Langer-Giedion Syndrome is a rare genetic disorder that affects multiple parts of the body. Ever wondered what makes this condition so unique? Langer-Giedion Syndrome is caused by a deletion of genetic material on chromosome 8, leading to distinctive facial features, bone abnormalities, and intellectual disabilities. This syndrome, also known as trichorhinophalangeal syndrome type II, impacts fewer than 1 in 1,000,000 people. Individuals with this condition often have sparse hair, a bulbous nose, and short stature. Understanding the complexities of Langer-Giedion Syndrome can help in recognizing its symptoms and providing better care for those affected. Let's dive into 22 intriguing facts about this rare condition to shed light on its characteristics and challenges.
Key Takeaways:
- Langer-Giedion Syndrome is a rare genetic disorder caused by a deletion on chromosome 8, impacting physical features, growth, and development. Early diagnosis and multidisciplinary care are crucial for management.
- Individuals with Langer-Giedion Syndrome may experience bone abnormalities, joint problems, dental issues, intellectual disability, and hearing loss. Treatment and support, including physical therapy, speech therapy, and hearing aids, can improve quality of life.
What is Langer-Giedion Syndrome?
Langer-Giedion Syndrome (LGS) is a rare genetic disorder. It affects multiple parts of the body. Understanding this condition can help those affected and their families.
-
LGS is caused by a deletion of genetic material on chromosome 8. This deletion impacts two genes, TRPS1 and EXT1, which are crucial for normal development.
-
The syndrome is also known as Trichorhinophalangeal Syndrome Type II. This name reflects the specific physical features and genetic causes of the disorder.
-
LGS affects approximately 1 in 1,000,000 people. Its rarity makes it a challenge to diagnose and study.
-
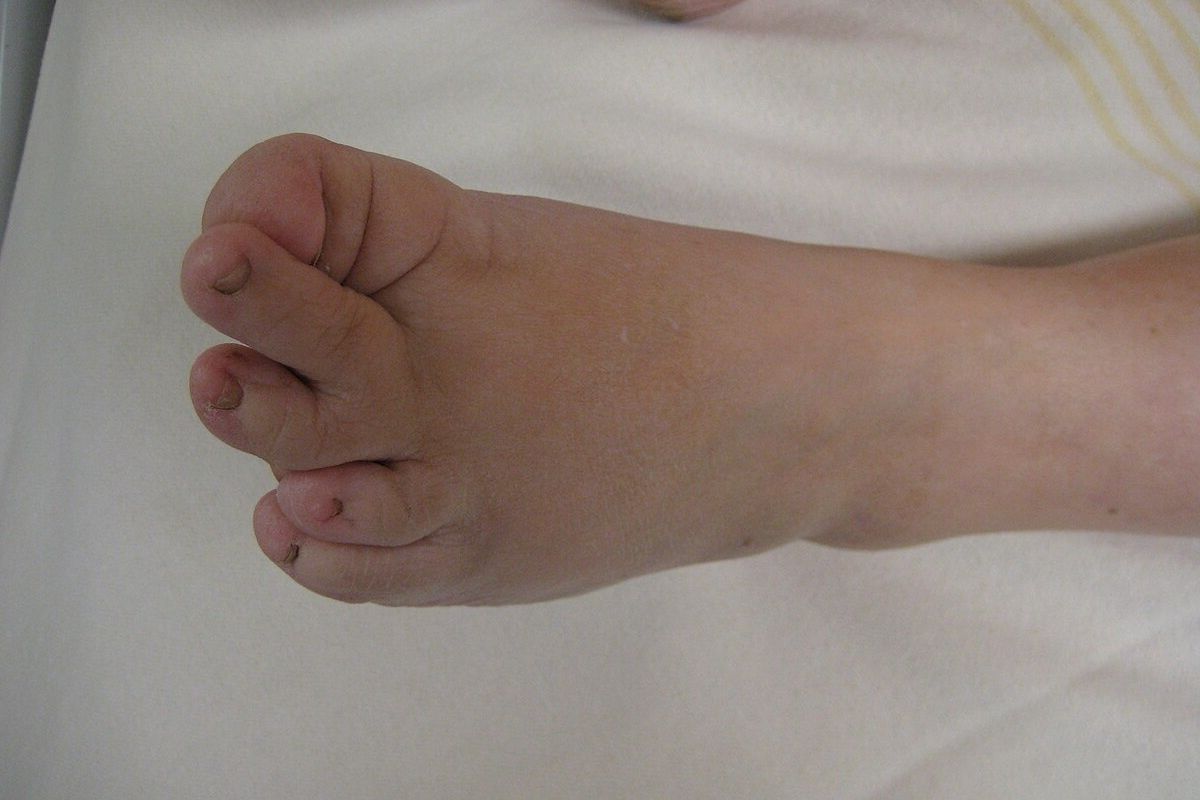
Characteristic facial features include a bulbous nose, sparse scalp hair, and prominent ears. These features become more pronounced with age.
-
Individuals with LGS often have short stature. Growth delays are common, and adult height is typically below average.
Physical and Developmental Characteristics
LGS impacts physical growth and development in various ways. Here are some key characteristics.
-
Bone abnormalities are a hallmark of LGS. These can include cone-shaped epiphyses and short, stubby fingers.
-
Joint problems are common. Many individuals experience joint pain and stiffness, particularly in the hips and knees.
-
Dental issues frequently occur. These can include delayed tooth eruption, missing teeth, and misalignment.
-
Intellectual disability is present in some cases. The severity can vary widely among individuals.
-
Hearing loss is another potential symptom. This can range from mild to severe and may require hearing aids.
Diagnosis and Genetic Testing
Diagnosing LGS involves a combination of physical examinations and genetic tests. Here’s what you need to know.
-
Genetic testing is crucial for a definitive diagnosis. This typically involves a chromosomal microarray analysis to detect deletions on chromosome 8.
-
Prenatal testing is possible. If there is a known risk, expectant parents can opt for tests like amniocentesis or chorionic villus sampling.
-
Early diagnosis can improve management. Identifying LGS early allows for timely interventions and support.
-
Family history plays a role. If a parent carries the genetic deletion, there is a 50% chance of passing it to their child.
-
Multidisciplinary care is often required. This includes specialists in genetics, orthopedics, audiology, and dentistry.
Treatment and Management
While there is no cure for LGS, various treatments can help manage symptoms and improve quality of life.
-
Physical therapy can aid mobility. Regular sessions help maintain joint function and reduce pain.
-
Speech therapy may be beneficial. This can address any speech delays or difficulties.
-
Hearing aids or cochlear implants can improve hearing. These devices are tailored to the individual's level of hearing loss.
-
Orthopedic surgery might be necessary. Procedures can correct bone deformities and improve function.
-
Regular dental care is essential. Specialized dental treatments can address the unique challenges faced by individuals with LGS.
Living with Langer-Giedion Syndrome
Living with LGS involves adapting to various challenges. Support from healthcare providers, family, and community is vital.
-
Support groups can provide emotional and practical help. Connecting with others who have LGS can be incredibly beneficial.
-
Educational support is often needed. Tailored educational plans can help children with LGS succeed in school.
Understanding Langer-Giedion Syndrome
Langer-Giedion Syndrome, also known as trichorhinophalangeal syndrome type II, is a rare genetic disorder. It affects bone growth, facial features, and hair. This condition results from deletions on chromosome 8. Symptoms include distinctive facial traits, sparse hair, and bone abnormalities. Early diagnosis and intervention can help manage symptoms and improve quality of life.
Genetic counseling is crucial for families affected by this syndrome. It provides information on inheritance patterns and risks for future pregnancies. Support groups and resources are available to help families navigate the challenges associated with Langer-Giedion Syndrome.
Raising awareness about this rare condition can lead to better understanding and support for those affected. By sharing knowledge and resources, we can improve the lives of individuals with Langer-Giedion Syndrome and their families. Stay informed, seek support, and advocate for continued research and awareness.
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
