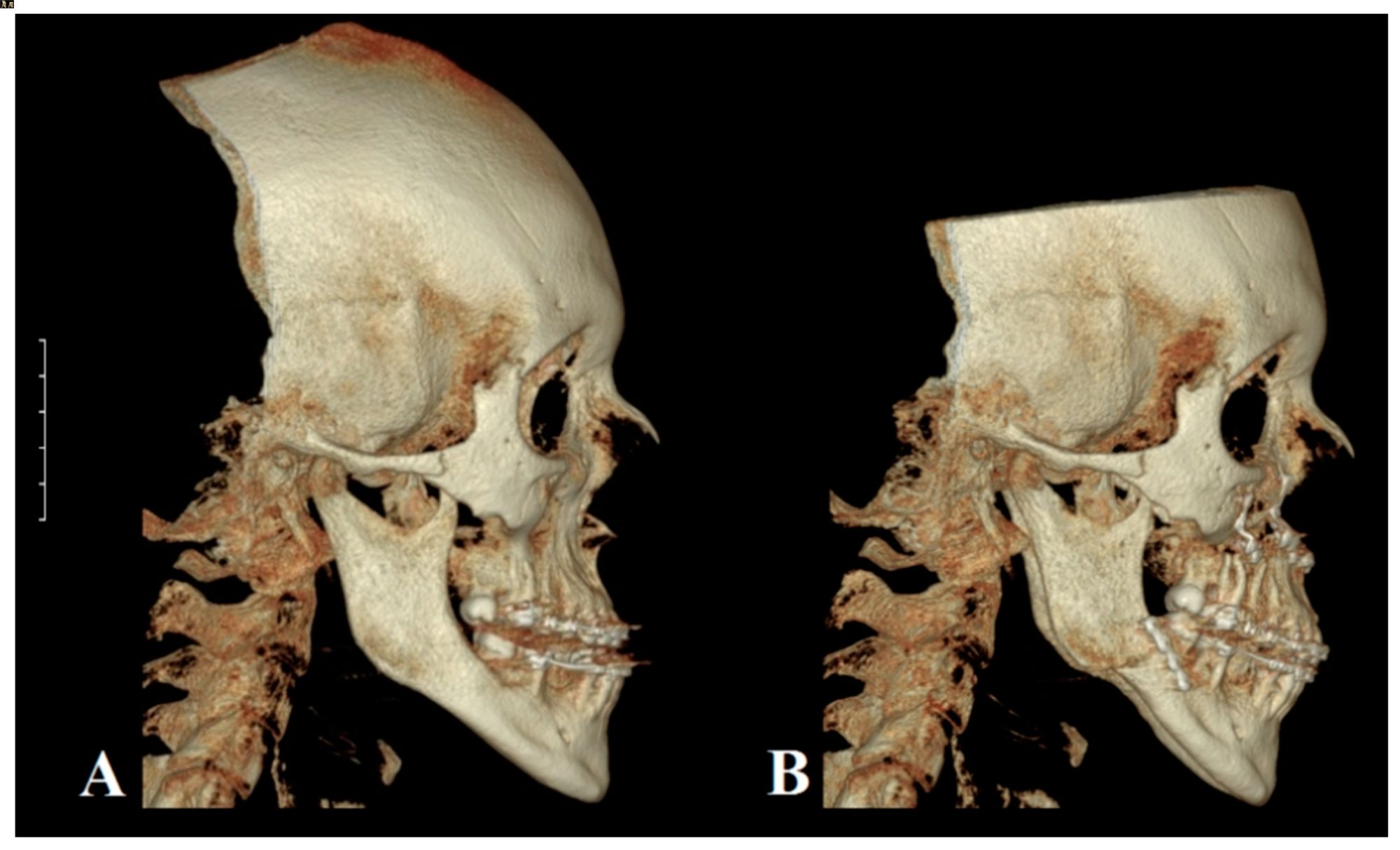
Prognathism is a condition where the jaw protrudes beyond the standard alignment of the face. This trait can be inherited or caused by environmental factors. Prognathism affects both humans and animals, often leading to unique facial features. In humans, it can influence speech, chewing, and overall facial aesthetics. Some famous historical figures, like the Habsburgs, exhibited this trait prominently. Understanding prognathism helps in fields like orthodontics and anthropology. Whether you're curious about its genetic roots or its impact on daily life, these 50 facts will shed light on this intriguing condition. Dive in to learn more about the fascinating world of prognathism!
Key Takeaways:
- Prognathism, a condition where the jaw protrudes, can be genetic or acquired, affecting speech and chewing. Early intervention and various treatments can help manage its symptoms and prevent complications.
- Factors like genetics, thumb sucking, and hormonal imbalances can contribute to prognathism. Different populations may experience varying prevalence rates, influencing access to treatment and management.
What is Prognathism?
Prognathism refers to the positional relationship of the mandible (lower jaw) or maxilla (upper jaw) to the skeletal base where either of the jaws protrudes beyond a predetermined imaginary line in the coronal plane of the skull. This condition can affect facial aesthetics and function.
- Prognathism can be genetic or acquired.
- Mandibular prognathism is when the lower jaw protrudes.
- Maxillary prognathism involves the upper jaw extending forward.
- Prognathism can be a sign of certain syndromes like Crouzon syndrome.
- Orthodontic treatment can sometimes correct prognathism.
- Surgical intervention may be necessary for severe cases.
- Prognathism can affect speech and chewing.
- Facial asymmetry is often associated with prognathism.
- Prognathism can be diagnosed through X-rays and physical examination.
- Early intervention can prevent complications later in life.
Causes of Prognathism
Understanding the causes of prognathism can help in managing and treating the condition effectively. Various factors contribute to its development.
- Genetic factors play a significant role in prognathism.
- Environmental factors like thumb sucking can influence jaw development.
- Hormonal imbalances during growth spurts can affect jaw alignment.
- Trauma to the jaw can lead to acquired prognathism.
- Tumors in the jaw area can cause prognathism.
- Nutritional deficiencies during childhood can impact jaw growth.
- Chronic mouth breathing can alter jaw positioning.
- Prolonged use of pacifiers in infants can contribute to prognathism.
- Certain medications during pregnancy can affect fetal jaw development.
- Infections in the jaw area can lead to structural changes.
Symptoms of Prognathism
Recognizing the symptoms of prognathism is crucial for early diagnosis and treatment. These symptoms can vary depending on the severity of the condition.
- Protruding jaw is the most noticeable symptom.
- Difficulty in chewing food properly.
- Speech difficulties due to jaw misalignment.
- Facial pain or discomfort.
- Headaches caused by jaw strain.
- Mouth breathing instead of nasal breathing.
- Gum problems due to improper bite.
- Tooth wear from misaligned teeth.
- Difficulty closing the lips over the protruding jaw.
- Self-esteem issues due to facial appearance.
Treatment Options for Prognathism
Various treatment options are available for managing prognathism, ranging from non-invasive methods to surgical interventions. The choice of treatment depends on the severity and underlying cause.
- Braces can help in aligning the teeth and jaw.
- Headgear is sometimes used to correct jaw positioning.
- Jaw exercises can strengthen and align the jaw muscles.
- Orthognathic surgery is performed for severe cases.
- Dental appliances like retainers can maintain jaw alignment.
- Physical therapy can help in managing symptoms.
- Pain management techniques for associated discomfort.
- Speech therapy to address speech difficulties.
- Nutritional support to ensure proper jaw development.
- Regular dental check-ups to monitor progress.
Prognathism in Different Populations
Prognathism can affect individuals differently based on their genetic background and environmental factors. Understanding its prevalence in various populations can provide insights into its management.
- African populations have a higher prevalence of mandibular prognathism.
- Asian populations often exhibit maxillary prognathism.
- European populations show varied prevalence rates.
- Indigenous populations may have unique genetic predispositions.
- Urban populations might experience different environmental influences.
- Rural populations may have limited access to treatment.
- Children are more likely to develop prognathism due to growth factors.
- Adults may experience worsening symptoms over time.
- Men and women can be equally affected by prognathism.
- Socioeconomic status can influence access to treatment and management.
Final Thoughts on Prognathism
Prognathism, a condition where the jaw protrudes beyond the standard alignment, affects many people worldwide. Understanding its causes, whether genetic or environmental, can help in managing and treating it. Treatments range from orthodontics to surgery, depending on severity. Early detection, especially in children, can lead to better outcomes. Awareness and education about prognathism are crucial for reducing stigma and providing support to those affected. By learning more about this condition, we can foster a more inclusive society. Remember, everyone’s unique features make them special. If you or someone you know has prognathism, consult with a healthcare professional to explore the best options. Stay informed, stay supportive, and embrace diversity in all its forms.
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
