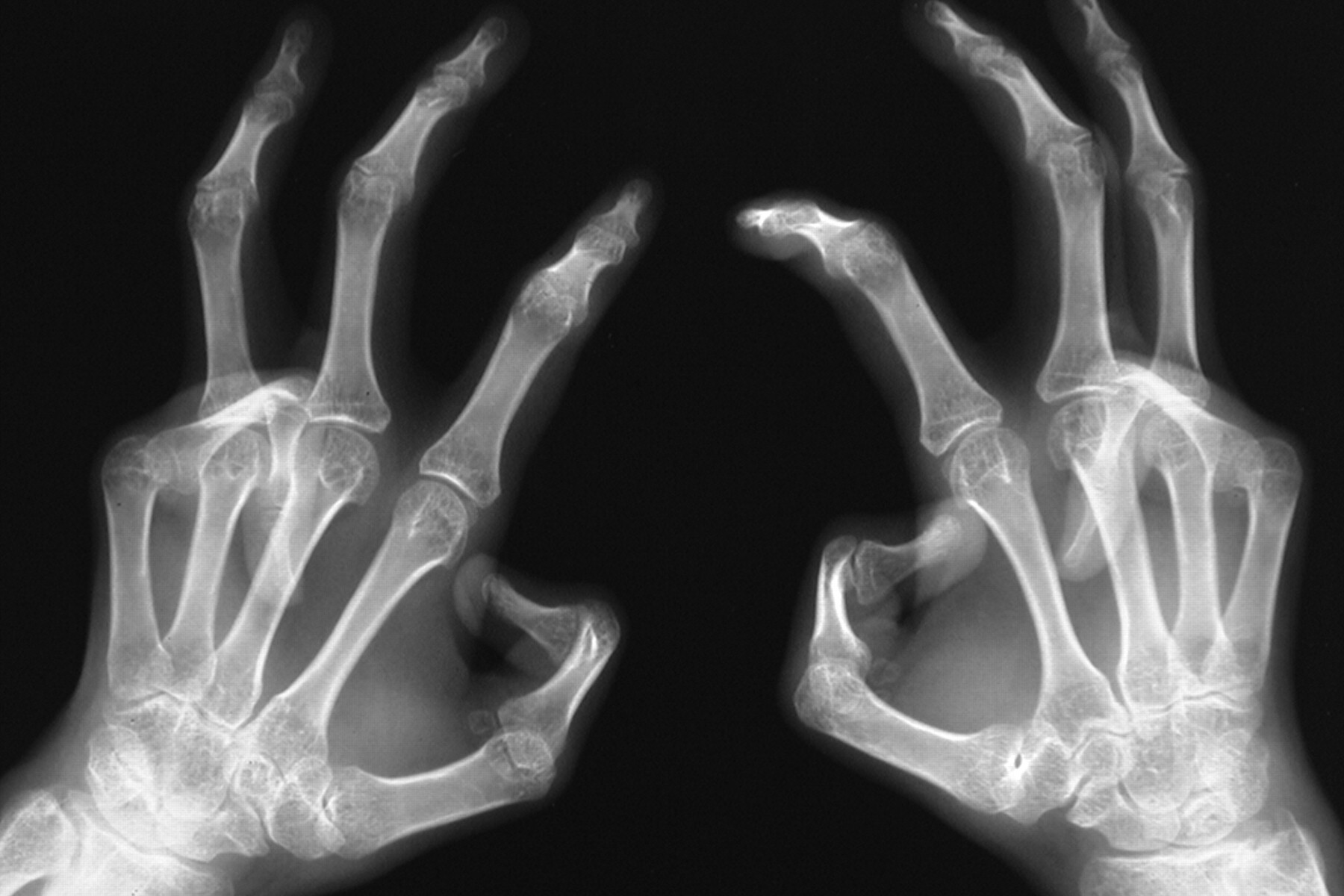
Camptodactyly-Arthropathy-Coxa Vara-Pericarditis Syndrome (CACP) might sound like a mouthful, but understanding it can be straightforward. This rare genetic disorder affects joints, bones, and the heart. Camptodactyly means bent fingers, arthropathy refers to joint disease, coxa vara indicates hip deformity, and pericarditis involves inflammation around the heart. Symptoms often appear in childhood, making early diagnosis crucial. Imagine having stiff fingers, painful joints, and hip problems all at once. That's what people with CACP face daily. This syndrome is inherited in an autosomal recessive manner, meaning both parents must carry the gene. Treatment focuses on managing symptoms, as there's no cure yet. Understanding CACP helps in supporting those affected and raising awareness for better research and care.
Key Takeaways:
- Camptodactyly-Arthropathy-Coxa Vara-Pericarditis (CACP) syndrome is a rare genetic disorder affecting joints, bones, and the heart. Early recognition and genetic testing are crucial for diagnosis and management.
- While there is no cure for CACP syndrome, treatments like physical therapy, surgery, and pain management can improve quality of life. Support groups and ongoing research offer hope for the future.
What is Camptodactyly-Arthropathy-Coxa Vara-Pericarditis Syndrome?
Camptodactyly-Arthropathy-Coxa Vara-Pericarditis (CACP) syndrome is a rare genetic disorder. It affects multiple parts of the body, including joints, bones, and the heart. Understanding this condition can help those affected and their families manage it better.
-
CACP syndrome is inherited in an autosomal recessive manner. This means both parents must carry the gene mutation for a child to be affected.
-
The syndrome is caused by mutations in the PRG4 gene. This gene provides instructions for making a protein called lubricin, which is crucial for joint function.
Symptoms and Diagnosis
Recognizing the symptoms early can lead to better management. Here are some key facts about the symptoms and diagnosis of CACP syndrome.
-
Camptodactyly refers to permanently bent fingers. This is often one of the first signs of the syndrome and can be noticed in infancy or early childhood.
-
Arthropathy involves joint swelling and pain. Unlike typical arthritis, this swelling is not due to inflammation but rather an accumulation of fluid in the joints.
-
Coxa vara is a deformity of the hip. It results in a reduced angle between the head and shaft of the femur, leading to hip pain and difficulty walking.
-
Pericarditis is inflammation of the pericardium. This is the sac surrounding the heart, and its inflammation can cause chest pain and other heart-related symptoms.
-
Diagnosis often involves genetic testing. Identifying mutations in the PRG4 gene confirms the diagnosis of CACP syndrome.
Treatment and Management
While there is no cure for CACP syndrome, various treatments can help manage the symptoms and improve quality of life.
-
Physical therapy can help improve joint function. Regular exercises can maintain mobility and reduce stiffness in affected joints.
-
Surgical interventions may be necessary. In severe cases, surgery can correct joint deformities or relieve pain.
-
Pain management is crucial. Medications and other therapies can help manage chronic pain associated with the syndrome.
Impact on Daily Life
Living with CACP syndrome presents unique challenges. Understanding these can help those affected navigate their daily lives more effectively.
-
Mobility aids may be required. Devices like braces, crutches, or wheelchairs can assist with movement and reduce strain on affected joints.
-
Regular medical check-ups are essential. Ongoing monitoring by healthcare professionals helps manage symptoms and prevent complications.
-
Support groups can provide emotional and practical support. Connecting with others who have the syndrome can offer valuable insights and encouragement.
Research and Future Directions
Ongoing research aims to better understand CACP syndrome and develop new treatments. Here are some promising areas of study.
-
Gene therapy is being explored. Scientists are investigating ways to correct the PRG4 gene mutation, potentially offering a long-term solution.
-
New medications are under development. Researchers are working on drugs that can better manage symptoms or slow the progression of the syndrome.
-
Stem cell research holds potential. Using stem cells to regenerate damaged tissues could offer new treatment options in the future.
-
Patient registries are helping advance research. Collecting data from individuals with CACP syndrome aids in understanding the condition and developing new therapies.
Final Thoughts on Camptodactyly-Arthropathy-Coxa Vara-Pericarditis Syndrome
Camptodactyly-Arthropathy-Coxa Vara-Pericarditis Syndrome (CACP) is a rare genetic disorder that affects joints, bones, and the heart. Understanding its symptoms, causes, and treatments can help those affected manage their condition better. Early diagnosis is crucial for effective treatment and improving quality of life. Genetic counseling can provide valuable insights for families dealing with CACP.
Staying informed and connected with medical professionals and support groups can make a significant difference. While there’s no cure yet, ongoing research offers hope for better treatments in the future. Awareness and education about CACP can lead to earlier detection and improved care for those affected.
By sharing knowledge and supporting research, we can contribute to a brighter future for individuals with CACP. Remember, every bit of information helps in the fight against rare diseases.
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
