Quantitative genetics is a fascinating field that explores how genes influence traits that vary continuously, like height or intelligence. Ever wondered how scientists predict the likelihood of inheriting certain traits? Quantitative genetics holds the answers. This branch of genetics uses statistical methods to study the inheritance of traits controlled by multiple genes. It helps us understand complex characteristics that don't follow simple Mendelian inheritance patterns. From agriculture to medicine, the applications are vast. Imagine breeding crops with higher yields or predicting disease risks based on genetic profiles. Quantitative genetics bridges the gap between our DNA and the traits we exhibit, making it a cornerstone of modern genetics. Ready to dive into 39 intriguing facts about this captivating subject? Let's get started!
What is Quantitative Genetics?
Quantitative genetics is a branch of genetics that deals with the inheritance of traits that are determined by multiple genes. These traits, known as quantitative traits, often show a continuous distribution, such as height, weight, or intelligence.
- Quantitative traits are influenced by multiple genes, each contributing a small effect.
- Environmental factors also play a significant role in the expression of quantitative traits.
- The study of quantitative genetics helps in understanding complex traits in both plants and animals.
- It is crucial for breeding programs aiming to improve crop yields or livestock quality.
The History of Quantitative Genetics
Understanding the history of quantitative genetics provides context for its current applications and future potential.
- The field began with the work of Sir Ronald A. Fisher in the early 20th century.
- Fisher's 1918 paper, "The Correlation Between Relatives on the Supposition of Mendelian Inheritance," laid the groundwork.
- The synthesis of Mendelian genetics with statistical methods marked the birth of quantitative genetics.
- Sewall Wright and J.B.S. Haldane also made significant contributions to the field.
Key Concepts in Quantitative Genetics
Several fundamental concepts form the backbone of quantitative genetics. These concepts help scientists understand how traits are inherited and expressed.
- Phenotype: The observable traits of an organism.
- Genotype: The genetic makeup of an organism.
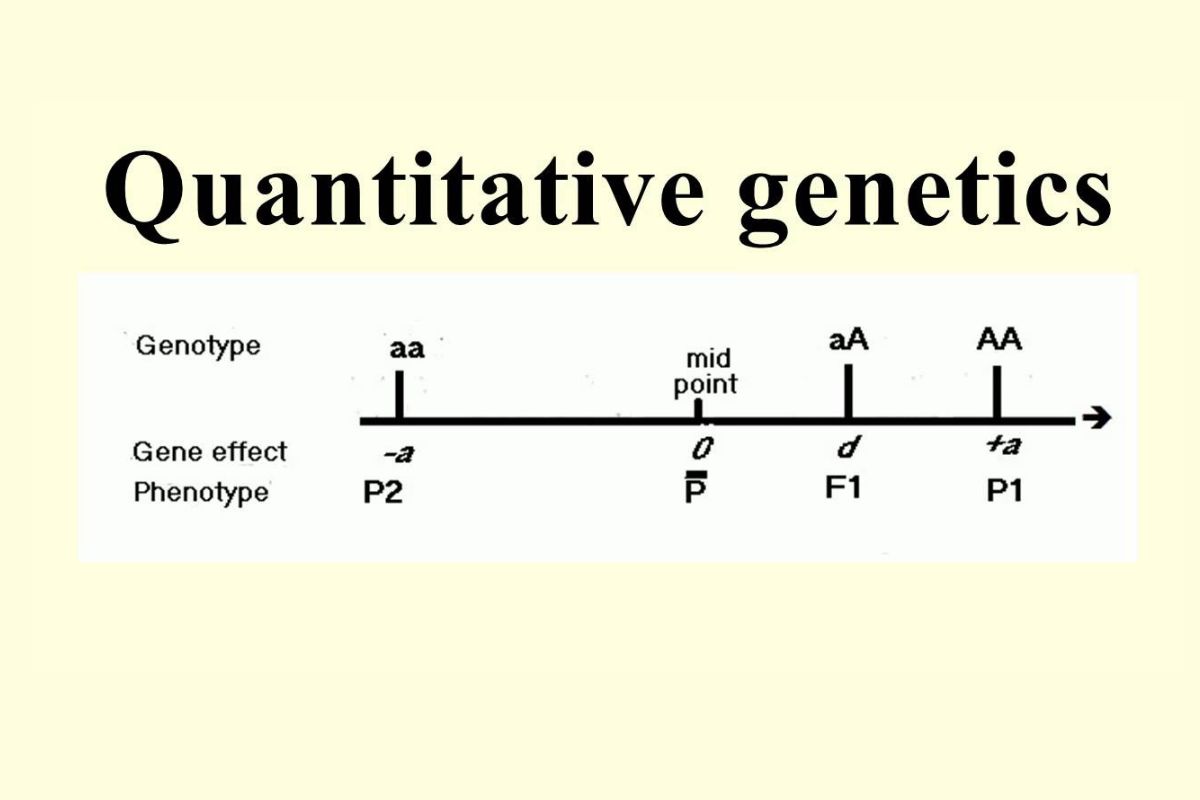
- Heritability: The proportion of phenotypic variation that can be attributed to genetic variation.
- Genetic variance: The diversity of alleles and genotypes within a population.
- Environmental variance: The variation in traits caused by environmental factors.
- Additive genetic variance: The sum of the average effects of individual alleles on a trait.
- Dominance variance: The interaction between alleles at a single locus.
- Epistasis: The interaction between genes at different loci.
Applications of Quantitative Genetics
Quantitative genetics has numerous applications in various fields, from agriculture to medicine.
- Plant breeding: Helps in developing high-yield, disease-resistant crops.
- Animal breeding: Aids in improving livestock traits like milk production and growth rate.
- Human genetics: Assists in understanding complex diseases like diabetes and heart disease.
- Conservation biology: Helps in managing genetic diversity in endangered species.
- Evolutionary biology: Provides insights into how traits evolve over time.
Tools and Techniques in Quantitative Genetics
Modern tools and techniques have revolutionized the study of quantitative genetics, making it more precise and comprehensive.
- Quantitative Trait Loci (QTL) mapping: Identifies regions of the genome associated with specific traits.
- Genome-Wide Association Studies (GWAS): Scans the entire genome to find genetic variations linked to traits.
- Marker-assisted selection: Uses molecular markers to select desirable traits in breeding programs.
- Genomic selection: Predicts the genetic value of an individual based on genome-wide markers.
- CRISPR-Cas9: Allows precise editing of genes to study their effects on traits.
Challenges in Quantitative Genetics
Despite its advancements, quantitative genetics faces several challenges that researchers are working to overcome.
- Complexity of traits: Many traits are influenced by numerous genes and environmental factors.
- Gene-environment interactions: Understanding how genes and environment interact is difficult.
- Epigenetics: Epigenetic changes can affect trait expression and are not always easy to study.
- Data analysis: Managing and analyzing large datasets requires advanced computational tools.
- Ethical considerations: Genetic research, especially in humans, raises ethical questions.
Future Directions in Quantitative Genetics
The future of quantitative genetics looks promising, with several exciting developments on the horizon.
- Precision breeding: Combining genomic selection with gene editing for more accurate breeding.
- Personalized medicine: Using genetic information to tailor medical treatments to individuals.
- Synthetic biology: Designing organisms with specific traits for industrial or medical applications.
- Big data: Leveraging large datasets to uncover new genetic insights.
- AI and machine learning: Using advanced algorithms to predict genetic outcomes and improve breeding programs.
Interesting Facts About Quantitative Genetics
Here are some intriguing tidbits that highlight the fascinating aspects of quantitative genetics.
- Twin studies: Identical twins are often used to study the heritability of traits.
- Polygenic scores: These scores predict an individual's risk of developing certain diseases based on their genetic makeup.
- Genetic architecture: The underlying genetic basis of a trait can be incredibly complex, involving many genes and interactions.
The Final Word on Quantitative Genetics
Quantitative genetics is a fascinating field that dives into how traits are inherited and expressed. It combines statistics, biology, and genetics to understand complex traits influenced by multiple genes. This area of study is crucial for advancements in agriculture, medicine, and evolutionary biology. By examining how traits like height, weight, and disease susceptibility are passed down, scientists can develop better crops, predict health risks, and understand evolutionary changes.
Understanding quantitative genetics helps us appreciate the complexity of life and the intricate dance of genes and environment. It's not just about numbers; it's about the stories those numbers tell. As research continues, the insights gained will undoubtedly lead to innovations that improve our world. So, next time you marvel at the diversity of life, remember the role quantitative genetics plays in shaping it.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
