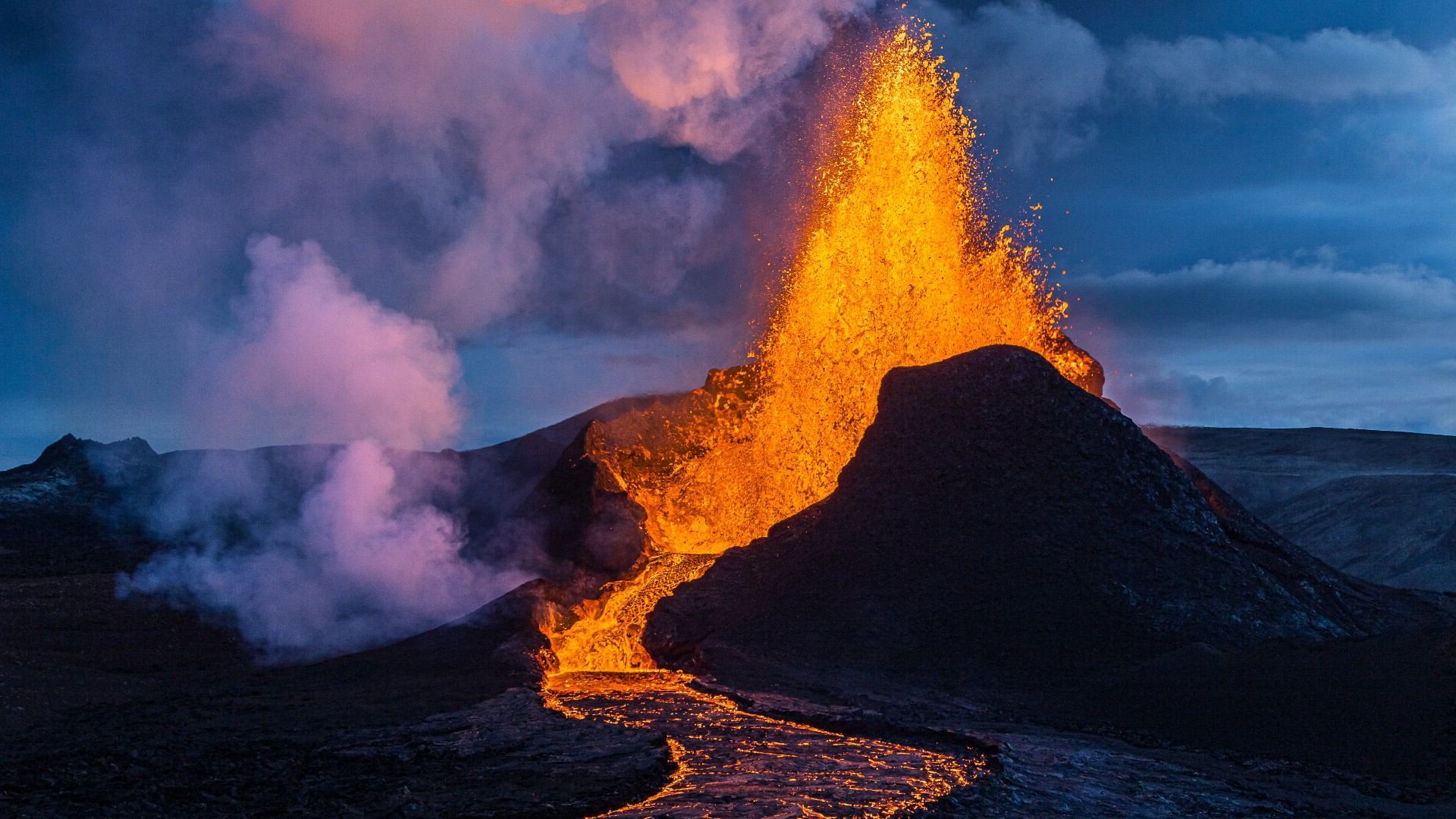
Ever wondered about the mighty mountains that spit fire? Yep, I'm talking about composite volcanoes, those awe-inspiring natural giants that dominate landscapes and sometimes, our news headlines. Composite volcanoes are fascinating, not just because of their explosive personalities but because they're packed with secrets and stories that stretch back millions of years. From their intricate layers to the devastating power of their eruptions, these geological wonders have a lot to teach us. But what makes them tick, and why should we keep an eye on them? Well, buckle up, because we're about to unearth 18 amazing facts about composite volcanoes that'll blow your mind, not just smoke!
Key Takeaways:
- Composite volcanoes, also known as stratovolcanoes, are steep and explosive, posing risks to nearby populations. They can create new habitats and enrich soil, but also have devastating effects on human settlements and climate.
- Mount St. Helens and Mount Vesuvius are famous composite volcanoes with destructive eruptions. Despite their dangers, volcanic eruptions also provide benefits such as fertile lands and cultural significance.
What is a Composite Volcano?
Composite volcanoes, also known as stratovolcanoes, are some of Earth's most picturesque yet potentially dangerous natural features. Characterized by their steep, conical shapes, these volcanoes are built up by many layers (strata) of hardened lava, tephra, pumice, and volcanic ash. Unlike shield volcanoes, which have gentle slopes and primarily effusive eruptions, composite volcanoes are known for their explosive eruptions, which can be highly destructive.
How Do Composite Volcanoes Form?
-
Formation process begins when magma from the Earth's mantle makes its way to the surface. Upon reaching the surface, it erupts, cooling and solidifying to form the volcano's structure. Over time, successive eruptions add layers of lava flows and ash, creating the steep, layered slopes that are characteristic of composite volcanoes.
-
Subduction zones are typically where these volcanoes are found. They form at convergent plate boundaries where one tectonic plate moves under another (subducts), leading to the melting of the mantle and the production of magma.
Characteristics of Composite Volcanoes
-
Height and shape: These volcanoes can rise to elevations of over 2,500 meters (8,200 feet), with Mount Fuji in Japan and Mount Rainier in the United States being prime examples of their imposing stature and symmetrical cone shapes.
-
Eruption style: Known for their violent and explosive eruptions, composite volcanoes can spew ash clouds, pyroclastic flows, and lava bombs over considerable distances, posing significant risks to nearby populations.
-
Lava composition: The lava that erupts from composite volcanoes is generally andesitic to rhyolitic in composition. This type of lava is more viscous than the basaltic lava of shield volcanoes, contributing to the explosive nature of eruptions.
Notable Composite Volcanoes Around the World
-
Mount St. Helens in the United States famously erupted in 1980, causing significant destruction and dramatically changing the landscape around it.
-
Mount Vesuvius, overlooking the city of Naples in Italy, is infamous for its eruption in 79 AD, which buried the ancient cities of Pompeii and Herculaneum under a thick layer of ash and pumice.
-
Mount Fuji, Japan's tallest peak, is not only a symbol of natural beauty but also an active composite volcano, last erupting in the early 18th century.
The Impact of Composite Volcano Eruptions
-
Human impact: Eruptions from composite volcanoes can have devastating effects on human settlements. The 1985 eruption of Nevado del Ruiz in Colombia triggered a deadly lahar that buried the town of Armero, claiming thousands of lives.
-
Climate effects: Large eruptions can inject vast amounts of ash and sulfur dioxide into the stratosphere, leading to temporary global cooling. The 1815 eruption of Mount Tambora in Indonesia resulted in the "Year Without a Summer" in 1816, with significant agricultural impact worldwide.
-
Ecological impact: Volcanic eruptions can also create new habitats and enrich the soil with minerals, leading to increased biodiversity in the long term.
The Role of Monitoring and Preparedness
-
Volcano monitoring: Scientists use a variety of tools, including seismographs, gas sensors, and satellite imagery, to monitor composite volcanoes for signs of impending eruptions, helping to mitigate risks to nearby communities.
-
Evacuation plans: Effective disaster preparedness and evacuation plans are crucial for minimizing casualties during explosive eruptions. Education and drills play key roles in ensuring community readiness.
-
Research and technology: Advances in volcanic research and technology continue to improve our ability to predict eruptions and understand the complex processes at work beneath composite volcanoes.
Fascinating Facts About Composite Volcanoes
-
Oldest dated composite volcano: Mount Etna, located on the island of Sicily in Italy, is one of the world's oldest continuously active volcanoes, with records of eruptions dating back to 1500 BC.
-
Highest composite volcano: Ojos del Salado on the Chile-Argentina border is the highest composite volcano in the world, standing at approximately 6,893 meters (22,615 feet).
-
Volcanic benefits: Despite their destructive power, volcanic eruptions provide benefits such as creating fertile lands for agriculture and contributing to the formation of mineral deposits, including precious metals.
-
Cultural significance: Many composite volcanoes hold deep cultural and spiritual significance for the communities that live near them, often being incorporated into myths, legends, and religious practices.
A Final Glimpse at Composite Volcanoes
Diving into the world of composite volcanoes has been an eye-opening adventure. These natural giants are not just stunning landscapes but also key players in Earth's geological drama. They're born from the most violent of processes, yet they contribute to the planet's regenerative cycle, creating fertile lands that support diverse ecosystems. Understanding composite volcanoes means appreciating the delicate balance between destruction and creation that shapes our world. From their explosive eruptions to their majestic peaks, these geological wonders remind us of nature's power and its intricate connection to life on Earth. So, next time you hear about a volcano erupting, remember, it's just part of Earth's way of telling its own, ever-evolving story.
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.