Nanopore sequencing is a cutting-edge technology transforming the world of genomics. But what makes it so special? Nanopore sequencing allows scientists to read DNA and RNA sequences directly, without the need for amplification or chemical labeling. This method uses tiny protein pores embedded in a membrane to detect changes in electrical current as nucleic acids pass through. The result? Faster, more accurate sequencing that can be done in real-time. Whether you're a student, a researcher, or just curious about the latest in genetic technology, understanding nanopore sequencing can open up a world of possibilities. Ready to dive into 37 fascinating facts about this revolutionary technique? Let's get started!
What is Nanopore Sequencing?
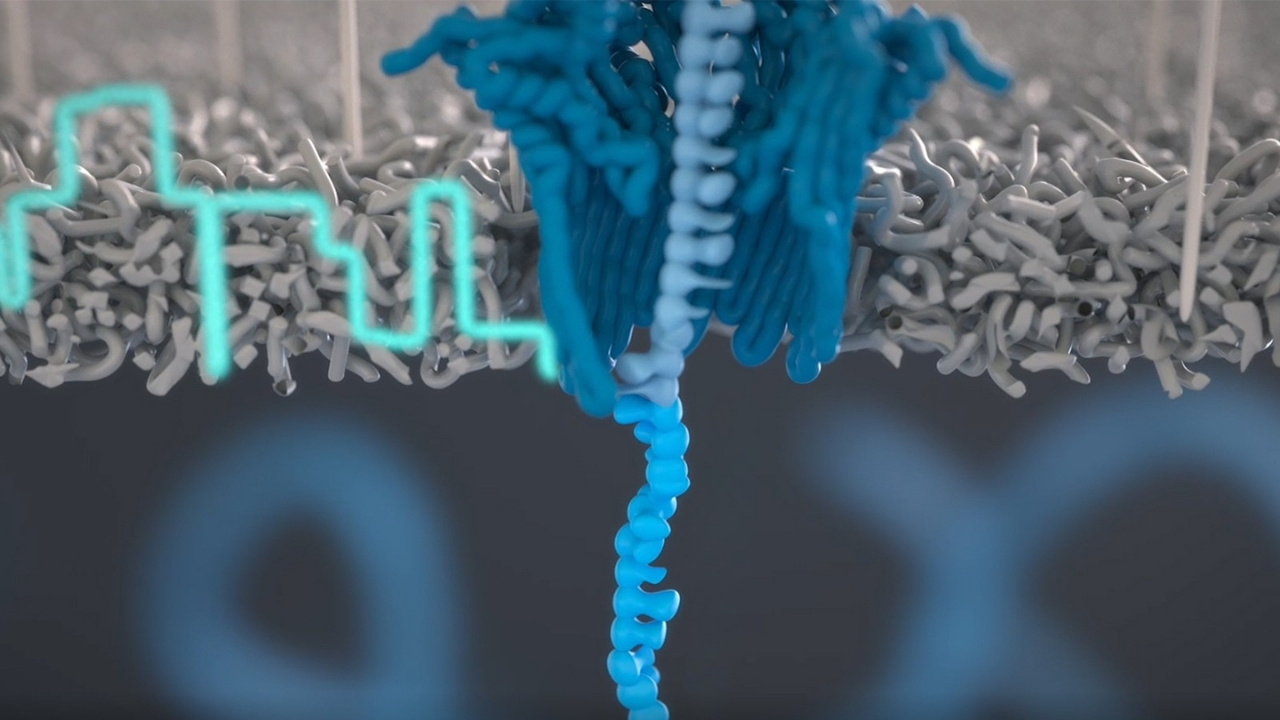
Nanopore sequencing is a cutting-edge technology that reads DNA sequences by passing them through tiny pores. This method has revolutionized genomics, making it faster and more accessible. Here are some fascinating facts about this technology.
-
Nanopore sequencing can read long DNA strands: Unlike traditional methods, nanopore sequencing can read very long DNA sequences, sometimes over a million bases in length.
-
Portable devices: Some nanopore sequencers are small enough to fit in your pocket, making them ideal for fieldwork and remote locations.
-
Real-time data: This technology provides real-time sequencing data, allowing scientists to make immediate decisions based on the results.
-
No need for PCR: Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) amplification is not required, simplifying the process and reducing potential errors.
-
Versatile applications: Nanopore sequencing is used in various fields, including medicine, agriculture, and environmental science.
How Does Nanopore Sequencing Work?
Understanding the mechanics behind nanopore sequencing can be quite intriguing. Here's a breakdown of how this technology operates.
-
Nanopores are tiny holes: These pores are only a few nanometers in diameter, just large enough for a single DNA strand to pass through.
-
Electric current: An electric current is applied across the nanopore, and as DNA passes through, it disrupts the current in a unique way.
-
Signal detection: The disruptions in the current are detected and analyzed to determine the DNA sequence.
-
Protein nanopores: Often, these nanopores are made from proteins, which are engineered to be highly specific and efficient.
-
Synthetic nanopores: Some nanopores are made from synthetic materials, offering different properties and advantages.
Advantages of Nanopore Sequencing
Nanopore sequencing offers several benefits over traditional sequencing methods. Here are some of the key advantages.
-
Speed: This method can sequence DNA much faster than older technologies.
-
Cost-effective: The overall cost of nanopore sequencing is lower, making it more accessible for various research projects.
-
Flexibility: It can be used for a wide range of applications, from small-scale studies to large genome projects.
-
Minimal sample preparation: Less preparation is needed, which saves time and reduces the risk of contamination.
-
Direct RNA sequencing: Nanopore technology can also sequence RNA directly, providing more comprehensive data.
Challenges in Nanopore Sequencing
Despite its many advantages, nanopore sequencing does come with some challenges. Here are a few to consider.
-
Error rates: The error rate can be higher compared to other sequencing methods, although it is improving.
-
Data analysis: Analyzing the data requires sophisticated software and expertise.
-
Sample quality: High-quality samples are essential for accurate results.
-
Technical expertise: Operating nanopore sequencers and interpreting the data requires specialized training.
-
Initial cost: While the running costs are low, the initial investment in equipment can be high.
Applications in Medicine
Nanopore sequencing has numerous applications in the medical field. Here are some ways it is being used.
-
Disease diagnosis: It helps in diagnosing genetic disorders and infectious diseases quickly.
-
Cancer research: Researchers use it to study cancer genomes and identify mutations.
-
Personalized medicine: This technology aids in tailoring treatments based on an individual's genetic makeup.
-
Pathogen detection: It can rapidly identify pathogens in clinical samples, crucial for outbreak management.
-
Prenatal testing: Non-invasive prenatal testing is possible, reducing risks for both mother and baby.
Applications in Agriculture
Nanopore sequencing is also making waves in agriculture. Here are some agricultural applications.
-
Crop improvement: It helps in identifying beneficial traits for crop breeding.
-
Pest resistance: Researchers can study pest genomes to develop resistant crop varieties.
-
Soil microbiome: Understanding soil microbiomes can lead to better soil management practices.
-
Livestock health: It aids in monitoring the health and genetics of livestock.
-
Food safety: Nanopore sequencing can detect contaminants in food products, ensuring safety.
Environmental Applications
The environment benefits greatly from nanopore sequencing. Here are some environmental applications.
-
Biodiversity studies: It helps in cataloging species and understanding ecosystems.
-
Pollution monitoring: Researchers can track pollutants and their effects on the environment.
-
Conservation efforts: Genetic data aids in conservation planning and monitoring endangered species.
-
Microbial ecology: Studying microbial communities in various environments provides insights into ecological processes.
-
Climate change research: Understanding genetic responses to climate change can inform mitigation strategies.
Future Prospects
The future of nanopore sequencing looks promising. Here are some exciting prospects.
-
Improved accuracy: Ongoing research aims to reduce error rates and improve reliability.
-
Broader accessibility: As costs continue to drop, more researchers and institutions will have access to this technology.
The Future of Nanopore Sequencing
Nanopore sequencing is changing the game in genomics. Its ability to read long DNA strands quickly and accurately is a big deal for research and medicine. Scientists can now study complex genetic information faster than ever. This tech is also becoming more affordable, making it accessible to more labs around the world.
Expect more breakthroughs in personalized medicine, where treatments are tailored to individual genetic profiles. Environmental studies will benefit too, with faster identification of microorganisms in various ecosystems. The potential for new discoveries is huge.
As the technology improves, we’ll see even more applications. From diagnosing diseases to exploring biodiversity, nanopore sequencing is set to make a lasting impact. Keep an eye on this exciting field—it’s just getting started.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
