Gregor Mendel is often called the father of genetics. His groundbreaking work with pea plants laid the foundation for understanding how traits are inherited. Mendel's laws—the Law of Segregation and the Law of Independent Assortment—explain how characteristics are passed from parents to offspring. These principles are still relevant in modern genetics, helping scientists predict genetic variations. Mendel's meticulous experiments and keen observations revealed patterns that were previously a mystery. His work wasn't recognized during his lifetime but has since become a cornerstone of biology. Ready to dive into 38 fascinating facts about Mendel's laws? Let's get started!
Mendel's Early Life and Education
Gregor Mendel, often called the father of genetics, had a fascinating journey that led to his groundbreaking discoveries. Let's dive into some intriguing facts about his early life and education.
- Mendel was born on July 20, 1822, in Heinzendorf, Austria (now Hynčice, Czech Republic).
- His birth name was Johann Mendel; he adopted the name Gregor upon entering the monastery.
- Mendel grew up on a farm, which sparked his interest in plant breeding and agriculture.
- He attended the University of Olomouc, where he studied physics and mathematics.
- Mendel joined the Augustinian Abbey of St. Thomas in Brno in 1843, where he became a monk and later a priest.
- He was sent to the University of Vienna to further his education in science, particularly in physics and botany.
Mendel's Experiments with Pea Plants
Mendel's experiments with pea plants laid the foundation for modern genetics. Here are some key facts about his groundbreaking work.
- Mendel chose pea plants for his experiments because they had easily observable traits and could be quickly bred.
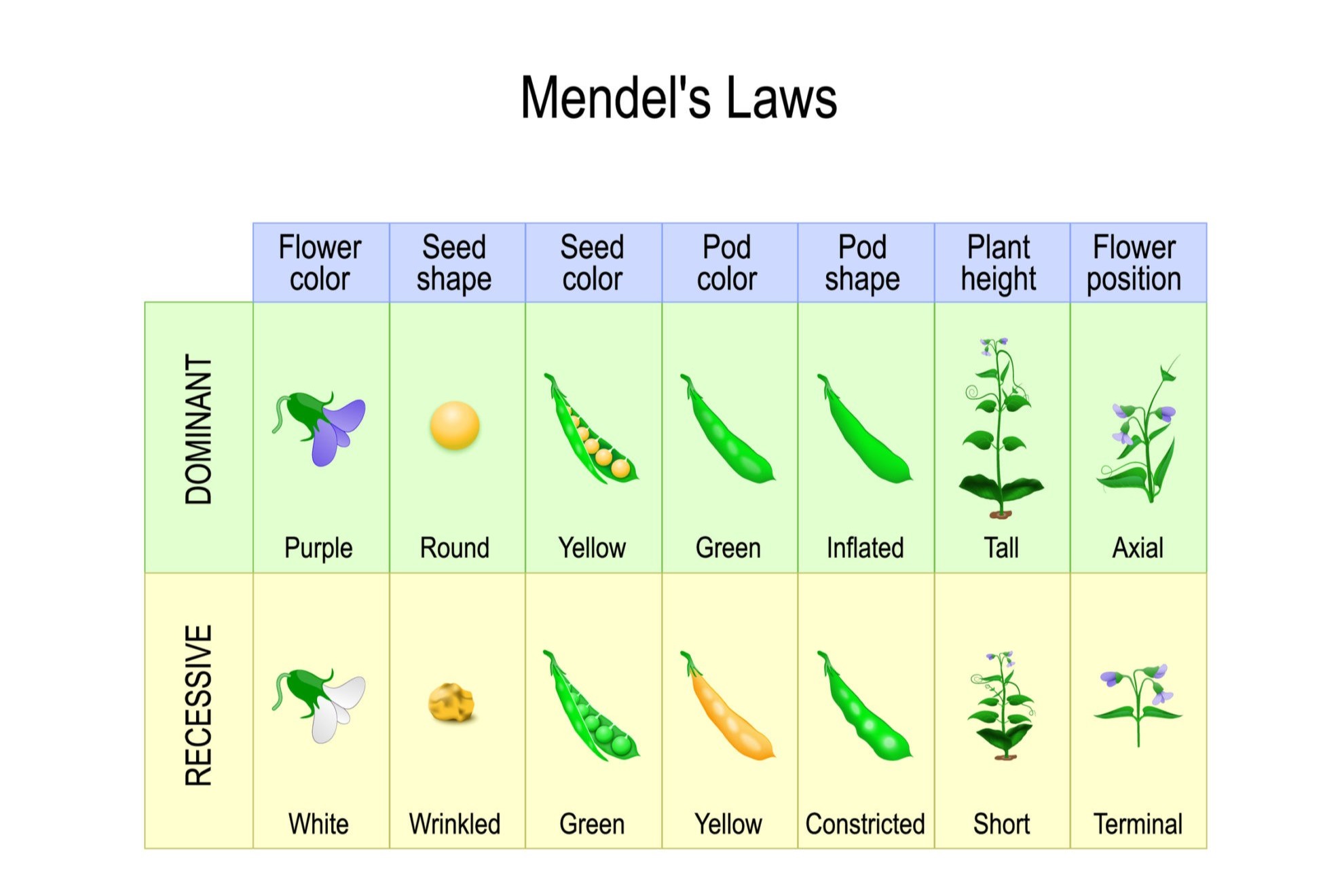
- He studied seven different traits in pea plants, including flower color, seed shape, and pod color.
- Mendel conducted his experiments over eight years, from 1856 to 1863.
- He meticulously cross-pollinated the plants and recorded the traits of the offspring.
- Mendel's work involved over 28,000 pea plants, ensuring a large sample size for accurate results.
- He discovered that traits are inherited in specific patterns, which led to the formulation of his laws of inheritance.
Mendel's Laws of Inheritance
Mendel's laws of inheritance are fundamental principles in genetics. Let's explore these laws and their significance.
- The Law of Segregation states that each organism carries two alleles for each trait, which separate during the formation of gametes.
- The Law of Independent Assortment explains that genes for different traits are inherited independently of each other.
- Mendel's laws apply to all sexually reproducing organisms, not just pea plants.
- His findings contradicted the blending theory of inheritance, which suggested that offspring were a mix of parental traits.
- Mendel's work introduced the concept of dominant and recessive alleles.
- He used mathematical ratios to predict the outcomes of genetic crosses, pioneering the use of statistics in biology.
Mendel's Legacy and Recognition
Although Mendel's work was not widely recognized during his lifetime, it has had a lasting impact on science. Here are some facts about his legacy and recognition.
- Mendel published his findings in 1866 in the journal "Proceedings of the Natural History Society of Brünn."
- His work went largely unnoticed by the scientific community for over 30 years.
- In 1900, three scientists—Hugo de Vries, Carl Correns, and Erich von Tschermak—independently rediscovered Mendel's work.
- Mendel's principles became the foundation of the field of genetics, influencing countless scientific advancements.
- The term "gene" was coined in 1909 by Danish botanist Wilhelm Johannsen, building on Mendel's concepts.
- Mendel's monastery in Brno is now a museum dedicated to his life and work.
- The Gregor Mendel Institute of Molecular Plant Biology in Vienna is named in his honor.
Interesting Tidbits About Mendel
Beyond his scientific achievements, Mendel's life had many interesting aspects. Here are some lesser-known facts about him.
- Mendel was an accomplished beekeeper and conducted experiments with bees.
- He served as the abbot of the Augustinian Abbey from 1868 until his death in 1884.
- Mendel was known for his meticulous record-keeping and attention to detail.
- He suffered from poor health throughout his life, including chronic kidney problems.
- Mendel was also interested in meteorology and maintained detailed weather records.
- He was a member of several scientific societies, including the Royal Bohemian Society of Sciences.
- Mendel's work influenced the development of the modern synthesis, which combines genetics with Darwinian evolution.
Mendel's Impact on Modern Genetics
Mendel's discoveries continue to shape our understanding of genetics today. Here are some ways his work has influenced modern science.
- Mendel's principles are taught in biology classes worldwide, forming the basis of genetic education.
- His work paved the way for the discovery of DNA as the genetic material.
- Mendel's laws are used in genetic counseling to predict the likelihood of inherited disorders.
- Modern plant and animal breeding programs rely on Mendelian genetics to develop new varieties.
- Mendel's concepts are applied in genetic research, including studies on gene expression and regulation.
- His legacy lives on in the field of genomics, which explores the structure, function, and evolution of genomes.
The Legacy of Mendel's Laws
Mendel's laws laid the groundwork for modern genetics. His principles of segregation and independent assortment explain how traits are inherited. These laws help us understand everything from genetic disorders to crop breeding. Mendel's work, initially overlooked, became the cornerstone of genetic research. Today, scientists build on his findings to explore DNA, gene therapy, and biotechnology. Mendel's insights continue to impact medicine, agriculture, and evolutionary biology. His legacy reminds us of the power of curiosity and perseverance in scientific discovery. Mendel's contributions remain vital, shaping our understanding of life's blueprint.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
