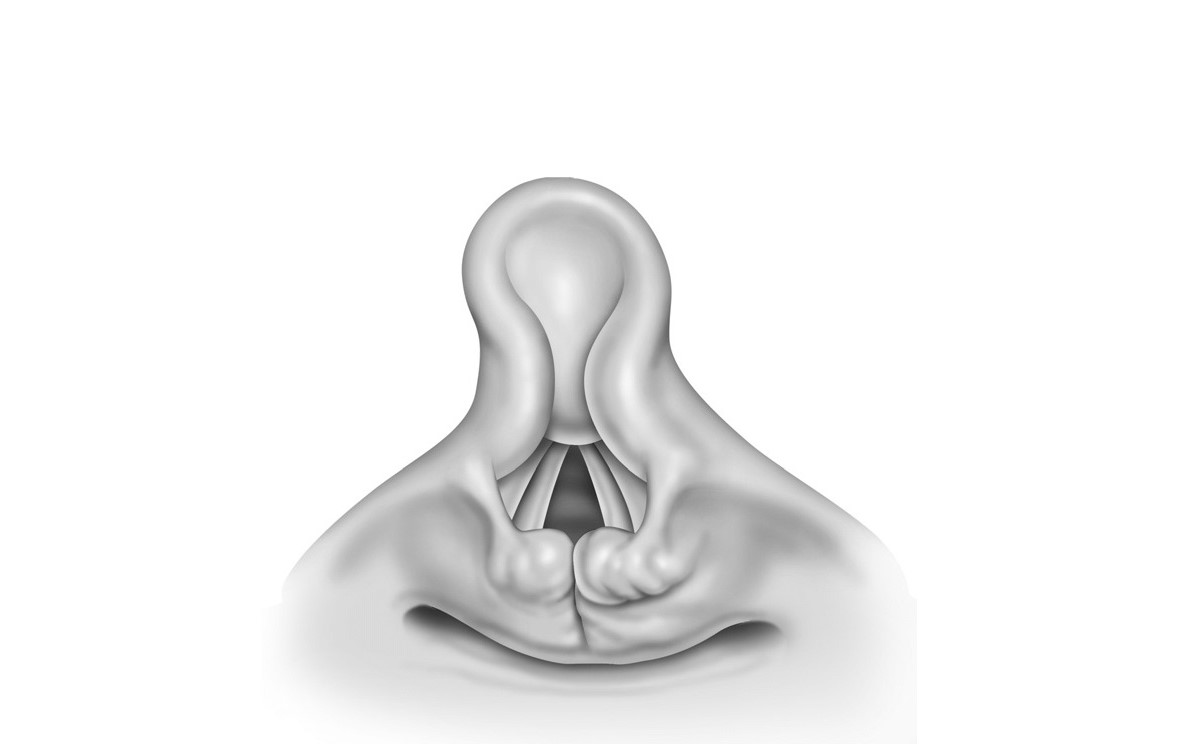
Laryngomalacia is a condition that might sound complicated, but it's actually quite common in newborns. This congenital issue involves the softening of the tissues of the larynx, or voice box, which can cause noisy breathing. Parents often notice a high-pitched sound when their baby breathes in, especially when lying on their back. While it can be alarming, most cases are mild and resolve on their own as the child grows. However, severe cases might need medical intervention. Understanding the symptoms, causes, and treatment options can help parents feel more at ease. Let's dive into 25 facts about laryngomalacia to shed light on this condition.
Key Takeaways:
- Laryngomalacia is a common condition in infants that causes noisy breathing. Most cases resolve on their own, but some may require medication or surgery for management.
- Understanding the symptoms, causes, and treatment options for laryngomalacia can help parents and caregivers effectively support infants with this condition. Regular monitoring and early intervention are crucial for a positive long-term outlook.
What is Laryngomalacia?
Laryngomalacia is a condition that affects the larynx, or voice box, in infants. It is the most common congenital laryngeal anomaly and often causes noisy breathing. Here are some intriguing facts about this condition:
- Laryngomalacia is derived from Greek words meaning "soft larynx."
- It is the most common cause of stridor, a high-pitched breathing sound, in infants.
- Approximately 60% of cases are diagnosed within the first two weeks of life.
- The condition is more prevalent in boys than girls.
- Most infants with laryngomalacia outgrow it by 18 to 24 months.
Symptoms and Diagnosis
Recognizing the symptoms and understanding how laryngomalacia is diagnosed can help parents and caregivers manage the condition effectively.
- Symptoms include noisy breathing, especially when the infant is feeding or lying on their back.
- Some infants may experience feeding difficulties and poor weight gain.
- Diagnosis is typically made through a physical examination and a procedure called laryngoscopy.
- In severe cases, infants may have difficulty breathing and require medical intervention.
- Stridor is usually louder when the infant is agitated or crying.
Causes and Risk Factors
Understanding the causes and risk factors associated with laryngomalacia can provide insight into why some infants develop this condition.
- The exact cause of laryngomalacia is unknown, but it is believed to be related to the immaturity of the laryngeal structures.
- Premature infants are at a higher risk of developing laryngomalacia.
- Some studies suggest a genetic component, as the condition can run in families.
- Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) is often associated with laryngomalacia.
- Infants with certain neurological conditions may be more prone to developing laryngomalacia.
Treatment and Management
While many cases of laryngomalacia resolve on their own, some infants may require treatment to manage symptoms and complications.
- Mild cases often do not require treatment and improve as the infant grows.
- For moderate to severe cases, treatment may include medications to manage GERD.
- In some instances, a surgical procedure called supraglottoplasty may be necessary to remove excess tissue from the larynx.
- Close monitoring by a pediatrician or an ENT specialist is essential for managing the condition.
- Parents can help by ensuring the infant is positioned correctly during feeding and sleeping.
Prognosis and Long-term Outlook
The long-term outlook for infants with laryngomalacia is generally positive, but understanding the potential challenges can help caregivers prepare.
- Most infants with laryngomalacia outgrow the condition without any long-term complications.
- In rare cases, severe laryngomalacia can lead to chronic respiratory issues.
- Regular follow-up appointments are crucial to monitor the infant's progress and address any concerns.
- Early intervention and appropriate management can significantly improve the quality of life for affected infants.
- Support groups and resources are available for parents and caregivers to share experiences and seek advice.
The Final Word on Laryngomalacia
Laryngomalacia, a dominant congenital condition, affects many newborns. Understanding its symptoms and treatment options can ease parents' worries. This condition often resolves on its own as the child grows. However, severe cases may need medical intervention. Recognizing stridor, feeding difficulties, and poor weight gain early can lead to timely treatment. Regular check-ups with a pediatrician ensure the child’s development stays on track. While it might seem daunting, most children with laryngomalacia lead healthy lives. Awareness and prompt action make a significant difference. Remember, you're not alone in this journey. Many resources and support groups are available to help. Stay informed, stay proactive, and trust in the medical community's expertise. Your child’s health and well-being are paramount.
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
