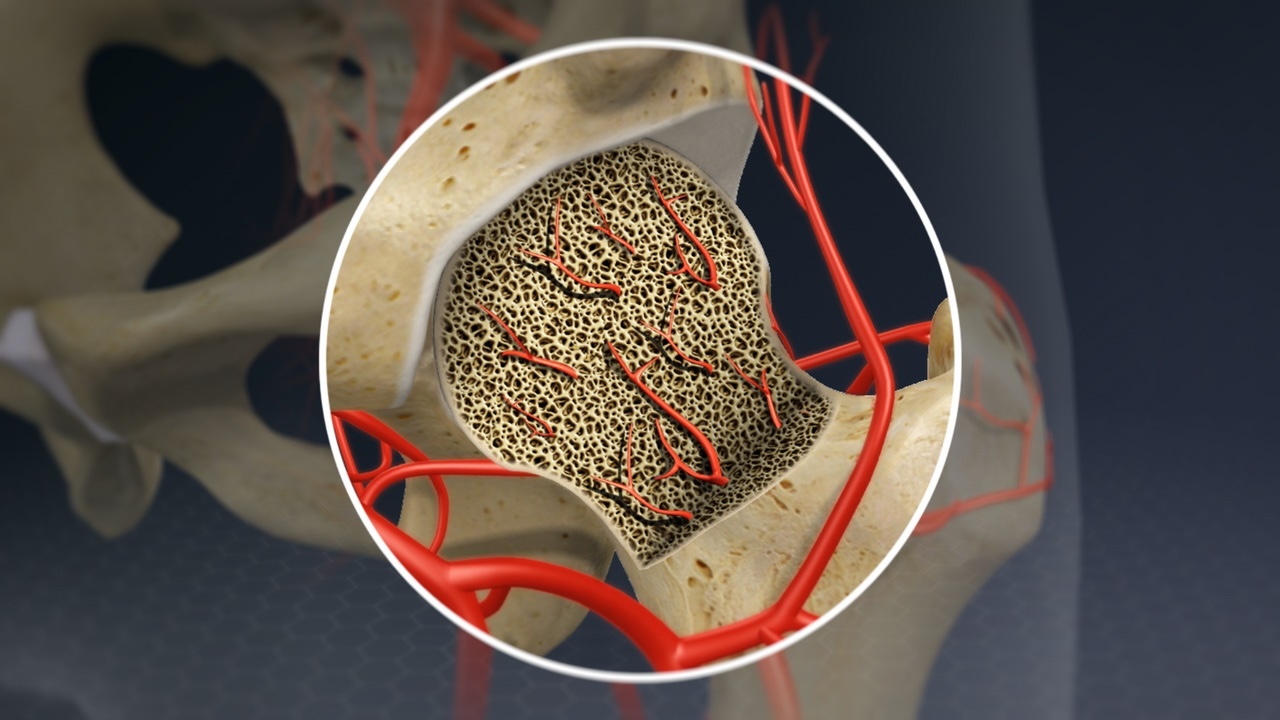
Necrosis is a medical term that describes the death of cells or tissues in the body. Unlike apoptosis, which is a natural and controlled process of cell death, necrosis occurs due to injury, infection, or lack of blood supply. This condition can affect any part of the body, leading to severe complications if not treated promptly. Common causes include trauma, infections, toxins, and chronic diseases like diabetes. Symptoms often involve pain, swelling, and discoloration of the affected area. Understanding necrosis is crucial for early detection and treatment, which can prevent further damage and improve recovery outcomes. Knowing these facts can help you recognize the signs and seek medical attention when necessary.
What is Necrosis?
Necrosis is a medical term for the death of cells in living tissue. This process can result from various factors, including injury, infection, or lack of blood supply. Understanding necrosis is crucial for medical professionals and anyone interested in health.
-
Necrosis vs. Apoptosis: Unlike apoptosis, which is a programmed and controlled cell death, necrosis is uncontrolled and often results from external damage.
-
Causes of Necrosis: Common causes include trauma, infections, toxins, and ischemia (lack of blood flow).
-
Types of Necrosis: There are several types, including coagulative, liquefactive, caseous, fat, and fibrinoid necrosis.
-
Coagulative Necrosis: Typically caused by ischemia, this type preserves the basic structure of dead tissue for a few days.
-
Liquefactive Necrosis: Often occurs in the brain due to bacterial infections, leading to a liquid mass of dead cells.
-
Caseous Necrosis: Characterized by a cheese-like appearance, commonly associated with tuberculosis.
-
Fat Necrosis: Results from the action of lipases on fatty tissues, often seen in acute pancreatitis.
-
Fibrinoid Necrosis: Involves immune reactions in blood vessels, leading to a fibrin-like appearance.
Symptoms and Diagnosis
Identifying necrosis early can be challenging but crucial for treatment. Symptoms vary depending on the affected area.
-
Pain and Swelling: Common symptoms include pain, swelling, and redness in the affected area.
-
Skin Changes: In cases of skin necrosis, the area may turn black or dark brown.
-
Foul Odor: Dead tissue can emit a foul smell due to bacterial activity.
-
Imaging Tests: MRI, CT scans, and ultrasounds can help diagnose necrosis by showing tissue damage.
-
Biopsy: A tissue biopsy can confirm necrosis by examining cells under a microscope.
-
Blood Tests: Elevated levels of certain enzymes can indicate tissue damage and necrosis.
Treatment Options
Treating necrosis involves addressing the underlying cause and removing dead tissue to prevent further damage.
-
Debridement: Surgical removal of dead tissue to promote healing.
-
Antibiotics: Used to treat infections that cause or result from necrosis.
-
Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy: Involves breathing pure oxygen in a pressurized room to enhance healing.
-
Amputation: In severe cases, removing the affected limb may be necessary to prevent the spread of necrosis.
-
Wound Care: Proper wound care is essential to prevent infection and promote healing.
-
Pain Management: Medications can help manage pain associated with necrosis.
Prevention and Risk Factors
Preventing necrosis involves managing risk factors and maintaining overall health.
-
Good Hygiene: Proper hygiene can prevent infections that lead to necrosis.
-
Healthy Diet: A balanced diet supports overall health and reduces the risk of conditions that cause necrosis.
-
Regular Exercise: Physical activity improves blood flow, reducing the risk of ischemia.
-
Avoiding Toxins: Limiting exposure to harmful chemicals and substances can prevent toxin-induced necrosis.
-
Managing Chronic Conditions: Proper management of diabetes, hypertension, and other chronic conditions can reduce the risk of necrosis.
-
Vaccinations: Staying up-to-date with vaccinations can prevent infections that cause necrosis.
Interesting Facts About Necrosis
Here are some lesser-known facts about necrosis that might surprise you.
-
Ancient Knowledge: Ancient civilizations, including the Egyptians, recognized and treated necrosis.
-
Animal Kingdom: Necrosis isn't limited to humans; animals can also suffer from it.
-
Space Travel: Astronauts face a higher risk of necrosis due to prolonged exposure to low gravity and radiation.
-
Regenerative Medicine: Advances in stem cell research offer potential treatments for necrosis.
-
Cancer Link: Tumors can cause necrosis by outgrowing their blood supply.
-
Frostbite: Severe frostbite can lead to necrosis due to prolonged exposure to freezing temperatures.
-
Snake Venom: Some snake venoms cause necrosis by destroying tissue at the bite site.
-
Autoimmune Diseases: Conditions like lupus can cause necrosis by attacking healthy tissues.
-
Radiation Therapy: While used to treat cancer, radiation can also cause necrosis in surrounding healthy tissues.
-
Burns: Severe burns can lead to necrosis due to extensive tissue damage.
-
Pressure Ulcers: Bedridden patients are at risk of necrosis from prolonged pressure on certain body parts.
-
Organ Transplants: Rejection of transplanted organs can result in necrosis of the new tissue.
Final Thoughts on Necrosis
Necrosis is a serious condition where body tissue dies due to lack of blood flow or infection. It can affect any part of the body, leading to severe complications if not treated promptly. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatments is crucial for early detection and management. From recognizing the signs like discoloration and swelling to knowing the importance of medical intervention, awareness can make a significant difference. Treatments range from medications to surgical procedures, depending on the severity. Prevention is also key, involving proper wound care, managing chronic conditions, and maintaining a healthy lifestyle. By staying informed and proactive, you can reduce the risk of necrosis and ensure better health outcomes. Always consult healthcare professionals if you suspect any symptoms. Knowledge and timely action are your best defenses against this potentially life-threatening condition. Stay vigilant, stay healthy.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
