Ever wondered how cells know when to grow, divide, or even die? The answer lies in the cell cycle regulation. This process ensures cells replicate accurately, maintaining healthy tissues and organs. Think of it as a highly organized traffic system, where signals control the flow of cellular activities. Mistakes in this regulation can lead to diseases like cancer. Understanding these mechanisms can help scientists develop treatments and improve health outcomes. From checkpoints to key proteins, each component plays a vital role. Ready to learn some fascinating facts about this essential biological process? Let’s dive into the world of cell cycle regulation!
Understanding the Cell Cycle
The cell cycle is a series of events that cells go through as they grow and divide. This process is crucial for growth, development, and repair in multicellular organisms. Here are some fascinating facts about cell cycle regulation:
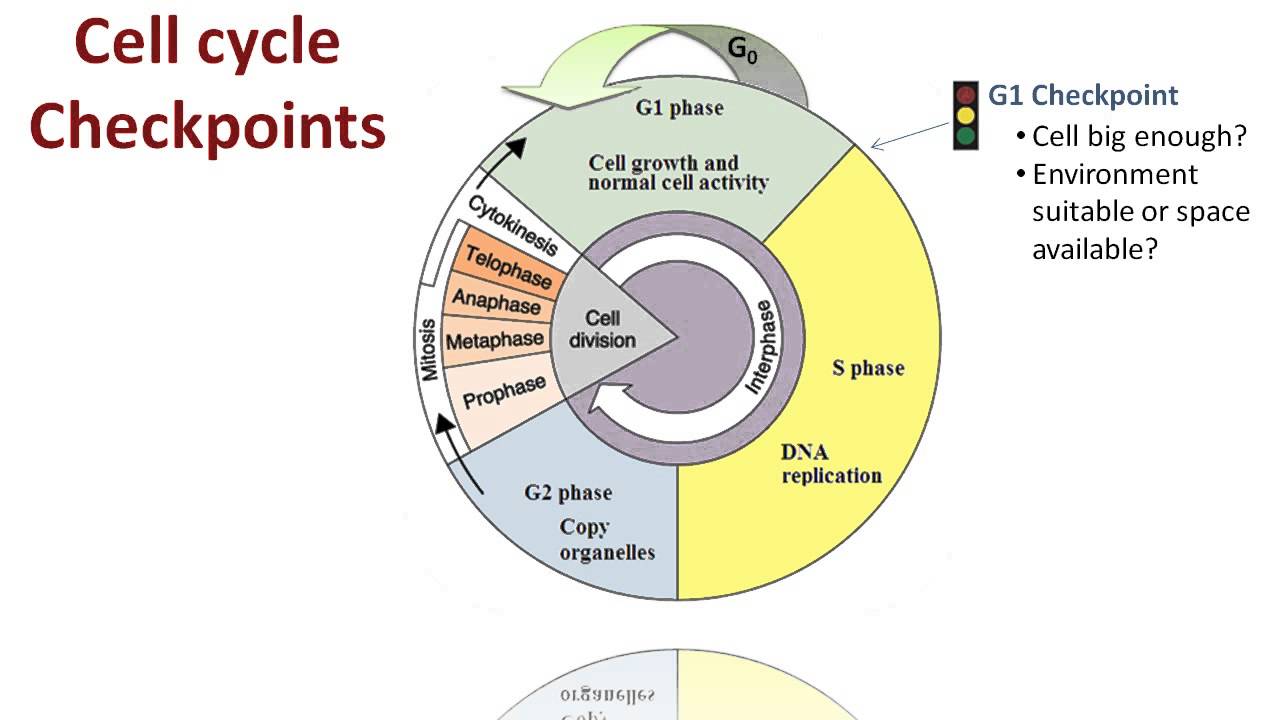
- The cell cycle consists of four main phases: G1, S, G2, and M.
- G1 phase is where the cell grows and synthesizes proteins necessary for DNA replication.
- During the S phase, DNA replication occurs, resulting in two identical sets of chromosomes.
- G2 phase involves further growth and preparation for cell division.
- M phase, or mitosis, is where the cell divides its copied DNA and cytoplasm to form two new cells.
Key Regulators of the Cell Cycle
Cell cycle regulation is controlled by a complex network of proteins and enzymes. These regulators ensure that cells only divide when it is safe and necessary.
- Cyclins are proteins that regulate the progression of cells through the cell cycle.
- Cyclin-dependent kinases (CDKs) are enzymes that, when activated by cyclins, can modify other proteins to drive the cell cycle forward.
- The CDK-cyclin complex is crucial for the transition between different phases of the cell cycle.
- Tumor suppressor proteins, like p53, can halt the cell cycle if DNA damage is detected.
- Retinoblastoma protein (Rb) prevents the cell from entering the S phase until it is ready.
Checkpoints in the Cell Cycle
Checkpoints are control mechanisms that ensure the accuracy of cell division. They prevent the cycle from progressing if errors or damage are detected.
- The G1 checkpoint ensures that the cell is ready for DNA synthesis.
- The G2 checkpoint verifies that DNA replication in the S phase has been completed correctly.
- The M checkpoint ensures that all chromosomes are properly aligned before the cell divides.
- If a cell fails a checkpoint, it can undergo apoptosis, or programmed cell death, to prevent the propagation of errors.
- Checkpoints are crucial for preventing cancer, as they stop cells with damaged DNA from dividing.
The Role of External Signals
External signals can influence the cell cycle, ensuring that cells divide only when necessary.
- Growth factors are proteins that stimulate cell division by binding to receptors on the cell surface.
- Contact inhibition occurs when cells stop dividing once they touch other cells, preventing overcrowding.
- Nutrient availability can affect the cell cycle, as cells need sufficient resources to grow and divide.
- Hormones can also regulate the cell cycle, with different hormones promoting or inhibiting cell division.
- Stress signals, such as DNA damage or oxidative stress, can halt the cell cycle to allow for repair.
Cell Cycle and Cancer
Cancer is often the result of uncontrolled cell division, which can occur when cell cycle regulation is disrupted.
- Mutations in genes that regulate the cell cycle can lead to cancer.
- Oncogenes are mutated genes that can cause cells to divide uncontrollably.
- Tumor suppressor genes, when mutated, lose their ability to halt the cell cycle, contributing to cancer development.
- Many cancer treatments target the cell cycle to stop the proliferation of cancer cells.
- Chemotherapy drugs often work by damaging DNA, triggering cell cycle checkpoints and leading to cell death.
Advances in Cell Cycle Research
Research into cell cycle regulation continues to provide insights into cell biology and potential treatments for diseases.
- Scientists are exploring how cell cycle regulation can be manipulated to treat cancer.
- New technologies, like CRISPR, allow for precise editing of genes involved in the cell cycle.
- Understanding the cell cycle can lead to better regenerative medicine techniques, such as growing tissues and organs.
- Research into cell cycle regulation can also improve our understanding of aging and age-related diseases.
- Advances in imaging techniques allow scientists to observe the cell cycle in real-time, providing new insights.
Fun Facts About the Cell Cycle
Here are some interesting tidbits about the cell cycle that you might not know.
- Some cells, like neurons, exit the cell cycle and enter a resting state called G0.
- The cell cycle duration can vary greatly between different cell types, from a few hours to several days.
- Certain viruses can hijack the cell cycle machinery to replicate themselves.
- The discovery of cyclins and CDKs earned scientists the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine in 2001.
- Plants have unique cell cycle regulators that allow them to grow continuously throughout their lives.
- The study of yeast cells has provided significant insights into cell cycle regulation, as their cell cycle is similar to that of human cells.
- Some cancer cells can become resistant to treatments by altering their cell cycle regulation mechanisms.
- Understanding the cell cycle is crucial for developing new antibiotics, as many bacteria rely on similar processes for division.
The Final Word on Cell Cycle Regulation
Cell cycle regulation is crucial for life. It ensures cells divide correctly, preventing chaos in our bodies. Key players like cyclins and CDKs act as the cell's traffic lights, guiding it through stages. Checkpoints are like security guards, stopping the process if something's wrong. Mutations in these regulators can lead to diseases like cancer, highlighting their importance.
Understanding these processes helps in developing treatments for various conditions. Scientists are always learning more, aiming to harness this knowledge for medical advancements. So, next time you hear about cell division, remember it's not just a simple split. It's a well-orchestrated dance, vital for health and growth.
Stay curious and keep exploring the wonders of biology. There's always more to learn about the tiny processes that keep us alive and thriving.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
