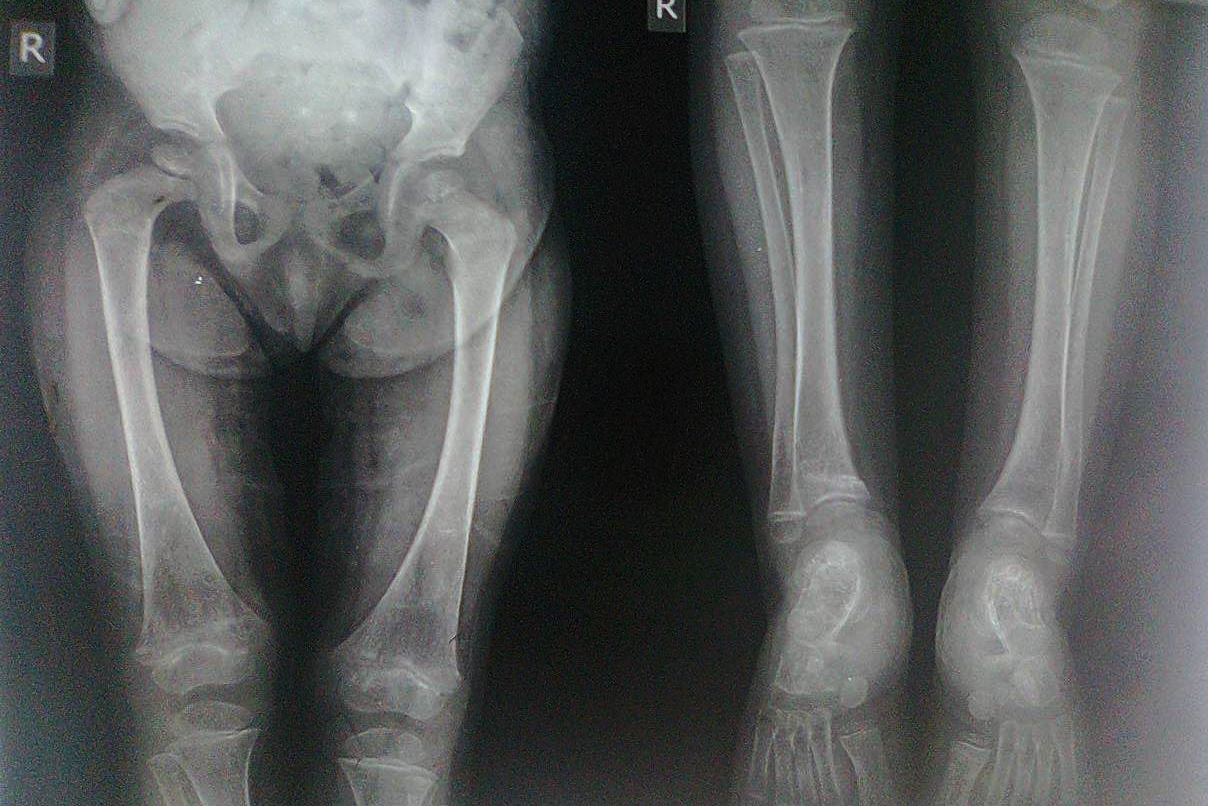
Lobstein Disease, also known as Osteogenesis Imperfecta, is a rare genetic disorder that affects the bones, making them fragile and prone to fractures. Imagine having bones as delicate as glass; that's what individuals with this condition experience. This disorder can vary in severity, from mild cases with few fractures to severe forms where bones break easily. Osteogenesis Imperfecta is caused by a defect in the gene responsible for producing collagen, a protein crucial for bone strength. Understanding this condition is essential for those affected and their families, as it impacts daily life and requires specialized care. Let's dive into 25 intriguing facts about Lobstein Disease to shed light on this challenging condition.
Key Takeaways:
- Lobstein Disease, also known as Osteogenesis Imperfecta, causes fragile bones that break easily. It has various types, from mild to severe, and affects more than just bones, including eyes, ears, and teeth.
- While there is no cure for Lobstein Disease, treatments like bisphosphonates, physical therapy, and surgical procedures can help manage symptoms and improve quality of life. Home modifications, education, and emotional support are also crucial for those living with the condition.
What is Lobstein Disease?
Lobstein Disease, also known as Osteogenesis Imperfecta (OI), is a genetic disorder affecting bones. People with this condition have fragile bones that break easily, often with little or no apparent cause. Let's dive into some fascinating facts about this rare condition.
Genetic Basis of Lobstein Disease
Understanding the genetic roots of Lobstein Disease helps in grasping its complexity.
-
Lobstein Disease is primarily caused by mutations in the COL1A1 or COL1A2 genes. These genes are responsible for producing type I collagen, a crucial protein for bone strength.
-
There are at least eight recognized types of Osteogenesis Imperfecta. Each type varies in severity, from mild forms with few fractures to severe forms that can be life-threatening.
-
Type I is the mildest and most common form of OI. Individuals with Type I OI typically have a normal lifespan and experience fewer fractures.
-
Type II is the most severe form of OI. Unfortunately, many infants with Type II do not survive past infancy due to the severity of bone fragility.
Symptoms and Physical Characteristics
Lobstein Disease manifests in various ways, affecting more than just bones.
-
Frequent bone fractures are a hallmark of OI. Even minor bumps or falls can result in broken bones.
-
People with OI often have blue sclerae. The whites of their eyes appear blue due to the thinness of the collagen in the eyes.
-
Hearing loss is common in OI patients. This typically occurs in adulthood and can result from abnormalities in the bones of the middle ear.
-
Individuals with OI may have dental issues. Brittle teeth, known as dentinogenesis imperfecta, are often seen in those with the condition.
Diagnosis and Detection
Early detection and accurate diagnosis are crucial for managing Lobstein Disease.
-
OI can be diagnosed through genetic testing. Identifying mutations in the COL1A1 or COL1A2 genes confirms the diagnosis.
-
Prenatal ultrasound can sometimes detect severe forms of OI. This is particularly true for Type II, where bone abnormalities are visible before birth.
-
Bone density scans help assess the severity of OI. These scans measure bone mineral density, which is typically lower in individuals with OI.
Treatment and Management
While there is no cure for Lobstein Disease, various treatments can help manage symptoms and improve quality of life.
-
Bisphosphonates are commonly used to treat OI. These drugs help increase bone density and reduce the risk of fractures.
-
Physical therapy is essential for OI patients. It helps maintain muscle strength and improve mobility, reducing the risk of fractures.
-
Surgical procedures can stabilize bones. Rodding surgery, where metal rods are inserted into long bones, helps prevent fractures and deformities.
-
Assistive devices like wheelchairs and braces are often necessary. These tools help individuals with OI maintain independence and mobility.
Living with Lobstein Disease
Daily life with OI involves various adaptations and considerations.
-
Home modifications can enhance safety. Installing grab bars, using non-slip mats, and ensuring good lighting can prevent falls and fractures.
-
Education and awareness are crucial. Schools and workplaces need to understand the condition to provide appropriate support and accommodations.
-
Emotional support is vital for OI patients. Counseling and support groups can help individuals and families cope with the challenges of the condition.
Research and Future Directions
Ongoing research aims to improve the lives of those with Lobstein Disease.
-
Gene therapy holds promise for OI treatment. Scientists are exploring ways to correct the genetic mutations causing the condition.
-
Stem cell therapy is another area of interest. Researchers hope that stem cells can be used to regenerate healthy bone tissue in OI patients.
-
New medications are being developed. These aim to strengthen bones and reduce fracture risk more effectively than current treatments.
Interesting Historical Facts
Lobstein Disease has a long history, with notable cases and discoveries.
-
The condition is named after Jean Lobstein. This French pathologist first described the disease in the 19th century.
-
OI has been documented in ancient history. Skeletal remains from ancient Egypt show signs of the condition.
-
Several famous individuals have had OI. For example, actor Atticus Shaffer, known for his role in "The Middle," lives with the condition.
-
Awareness of OI has increased over the years. Organizations like the Osteogenesis Imperfecta Foundation work tirelessly to support research and provide resources for those affected.
Final Thoughts on Lobstein Disease
Lobstein Disease, also known as Osteogenesis Imperfecta, affects bones, making them fragile and prone to fractures. This genetic disorder varies in severity, from mild cases with few fractures to severe forms causing numerous breaks. Understanding the symptoms and treatment options is crucial for managing the condition. Regular medical check-ups, physical therapy, and sometimes surgery can help improve the quality of life for those affected. Advances in genetic research offer hope for better treatments in the future. Awareness and education about Lobstein Disease can lead to early diagnosis and better support for patients and families. Remember, knowledge is power. By staying informed, we can make a difference in the lives of those living with this challenging condition.
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
