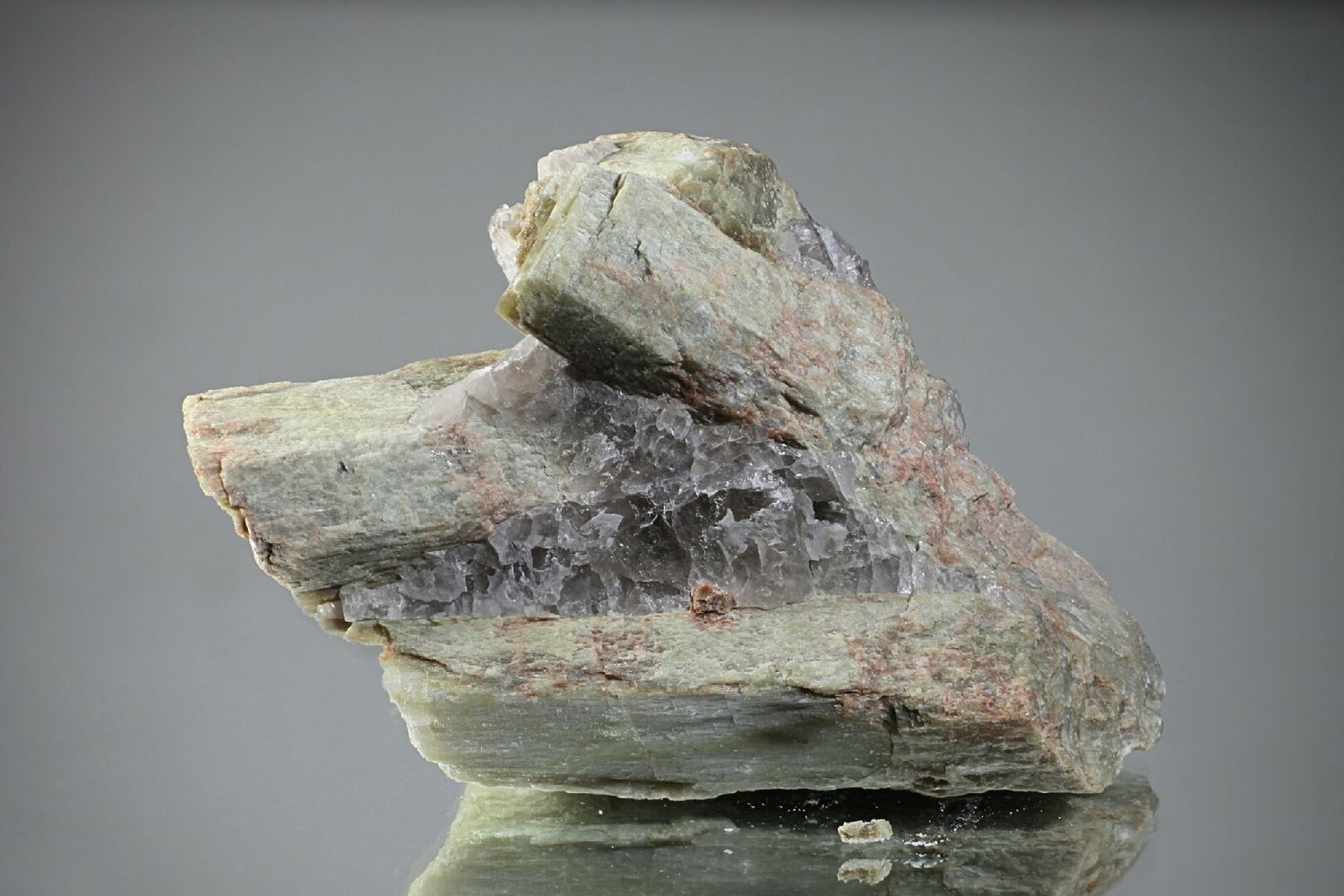
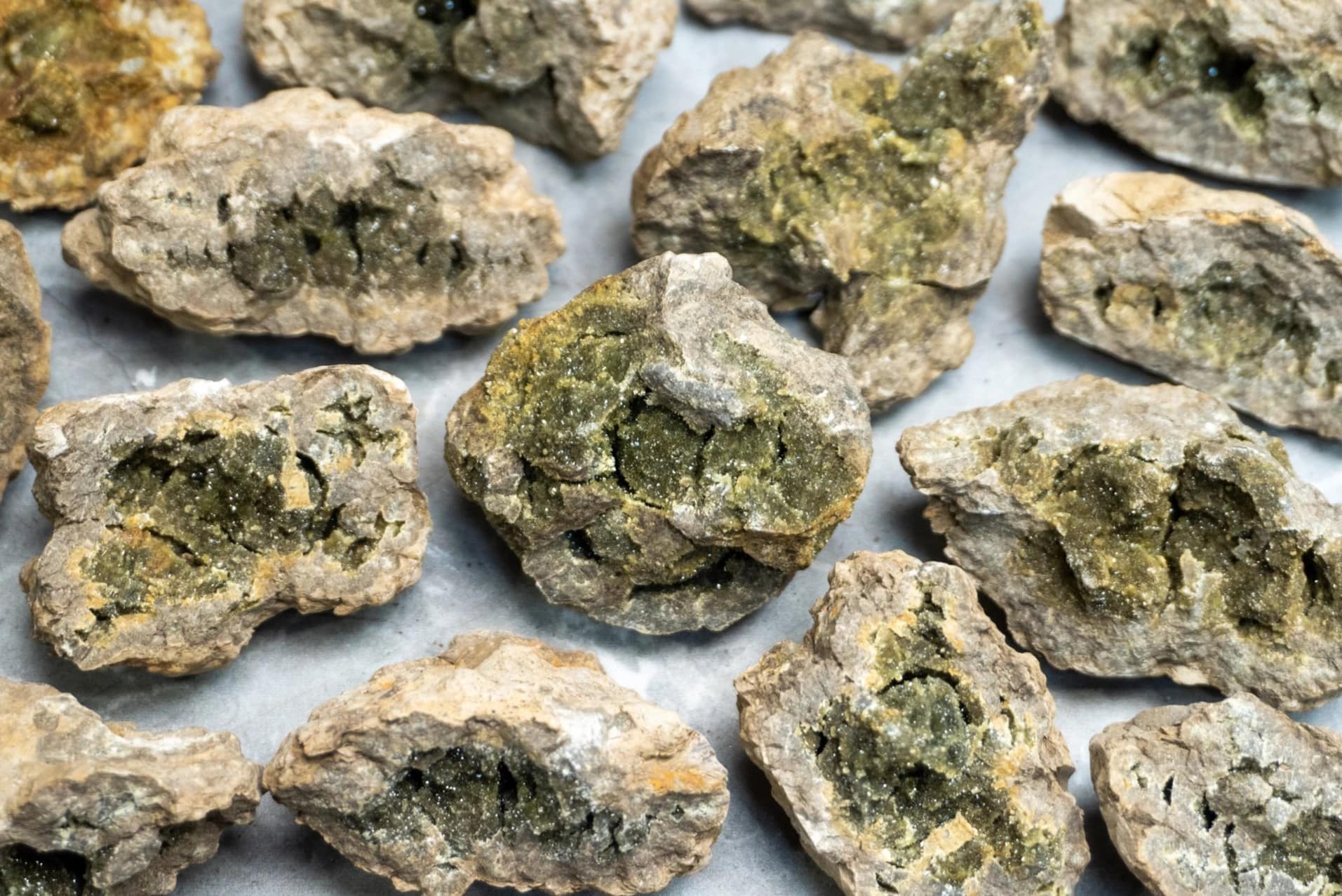
What makes anorthite so special? This rare mineral, part of the plagioclase feldspar group, boasts unique chemical and physical properties that captivate geologists and collectors alike. With a chemical formula of CaAl₂Si₂O₈, anorthite crystallizes in the triclinic system, displaying a vitreous luster and a Mohs hardness of 6. Found in mafic igneous rocks, metamorphic rocks, and even on the Moon, its presence tells stories of high-pressure and high-temperature conditions. Anorthite's significance extends beyond Earth, appearing in lunar highlands and comet samples. Its rarity and scientific importance make it a gem in the world of minerals.
Key Takeaways:
- Anorthite is a rare mineral with unique properties, found in various colors and geological environments. Its significance extends to the Moon and even comet samples, making it a prized addition for collectors and a subject of extensive scientific research.
- Anorthite's high-pressure behavior, breakdown reactions, and association with other minerals provide valuable insights into Earth's geological processes. Its historical significance in lunar samples and terrestrial rocks adds to its importance in the study of minerals.
What is Anorthite?
Anorthite is a rare mineral that belongs to the plagioclase group of feldspars. Its unique properties and occurrences make it a subject of interest in geology and mineralogy. Let's dive into some fascinating facts about this mineral.
-
Chemical Formula: The chemical formula of pure anorthite is CaAl₂Si₂O₈. This composition makes it distinct from other feldspars.
-
IMA Symbol: Anorthite is represented by the IMA symbol "An". This symbol is used in scientific literature to denote the mineral.
-
Strunz Classification: Anorthite falls under the Strunz classification 9.FA.35. This classification helps in identifying and categorizing minerals based on their chemical composition and crystal structure.
Crystal Structure and Physical Properties
Anorthite's crystal structure and physical properties are key to understanding its behavior and appearance.
-
Crystal System: Anorthite crystallizes in the triclinic crystal system. This means its crystals have three unequal axes that are not at right angles to each other.
-
Crystal Class: It belongs to the pinacoidal crystal class (1). This class is characterized by its simple crystal forms.
-
Space Group: The space group of anorthite is P1. This denotes the symmetry and arrangement of atoms in the crystal.
-
Unit Cell: The unit cell dimensions of anorthite are a = 8.1768 Å, b = 12.8768 Å, c = 14.169 Å, α = 93.17°, β = 115.85°, γ = 92.22°, and Z = 8. These measurements describe the smallest repeating unit in the crystal lattice.
-
Formula Mass: The formula mass of anorthite is 278.203 g·mol⁻¹. This is the mass of one mole of anorthite molecules.
Appearance and Physical Characteristics
Anorthite's appearance and physical characteristics can vary, making it a visually interesting mineral.
-
Color: Anorthite can occur in various colors including white, grayish, and reddish. These colors are due to impurities and the conditions under which the mineral formed.
-
Crystal Habit: It typically exhibits an anhedral to subhedral granular crystal habit. This means the crystals are often irregularly shaped.
-
Twinning: Common twinning is observed in anorthite. Twinning occurs when two or more crystals grow together in a symmetrical manner.
-
Cleavage: Anorthite has perfect cleavage along the [001] plane and good cleavage along the [010] plane, with poor cleavage along the [110] plane. Cleavage refers to the way a mineral breaks along specific planes.
-
Fracture: The fracture of anorthite is uneven to conchoidal. This describes how the mineral breaks when it does not follow cleavage planes.
-
Tenacity: It is brittle in nature. Brittle minerals break or powder easily.
-
Mohs Scale Hardness: Anorthite has a Mohs scale hardness of 6. This means it is relatively hard and can scratch glass.
-
Luster: The luster of anorthite is vitreous. This gives it a glassy appearance.
-
Streak: The streak of anorthite is white. Streak is the color of the mineral in powdered form.
-
Diaphaneity: It is transparent to translucent. This describes how much light can pass through the mineral.
-
Specific Gravity: The specific gravity of anorthite ranges from 2.72 to 2.75. This is a measure of its density compared to water.
Optical Properties
Anorthite's optical properties are important for identifying the mineral under a microscope.
-
Optical Properties: Anorthite is biaxial with a negative optical sign. This means it has two different refractive indices and bends light in a specific way.
-
Refractive Index: The refractive indices of anorthite are nα = 1.573–1.577, nβ = 1.580–1.585, and nγ = 1.585–1.590. These values describe how light bends as it passes through the mineral.
-
Birefringence: The birefringence of anorthite is δ = 0.012–0.013. This measures the difference in refractive indices within the mineral.
-
2V Angle: The 2V angle of anorthite ranges from 78° to 83°. This angle is important for identifying the mineral's optical properties.
Occurrence and Significance
Anorthite is found in various geological environments and has significant scientific importance.
-
Melting Point: Pure anorthite melts at 1,553 °C (2,827 °F) at standard pressure. This high melting point is characteristic of many feldspars.
-
Occurrence: Anorthite is found in mafic igneous rocks, metamorphic rocks of granulite facies, and metamorphosed carbonate rocks. These environments provide the conditions necessary for anorthite to form.
-
Type Localities: The type localities of anorthite are Monte Somma and Valle di Fassa, Italy. These locations are where the mineral was first described.
-
Discovery: Anorthite was first described in 1823. This historical context adds to its significance in mineralogy.
-
Weathering Potential: Due to its high weathering potential, anorthite is more rare in surficial rocks than it normally would be. Weathering breaks down the mineral over time.
-
Lunar Highlands: Anorthite makes up much of the lunar highlands, with the Genesis Rock collected during the 1971 Apollo 15 mission being composed largely of anorthosite, a rock composed largely of anorthite. This highlights its extraterrestrial significance.
-
Comet Wild 2: Anorthite was discovered in samples from comet Wild 2. This finding expands our understanding of the mineral's distribution in the solar system.
-
Ca-Al-Rich Inclusions: The mineral is an important constituent of Ca-Al-rich inclusions in rare varieties of chondritic meteorites. These inclusions provide clues about the early solar system.
Plagioclase Series and Composition
Anorthite is part of the plagioclase series, which includes a range of feldspar minerals.
-
Plagioclase Series: Anorthite is the calcium-rich endmember of the plagioclase solid solution series, with albite (NaAlSi₃O₈) being the sodium-rich endmember. This series shows the range of compositions between these two minerals.
-
Composition: The composition of plagioclases is often expressed as a molar percentage of An%, or (for a specific quantity) An n, where n = Ca/(Ca + Na) × 100. This formula helps in determining the exact composition of the mineral.
-
Terrestrial Context: This equation predominantly works in a terrestrial context; exotic locales and in particular Lunar rocks may need to account for other cations, such as Fe²⁺, to explain differences between optically and structurally derived An% data observed in Lunar anorthites. This highlights the complexity of mineral compositions in different environments.
High-Pressure Behavior and Breakdown
Anorthite exhibits interesting behavior under high-pressure conditions.
-
High-Pressure Structure: At high pressures, anorthite exhibits structural variations associated with compositional changes and order-disorder behavior. These changes can affect its physical properties.
-
Breakdown Reactions: Anorthite undergoes breakdown reactions at high pressures, forming minerals like grossular and sillimanite. These reactions provide insights into the conditions deep within the Earth.
-
Breakdown Pressure: The breakdown pressure of anorthite at 650 °C is approximately 13.8 kbar, neglecting the effect of compressibilities on AZ and entropy. This pressure is significant for understanding geological processes.
Associated Minerals and Geological Importance
Anorthite is often found with other minerals and has important geological implications.
-
Associated Minerals: Anorthite is commonly associated with minerals such as hessonite, clinozoisite, albite, vesuvianite, pyrrhotite, quartz, epidote, hedenbergite, titanite, and ruby. These associations help in identifying the mineral in the field.
-
Mineralogical Importance: Anorthite is an important mineral in petrology, providing insights into the high-pressure and high-temperature conditions of the Earth's crust and mantle. Its presence can indicate specific geological environments.
-
Geological Environment: Anorthite is found in various geological environments, including mafic igneous rocks, metamorphic rocks, and corundum deposits. These environments provide the conditions necessary for its formation.
-
Distribution: While anorthite is rare on Earth, it is abundant on the Moon, particularly in the lunar highlands. This distribution highlights its significance in planetary geology.
-
Notable Occurrences: Notable occurrences of anorthite include Lake County, California; Franklin, New Jersey; Italy; and the Moon. These locations are known for their high-quality anorthite specimens.
Collectibility and Research
Due to its rarity and unique properties, anorthite is highly valued by collectors and researchers.
-
Collectibility: Due to its rarity and unique properties, anorthite is highly sought after by mineral collectors. Its distinct appearance and characteristics make it a prized addition to any collection.
-
Scientific Research: Anorthite has been the subject of extensive scientific research, particularly in the fields of mineralogy and petrology, to understand its high-pressure structure and breakdown reactions. This research contributes to our knowledge of geological processes.
-
Historical Significance: Anorthite has historical significance in the field of geology, providing valuable information about the Earth's and Moon's geological history through its occurrence in lunar samples and terrestrial rocks. This historical context adds to its importance in the study of minerals.
Anorthite's Unique Role in Geology
Anorthite, a rare mineral in the plagioclase group, stands out due to its unique chemical composition and physical properties. With a chemical formula of CaAl₂Si₂O₈, it crystallizes in the triclinic system and exhibits perfect cleavage and a vitreous luster. Found in mafic igneous rocks, metamorphic rocks, and even the lunar highlands, anorthite plays a crucial role in understanding geological processes. Its presence in Ca-Al-rich inclusions in meteorites and samples from comet Wild 2 highlights its significance beyond Earth. Anorthite's high-pressure structure and breakdown reactions offer insights into the Earth's crust and mantle conditions. Collectors and scientists alike value this mineral for its rarity and the wealth of information it provides. From its discovery in 1823 to its role in lunar geology, anorthite remains a fascinating subject in the field of mineralogy.
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.