What is transmissivity? Simply put, transmissivity measures how easily water can flow through a material, like soil or rock. Imagine trying to pour water through a sponge versus a brick. The sponge lets water pass quickly, showing high transmissivity, while the brick barely lets any water through, indicating low transmissivity. This concept is crucial in fields like hydrology, environmental science, and engineering. It helps experts understand groundwater movement, design efficient irrigation systems, and even predict flood risks. Knowing about transmissivity can make a big difference in managing water resources effectively. Ready to dive into some intriguing facts about transmissivity? Let's get started!
What is Transmissivity?
Transmissivity is a term used in various fields like physics, hydrology, and engineering. It measures how easily a substance allows energy or fluid to pass through it. Understanding transmissivity helps in designing better systems and solving real-world problems.
-
Transmissivity is often used in groundwater studies to measure how easily water can move through an aquifer.
-
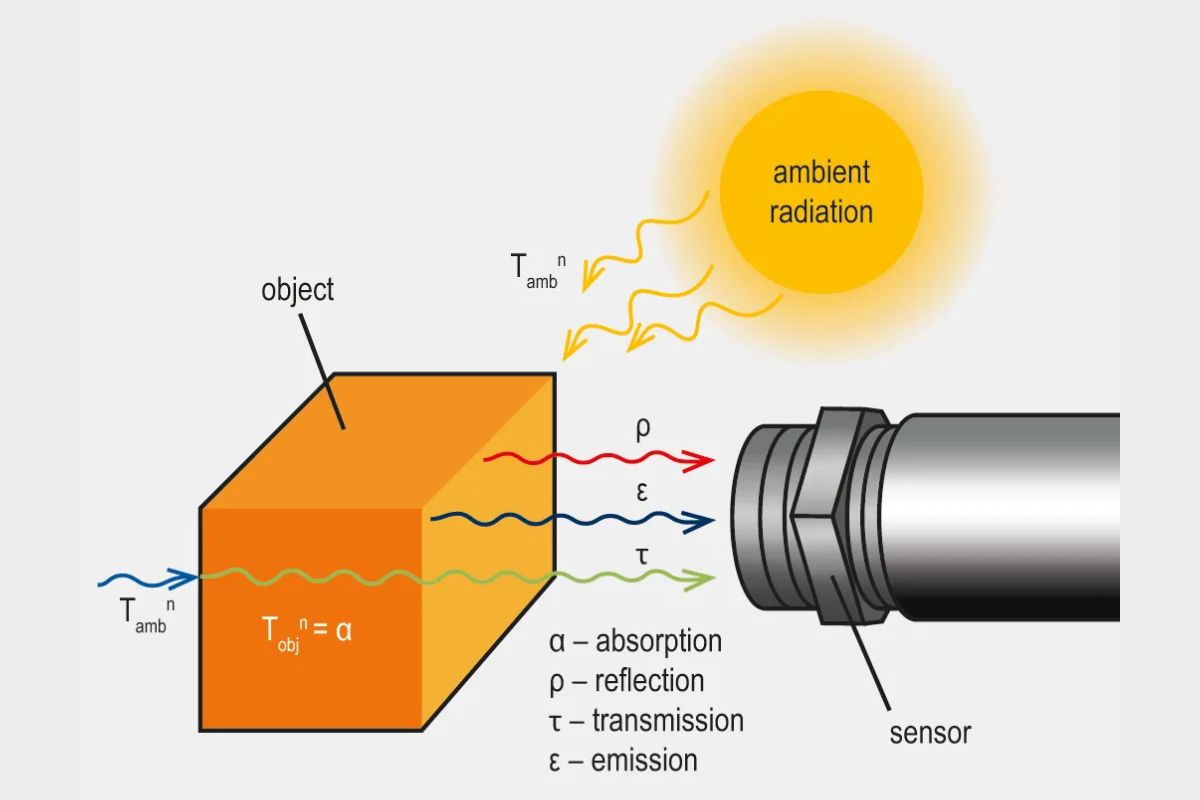
In optics, transmissivity refers to the fraction of light that passes through a material without being absorbed.
-
Engineers use transmissivity to design efficient solar panels by selecting materials that allow maximum light to pass through.
Transmissivity in Hydrology
Hydrology focuses on the movement and distribution of water. Transmissivity plays a crucial role in understanding aquifers and groundwater flow.
-
Transmissivity in hydrology is calculated by multiplying the hydraulic conductivity of the aquifer by its thickness.
-
High transmissivity in an aquifer means water can move quickly, which is good for wells and water supply systems.
-
Low transmissivity indicates that water moves slowly, which can lead to issues like waterlogging and poor drainage.
Transmissivity in Optics
Optics deals with the behavior of light. Transmissivity helps in understanding how light interacts with different materials.
-
Glass has high transmissivity for visible light, making it ideal for windows and lenses.
-
Transmissivity is crucial in designing optical fibers, which are used for high-speed internet and telecommunications.
-
Materials with low transmissivity are used in sunglasses and protective eyewear to block harmful UV rays.
Factors Affecting Transmissivity
Several factors can influence the transmissivity of a material or medium. Understanding these factors helps in optimizing systems for better performance.
-
The thickness of a material can affect its transmissivity. Thicker materials generally have lower transmissivity.
-
The composition of a material also plays a role. For example, pure water has higher transmissivity than muddy water.
-
Temperature can impact transmissivity. Higher temperatures can increase the transmissivity of gases and liquids.
Measuring Transmissivity
Accurate measurement of transmissivity is essential for various applications. Different methods are used depending on the field of study.
-
In hydrology, transmissivity is measured using pumping tests, where water is pumped from a well and the rate of flow is observed.
-
Optical transmissivity is measured using spectrophotometers, which analyze how much light passes through a material.
-
Engineers use computational models to estimate transmissivity in complex systems like buildings and industrial processes.
Applications of Transmissivity
Transmissivity has a wide range of applications, from environmental science to engineering and technology.
-
In environmental science, transmissivity helps in assessing the health of ecosystems by studying water and light penetration.
-
Architects use transmissivity data to design energy-efficient buildings with optimal natural lighting.
-
In agriculture, transmissivity is used to design irrigation systems that ensure efficient water distribution.
Challenges in Transmissivity Studies
Studying transmissivity comes with its own set of challenges. Overcoming these challenges is crucial for accurate data and effective solutions.
-
Variability in natural conditions can make it difficult to measure transmissivity accurately.
-
Human activities like construction and pollution can alter the transmissivity of natural systems.
-
Advanced technology and equipment are often required for precise measurement, which can be costly.
Future of Transmissivity Research
Research in transmissivity is continually evolving. New discoveries and technologies promise to enhance our understanding and application of this concept.
-
Nanotechnology is being explored to create materials with customizable transmissivity for various applications.
-
Climate change studies are increasingly focusing on transmissivity to understand its impact on water resources and ecosystems.
-
Renewable energy research uses transmissivity to develop more efficient solar panels and wind turbines.
Interesting Facts about Transmissivity
Here are some intriguing facts that highlight the importance and versatility of transmissivity.
-
The transmissivity of the Earth's atmosphere affects how much solar energy reaches the surface, influencing weather and climate.
-
In medical imaging, transmissivity is used to create detailed images of the body's interior using X-rays and MRI scans.
-
Transmissivity data helps in disaster management by predicting the movement of pollutants and contaminants in water bodies.
The Final Word on Transmissivity
Transmissivity, a key concept in hydrogeology, measures how easily water moves through an aquifer. It's crucial for understanding groundwater flow and managing water resources. Knowing transmissivity helps in designing wells, predicting aquifer behavior, and ensuring sustainable water use.
From its role in determining aquifer productivity to its impact on environmental studies, transmissivity is a vital piece of the puzzle. Whether you're a student, a researcher, or just curious, grasping this concept can deepen your appreciation for the natural world.
Remember, water is life. Understanding how it moves beneath our feet can help us protect this precious resource. So next time you think about groundwater, consider the unseen forces at play, and how transmissivity shapes our world.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
