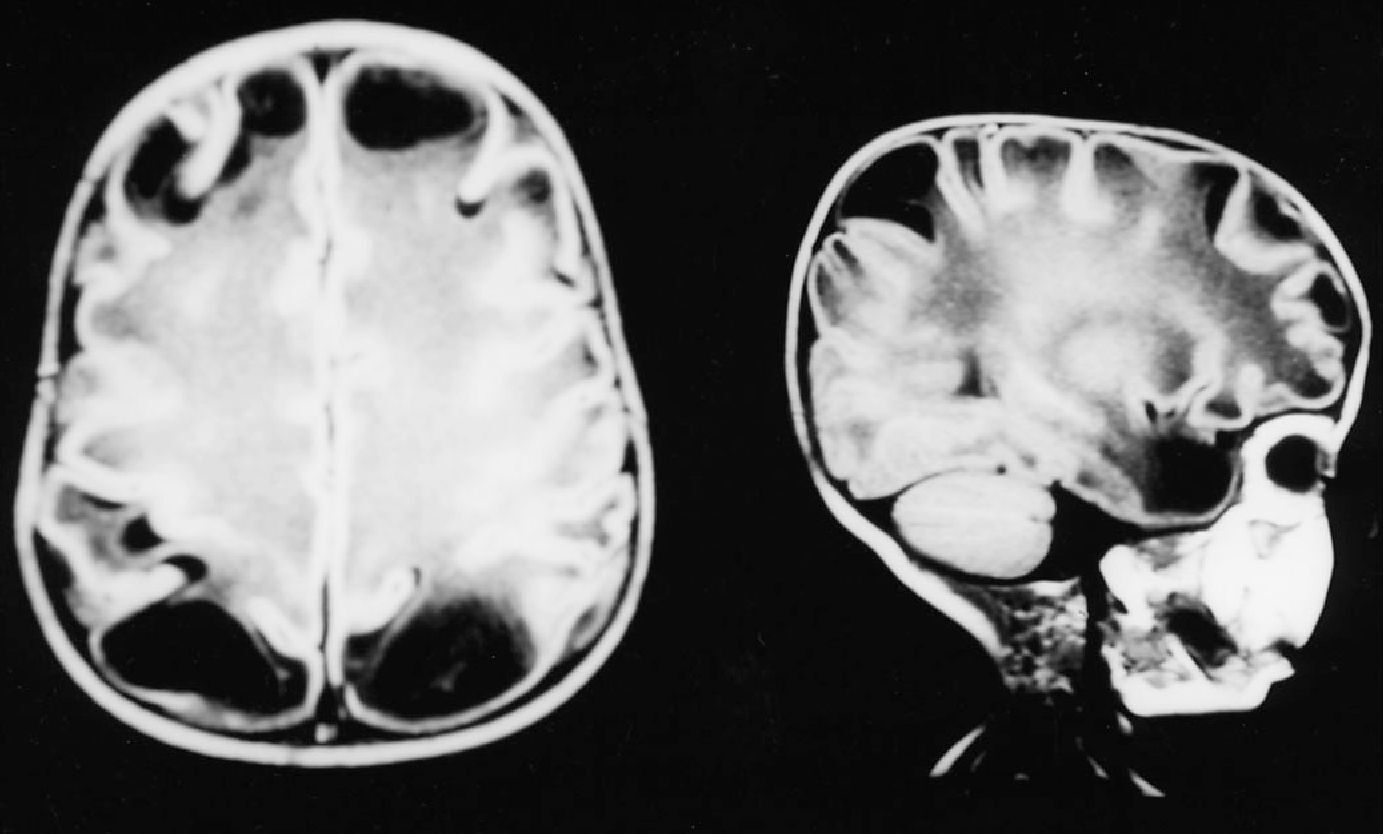
Megalencephaly-Cystic Leukodystrophy is a rare genetic disorder affecting brain development. This condition causes an abnormal increase in brain size, known as megalencephaly, and impacts the white matter, leading to cystic changes. Symptoms often appear in infancy or early childhood and can include developmental delays, motor skill issues, and seizures. Genetic mutations in specific genes, such as the MLC1 gene, are usually responsible for this disorder. Diagnosis typically involves MRI scans and genetic testing to identify these mutations. Treatment focuses on managing symptoms since there is no cure. Understanding this condition can help families and caregivers provide better support for affected individuals.
Key Takeaways:
- Megalencephaly-Cystic Leukodystrophy is a rare genetic disorder causing an abnormally large brain and white matter cysts. It affects development, leading to seizures and motor skill difficulties.
- There is no cure for Megalencephaly-Cystic Leukodystrophy, but treatments like therapy and supportive care can help manage symptoms and improve quality of life. Ongoing research aims to find potential treatments for the future.
What is Megalencephaly-Cystic Leukodystrophy?
Megalencephaly-Cystic Leukodystrophy is a rare genetic disorder that affects brain development. It leads to an abnormally large brain and cysts within the white matter. Here are some intriguing facts about this condition.
-
Megalencephaly means "large brain." Individuals with this disorder have a brain size significantly larger than average.
-
Leukodystrophy refers to a group of disorders that affect the white matter of the brain. In this case, it involves cysts forming within the white matter.
-
Genetic Mutation: The disorder is caused by mutations in the MLC1 gene. This gene is crucial for normal brain development.
-
Autosomal Recessive Inheritance: Both parents must carry a copy of the mutated gene for a child to be affected.
-
Symptoms: Common symptoms include developmental delays, seizures, and motor skill difficulties.
-
Diagnosis: MRI scans are typically used to identify the characteristic brain abnormalities associated with this disorder.
-
Prevalence: It is extremely rare, with only a few hundred cases reported worldwide.
-
Life Expectancy: Life expectancy varies but can be significantly reduced due to complications.
-
No Cure: Currently, there is no cure for Megalencephaly-Cystic Leukodystrophy. Treatment focuses on managing symptoms.
How Does It Affect the Brain?
Understanding how this disorder impacts the brain helps in grasping its severity and the challenges faced by those affected.
-
White Matter Damage: The cysts in the white matter disrupt normal brain function, leading to various neurological issues.
-
Brain Swelling: The enlarged brain can cause increased pressure within the skull, leading to headaches and other complications.
-
Seizures: Many individuals experience frequent seizures due to abnormal brain activity.
-
Motor Skills: Damage to the white matter affects motor skills, making tasks like walking and coordination difficult.
-
Cognitive Impact: Cognitive development is often delayed, affecting learning and memory.
Genetic and Environmental Factors
Exploring the genetic and environmental aspects provides insight into the causes and potential risk factors.
-
MLC1 Gene: Mutations in the MLC1 gene are the primary cause. This gene plays a role in maintaining the brain's white matter.
-
Environmental Triggers: While the disorder is genetic, environmental factors can influence the severity of symptoms.
-
Family History: A family history of the disorder increases the risk of having a child with the condition.
-
Carrier Testing: Genetic testing can identify carriers of the mutated gene, helping in family planning.
Treatment and Management
Although there is no cure, various treatments can help manage the symptoms and improve quality of life.
-
Seizure Management: Anti-seizure medications are commonly prescribed to control seizures.
-
Physical Therapy: Helps improve motor skills and coordination.
-
Speech Therapy: Assists with communication difficulties.
-
Occupational Therapy: Aids in developing daily living skills.
-
Supportive Care: Includes regular monitoring and supportive treatments to manage symptoms and complications.
Research and Future Directions
Ongoing research aims to better understand the disorder and develop potential treatments.
-
Gene Therapy: Researchers are exploring gene therapy as a potential treatment to correct the genetic mutation.
-
Clinical Trials: Various clinical trials are underway to find effective treatments and improve patient outcomes.
Final Thoughts on Megalencephaly-Cystic Leukodystrophy
Megalencephaly-Cystic Leukodystrophy is a rare genetic disorder that affects brain development. It causes the brain to grow abnormally large and leads to cysts forming in the white matter. Symptoms can include developmental delays, seizures, and motor skill issues. Early diagnosis is crucial for managing the condition, though there's no cure yet. Treatments focus on alleviating symptoms and improving quality of life. Genetic counseling can help families understand the risks and implications. Research is ongoing, offering hope for better treatments in the future. Awareness and support are vital for those affected. By understanding the facts, we can better support individuals and families dealing with this challenging condition.
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
