Integrins are proteins that play a crucial role in cell signaling and adhesion. These proteins help cells stick to each other and to the extracellular matrix, which is vital for tissue structure and function. Integrins are involved in various processes like immune response, wound healing, and even cancer progression. They act as bridges, connecting the inside of the cell to the outside environment. Understanding integrins can shed light on how cells communicate and interact with their surroundings. This knowledge is essential for developing new medical treatments and therapies. Ready to dive into 39 fascinating facts about integrins? Let's get started!
What Are Integrins?
Integrins are proteins that play a crucial role in cell adhesion and signal transduction. They help cells stick to each other and to the extracellular matrix, which is vital for tissue structure and function. Here are some fascinating facts about integrins:
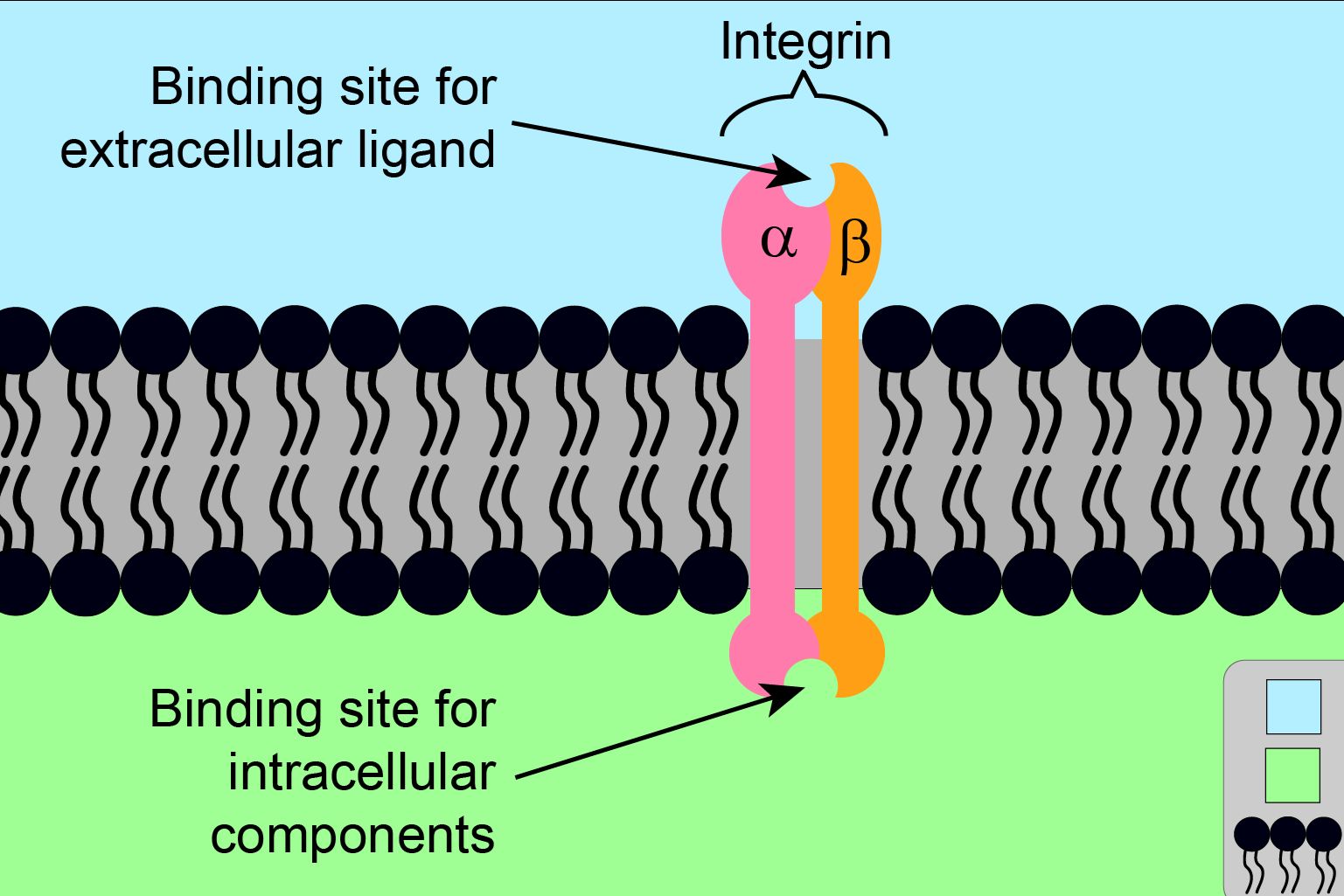
- Integrins are transmembrane receptors that facilitate cell-extracellular matrix (ECM) adhesion.
- They are composed of alpha and beta subunits, which combine to form different integrin types.
- Humans have 18 alpha and 8 beta subunits, creating 24 unique integrin combinations.
- Integrins are involved in transmitting signals from the ECM to the cell, influencing cell behavior.
- They play a role in various cellular processes, including cell migration, proliferation, and survival.
The Structure of Integrins
Understanding the structure of integrins helps in grasping their function. These proteins have a complex architecture that allows them to interact with multiple ligands.
- Each integrin has a large extracellular domain, a single transmembrane helix, and a short cytoplasmic tail.
- The extracellular domain binds to ECM proteins like fibronectin, collagen, and laminin.
- The cytoplasmic tail interacts with the cell's cytoskeleton and signaling molecules.
- Integrins can exist in different conformations: inactive (bent) and active (extended).
- The activation of integrins is regulated by inside-out and outside-in signaling mechanisms.
Integrins in Cell Migration
Cell migration is essential for various physiological and pathological processes, such as wound healing and cancer metastasis. Integrins are key players in this process.
- Integrins mediate the attachment and detachment of cells during migration.
- They form focal adhesions, which are contact points between the cell and the ECM.
- Focal adhesions act as signaling hubs, coordinating the assembly and disassembly of the cytoskeleton.
- Integrins interact with actin filaments, aiding in cell movement.
- The dynamic regulation of integrin activity is crucial for efficient cell migration.
Integrins in Immune Response
Integrins are vital for the immune system, helping immune cells navigate through tissues and reach sites of infection or injury.
- Leukocytes (white blood cells) use integrins to adhere to endothelial cells and migrate to inflamed tissues.
- Integrins like LFA-1 and Mac-1 are essential for leukocyte adhesion and transmigration.
- They play a role in the formation of the immunological synapse between T cells and antigen-presenting cells.
- Integrins help in the phagocytosis of pathogens by macrophages.
- Dysregulation of integrin function can lead to immune disorders and chronic inflammation.
Integrins in Development and Tissue Repair
Integrins are indispensable during embryonic development and tissue repair processes.
- They are involved in the formation of the blastocyst and implantation of the embryo.
- Integrins regulate the differentiation of stem cells into various cell types.
- They play a role in angiogenesis, the formation of new blood vessels.
- During wound healing, integrins help in re-epithelialization and tissue remodeling.
- Mutations in integrin genes can lead to developmental defects and impaired wound healing.
Integrins in Cancer
Integrins have a dual role in cancer, contributing to both tumor progression and suppression.
- They facilitate tumor cell invasion and metastasis by aiding in cell migration.
- Integrins interact with growth factor receptors, enhancing cell proliferation.
- They help in the formation of the tumor microenvironment, supporting cancer cell survival.
- Some integrins, like αvβ3, are associated with poor prognosis in certain cancers.
- Targeting integrins with inhibitors is being explored as a therapeutic strategy in cancer treatment.
Integrins in Cardiovascular Diseases
Integrins also play a significant role in cardiovascular health and disease.
- They are involved in the adhesion of platelets to the vascular endothelium, a key step in thrombosis.
- Integrins like αIIbβ3 are targets for antiplatelet drugs used to prevent heart attacks and strokes.
- They contribute to the development of atherosclerosis by mediating the adhesion of monocytes to the endothelium.
- Integrins are implicated in the remodeling of blood vessels in response to injury.
- Abnormal integrin signaling can lead to cardiovascular diseases such as hypertension and heart failure.
Future Directions in Integrin Research
Research on integrins continues to uncover new insights and potential therapeutic applications.
- Advances in imaging techniques are helping to visualize integrin dynamics in live cells.
- Integrin-targeted therapies are being developed for diseases like fibrosis, cancer, and autoimmune disorders.
- Understanding the crosstalk between integrins and other signaling pathways could lead to novel treatment strategies.
- Integrins are being explored as biomarkers for disease diagnosis and prognosis.
Integrins: The Unsung Heroes of Cellular Function
Integrins play a crucial role in cellular communication and function. These proteins, found on cell surfaces, help cells stick to each other and their surroundings. This is vital for processes like wound healing, immune responses, and even cancer progression. Without integrins, cells would struggle to move, divide, or respond to their environment.
Research continues to uncover new aspects of integrin function, showing their importance in health and disease. Scientists are exploring ways to target integrins for therapies, aiming to treat conditions like cancer and autoimmune diseases. Understanding integrins better could lead to breakthroughs in medicine.
So, next time you think about how your body works, remember the tiny but mighty integrins. They might not get much attention, but they’re essential for keeping everything running smoothly. Keep an eye on future discoveries about these fascinating proteins.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
