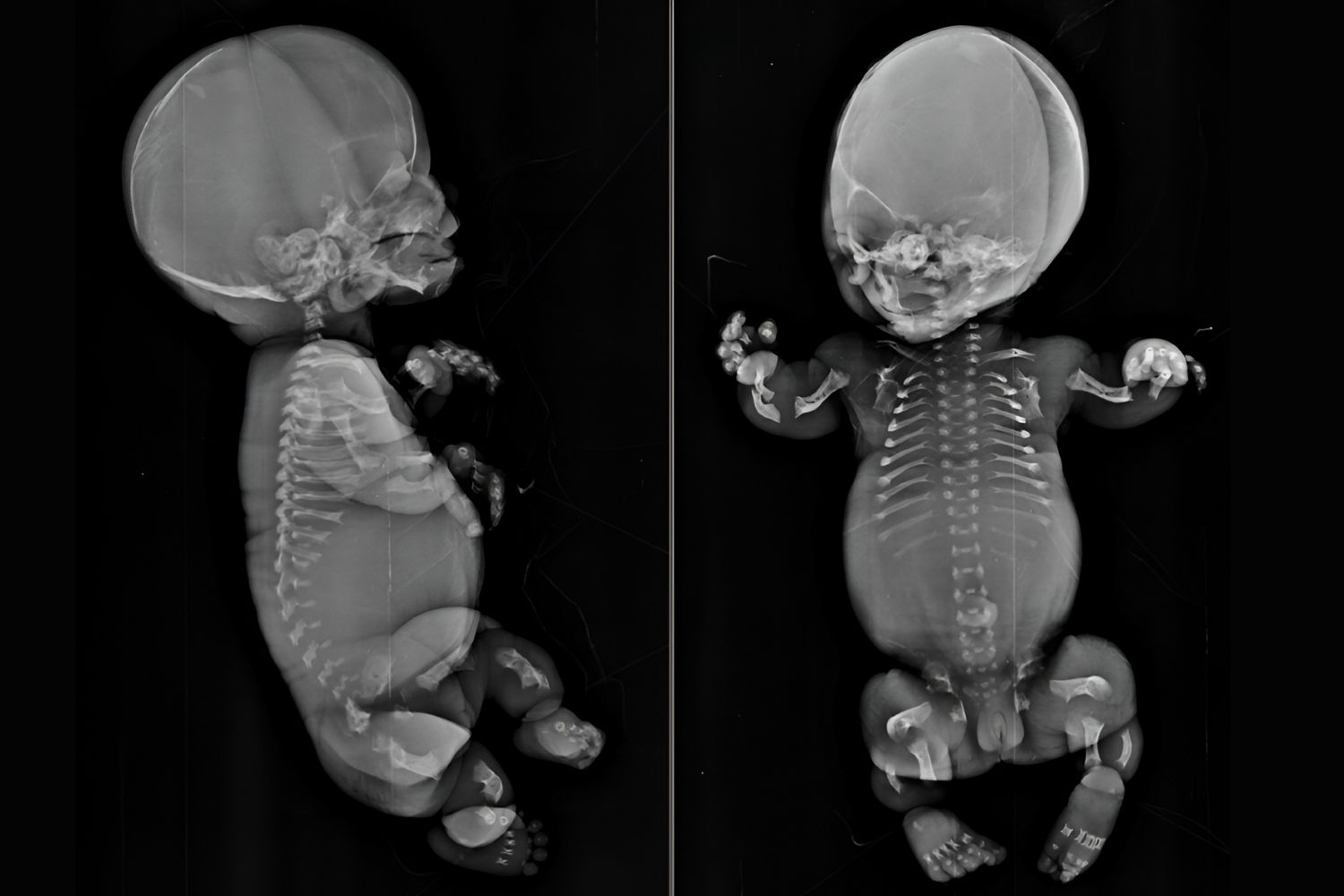
What is Platyspondylic Lethal Skeletal Dysplasia? This rare genetic disorder affects bone development, leading to severe skeletal abnormalities. Characterized by short limbs, a narrow chest, and flattened vertebrae, it often results in life-threatening complications. Caused by mutations in specific genes, this condition disrupts normal bone growth and development. Infants with this disorder typically face respiratory issues due to the small chest cavity, making breathing difficult. Diagnosis usually occurs through prenatal imaging or genetic testing. While there is no cure, supportive care can help manage symptoms. Understanding this condition is crucial for early intervention and providing the best possible care for affected individuals.
Key Takeaways:
- Platyspondylic Lethal Skeletal Dysplasia (PLSD) is a rare genetic disorder causing severe skeletal abnormalities and often leading to life-threatening complications, making early diagnosis crucial for managing the condition.
- While there is no cure for PLSD, treatments like respiratory support, physical therapy, and surgical interventions can help manage symptoms and improve the quality of life for affected individuals.
What is Platyspondylic Lethal Skeletal Dysplasia?
Platyspondylic Lethal Skeletal Dysplasia (PLSD) is a rare genetic disorder affecting bone development. It leads to severe skeletal abnormalities, often resulting in life-threatening complications. Here are some key facts about this condition:
- PLSD is characterized by flattened vertebrae, known as platyspondyly.
- The condition is typically diagnosed through prenatal imaging techniques like ultrasound.
- Mutations in the TRPV4 gene are often responsible for PLSD.
- PLSD can be inherited in an autosomal dominant manner, meaning only one copy of the mutated gene is needed to cause the disorder.
- The disorder is considered lethal because it often leads to death before or shortly after birth.
Symptoms and Physical Characteristics
PLSD presents with various physical symptoms that can be identified through medical examinations. These symptoms are critical for diagnosing the condition early.
- Infants with PLSD often have a small chest cavity, leading to respiratory issues.
- Shortened limbs and a disproportionately large head are common physical traits.
- The condition can also cause joint dislocations and limited joint mobility.
- Facial abnormalities, such as a flat nasal bridge and a small jaw, are frequently observed.
- Rib abnormalities, including short and broad ribs, are another hallmark of PLSD.
Diagnosis and Genetic Testing
Early diagnosis of PLSD is crucial for managing the condition and providing appropriate care. Genetic testing plays a significant role in confirming the diagnosis.
- Prenatal ultrasound can detect skeletal abnormalities indicative of PLSD.
- Genetic testing can identify mutations in the TRPV4 gene, confirming the diagnosis.
- Amniocentesis, a procedure to sample amniotic fluid, can be used for genetic testing during pregnancy.
- Postnatal X-rays can reveal characteristic skeletal abnormalities.
- A detailed family history can help identify potential carriers of the mutated gene.
Treatment and Management
While there is no cure for PLSD, various treatments can help manage symptoms and improve the quality of life for affected individuals.
- Respiratory support, such as mechanical ventilation, may be necessary for infants with severe respiratory issues.
- Physical therapy can help improve joint mobility and muscle strength.
- Surgical interventions may be required to address severe skeletal deformities.
- Pain management strategies are essential for improving comfort and quality of life.
- Genetic counseling can provide valuable information for families affected by PLSD.
Research and Future Directions
Ongoing research aims to better understand PLSD and develop more effective treatments. Advances in genetic research hold promise for the future.
- Researchers are exploring gene therapy as a potential treatment for PLSD.
- Animal models are being used to study the effects of TRPV4 mutations on skeletal development.
- Clinical trials are investigating new medications to manage symptoms and improve outcomes.
- Advances in prenatal imaging techniques are improving early detection of PLSD.
- Collaboration between researchers, clinicians, and families is essential for advancing our understanding of PLSD and developing new treatments.
Final Thoughts on Platyspondylic Lethal Skeletal Dysplasia
Platyspondylic Lethal Skeletal Dysplasia (PLSD) is a rare genetic disorder that affects bone development. Understanding this condition helps in recognizing its symptoms early, which can lead to better management and support for affected families. PLSD often results in severe skeletal abnormalities, including short limbs and a small chest, which can be life-threatening. Genetic counseling is crucial for families with a history of PLSD, as it provides valuable information about the risks and implications of the disorder. While there is no cure, ongoing research offers hope for improved treatments and interventions. Raising awareness about PLSD can lead to better resources and support networks for those affected. By staying informed and advocating for research, we can contribute to a better quality of life for individuals with PLSD and their families.
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
