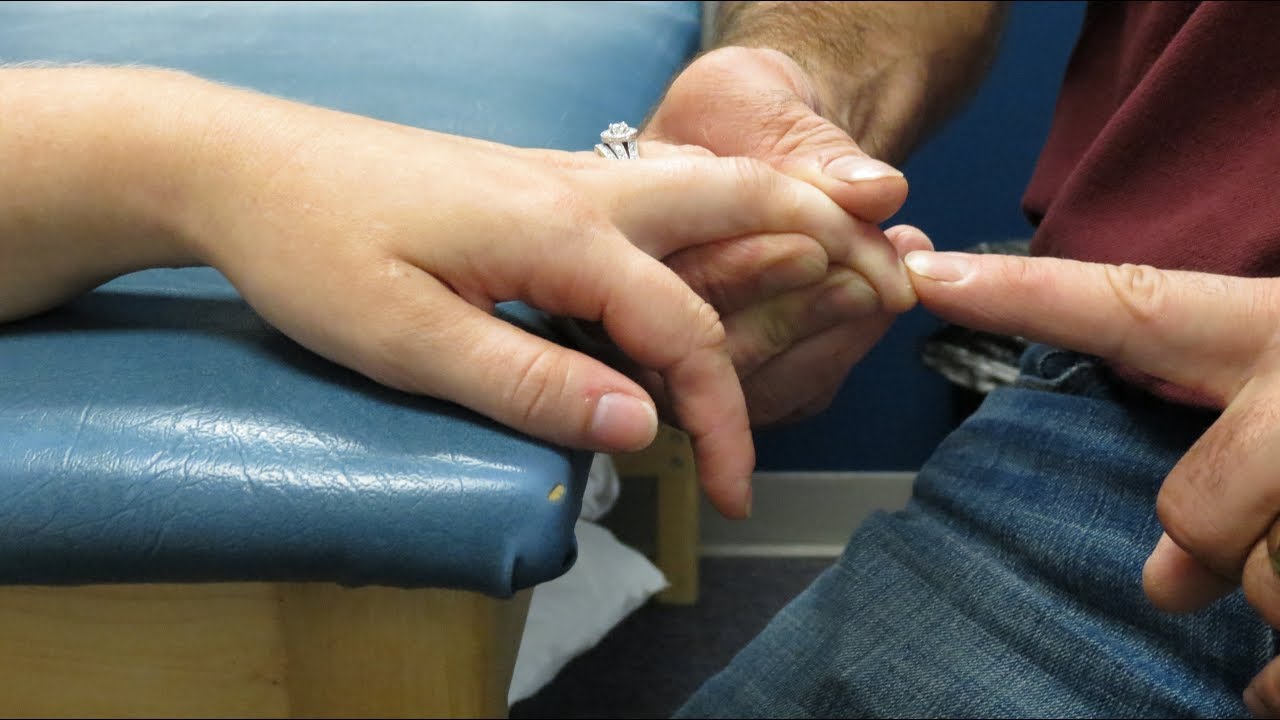
What is Hoffmann's Sign? Hoffmann's Sign is a neurological test used to check for issues in the spinal cord or brain. How is it performed? A doctor flicks the nail of the middle finger and watches for a reflex movement in the thumb or index finger. Why is it important? This test helps detect conditions like multiple sclerosis or cervical myelopathy. What does a positive result mean? A positive Hoffmann's Sign indicates potential nerve damage or disease. Is it always accurate? Not always. Other factors can influence the result, so doctors use it alongside other tests. Who should get tested? People with symptoms like muscle weakness, numbness, or coordination problems might need this test.
Key Takeaways:
- Hoffmann's Sign is a neurological test that involves flicking the middle finger to check for reflexive movement of the thumb and index finger. It helps diagnose spinal cord compression and other neurological disorders.
- A positive Hoffmann's Sign can indicate hyperreflexia and conditions like multiple sclerosis, spinal cord injury, and cervical spondylosis. However, it's not specific to any one condition and should be interpreted by a healthcare professional.
What is Hoffmann's Sign?
Hoffmann's sign is a neurological test used to assess the presence of spinal cord compression or other neurological disorders. It involves a simple flick of the middle finger to observe the reflexive movement of the thumb and index finger. This test can provide crucial insights into the health of the nervous system.
- Hoffmann's sign is named after Johann Hoffmann, a German neurologist who first described it in the early 20th century.
- The test is often used to detect cervical myelopathy, a condition where the spinal cord in the neck is compressed.
- A positive Hoffmann's sign indicates hyperreflexia, which means the reflexes are more active than normal.
- This test is similar to the Babinski sign, another neurological test used to assess the central nervous system.
- A positive result can suggest issues such as multiple sclerosis, spinal cord injury, or other neurological disorders.
How is Hoffmann's Sign Performed?
Performing Hoffmann's sign is straightforward but requires careful observation. Here's how it's done:
- The patient’s hand is held loosely by the examiner.
- The examiner flicks the nail of the middle finger.
- A positive sign is when the thumb and index finger flex involuntarily.
- This reflex action is due to the corticospinal tract, which is part of the central nervous system.
- The test is usually performed on both hands to compare results.
Clinical Significance of Hoffmann's Sign
Understanding the clinical significance of Hoffmann's sign helps in diagnosing various conditions. Here are some key points:
- A positive Hoffmann's sign can indicate upper motor neuron lesions.
- It is often used in conjunction with other tests to diagnose cervical spondylotic myelopathy.
- The presence of this sign can help differentiate between peripheral and central nervous system disorders.
- It is not a definitive test but rather a screening tool.
- A positive sign warrants further investigation through imaging studies like MRI or CT scans.
Conditions Associated with a Positive Hoffmann's Sign
Several medical conditions can be associated with a positive Hoffmann's sign. Here are some of them:
- Multiple sclerosis is a chronic disease that affects the central nervous system.
- Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), also known as Lou Gehrig's disease, can show a positive Hoffmann's sign.
- Cervical spondylosis, a degenerative condition of the cervical spine, often presents with this sign.
- Spinal cord tumors can also cause a positive Hoffmann's sign.
- Traumatic spinal cord injuries may result in a positive test.
Limitations and Considerations
While Hoffmann's sign is useful, it has its limitations. Here are some considerations:
- A positive Hoffmann's sign is not specific to any one condition.
- It can sometimes be present in healthy individuals without any neurological issues.
- The test should be part of a comprehensive neurological examination.
- False positives can occur due to anxiety or heightened reflexes.
- Interpretation of the test should always be done by a qualified healthcare professional.
The Final Word on Hoffmann's Sign
Hoffmann's sign, a simple yet powerful neurological test, can reveal a lot about the state of the nervous system. This test, involving a flick of the middle finger, helps doctors identify potential issues like spinal cord compression or multiple sclerosis. It's quick, non-invasive, and can be a crucial first step in diagnosing serious conditions.
Understanding Hoffmann's sign can empower patients to seek timely medical advice. If you or someone you know experiences symptoms like muscle weakness, numbness, or tingling, don't ignore them. Early detection can make a significant difference in treatment outcomes.
Knowledge is power. By learning about Hoffmann's sign, you're better equipped to advocate for your health. Always consult a healthcare professional for a thorough evaluation if you suspect any neurological issues. Stay informed, stay proactive, and take charge of your health.
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
