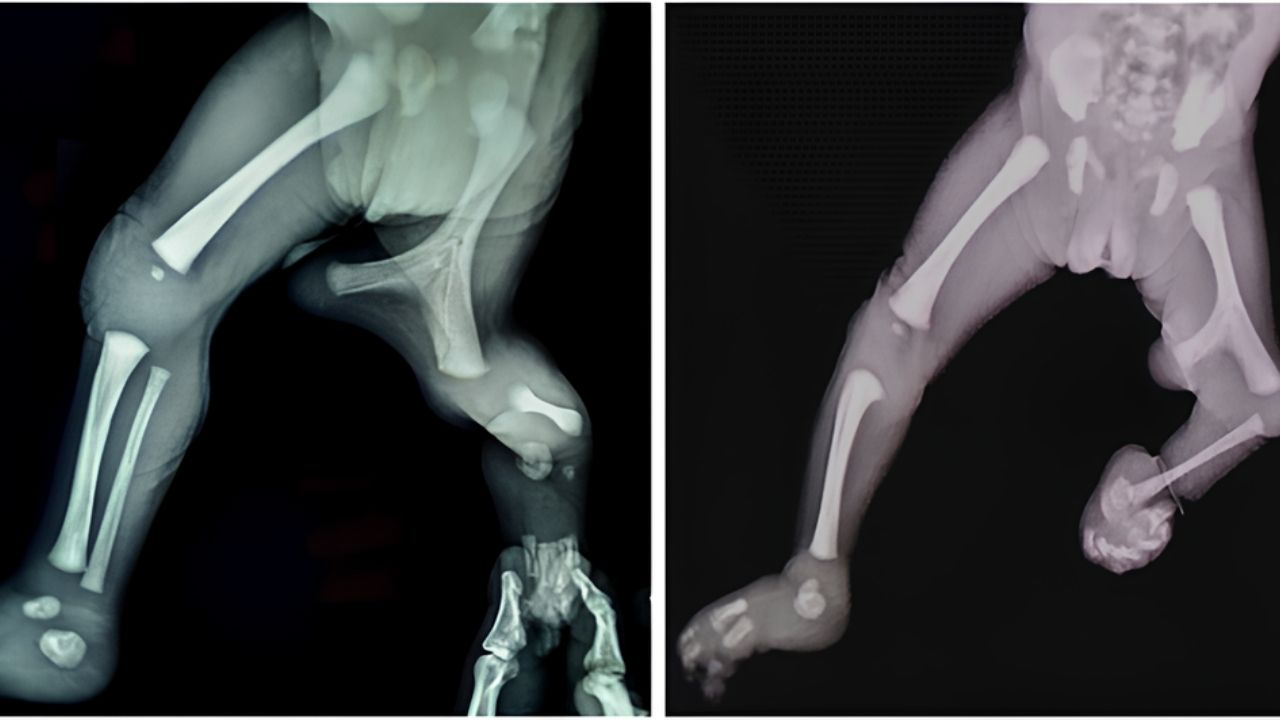
Femur bifid with monodactylous ectrodactyly sounds like a mouthful, right? This rare condition combines two unique skeletal anomalies. Femur bifid means the thigh bone splits into two parts. Monodactylous ectrodactyly refers to having only one finger or toe on a hand or foot. Imagine the challenges and adaptations someone with this condition might face. Understanding these terms helps us appreciate the complexity of human anatomy. This post will share 25 intriguing facts about this condition, shedding light on its causes, symptoms, and impact on daily life. Ready to learn something new? Let's dive in!
Key Takeaways:
- Femur bifid with monodactylous ectrodactyly is a rare condition affecting the thigh bone and digits. It can impact mobility and hand function, but with the right support, individuals can lead fulfilling lives.
- Genetic mutations and inherited patterns are the primary causes of this condition. Early diagnosis and a combination of medical and surgical approaches can help improve treatment outcomes.
What is Femur Bifid With Monodactylous Ectrodactyly?
Femur bifid with monodactylous ectrodactyly is a rare congenital condition affecting the skeletal system. It involves abnormalities in the femur (thigh bone) and the digits (fingers or toes). This condition can significantly impact mobility and hand function.
- Femur bifid refers to a split or cleft in the femur bone.
- Monodactylous ectrodactyly means having only one digit on a hand or foot.
Causes of Femur Bifid With Monodactylous Ectrodactyly
Understanding the causes can help in early diagnosis and management. This condition is often linked to genetic factors.
- Genetic mutations are the primary cause of this condition.
- Inherited patterns suggest it can run in families.
- Environmental factors during pregnancy might contribute, though less common.
Symptoms and Diagnosis
Recognizing the symptoms early can lead to better treatment outcomes. Diagnosis usually involves physical examinations and imaging tests.
- Visible deformities in the thigh and digits are common.
- Limited mobility in the affected limb.
- X-rays and MRIs are used for detailed imaging.
- Genetic testing can confirm the diagnosis.
Treatment Options
Treatment varies based on the severity of the condition. It often involves a combination of medical and surgical approaches.
- Physical therapy helps improve mobility and strength.
- Surgical intervention may be necessary to correct bone deformities.
- Prosthetics can aid in function and mobility.
- Pain management is crucial for improving quality of life.
Impact on Daily Life
Living with femur bifid with monodactylous ectrodactyly can be challenging. However, with the right support, individuals can lead fulfilling lives.
- Adaptive devices can assist with daily activities.
- Support groups provide emotional and social support.
- Educational accommodations may be needed for children.
- Workplace modifications can help adults maintain employment.
Research and Future Directions
Ongoing research aims to improve understanding and treatment of this condition. Advances in genetics and medical technology hold promise.
- Gene therapy is being explored as a potential treatment.
- Stem cell research offers hope for regenerating damaged tissues.
- 3D printing is being used to create custom prosthetics.
- Clinical trials are testing new medications and therapies.
Real-Life Stories
Hearing from those who live with femur bifid with monodactylous ectrodactyly can be inspiring and informative.
- Personal stories highlight the resilience and adaptability of individuals.
- Community support plays a significant role in coping with the condition.
- Awareness campaigns help educate the public and reduce stigma.
- Advocacy efforts aim to improve healthcare access and funding for research.
Final Thoughts on Femur Bifid With Monodactylous Ectrodactyly
Femur bifid with monodactylous ectrodactyly is a rare and fascinating condition. Understanding its complexities helps shed light on the diversity of human anatomy. This condition involves a split femur and a single finger or toe, often leading to unique challenges and adaptations for those affected. Medical professionals continue to study it to improve diagnosis and treatment options. Awareness and education about such rare conditions can foster empathy and support for individuals living with them. By learning more about femur bifid with monodactylous ectrodactyly, we can appreciate the incredible variations in human development and the resilience of those who navigate life with these differences.
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
