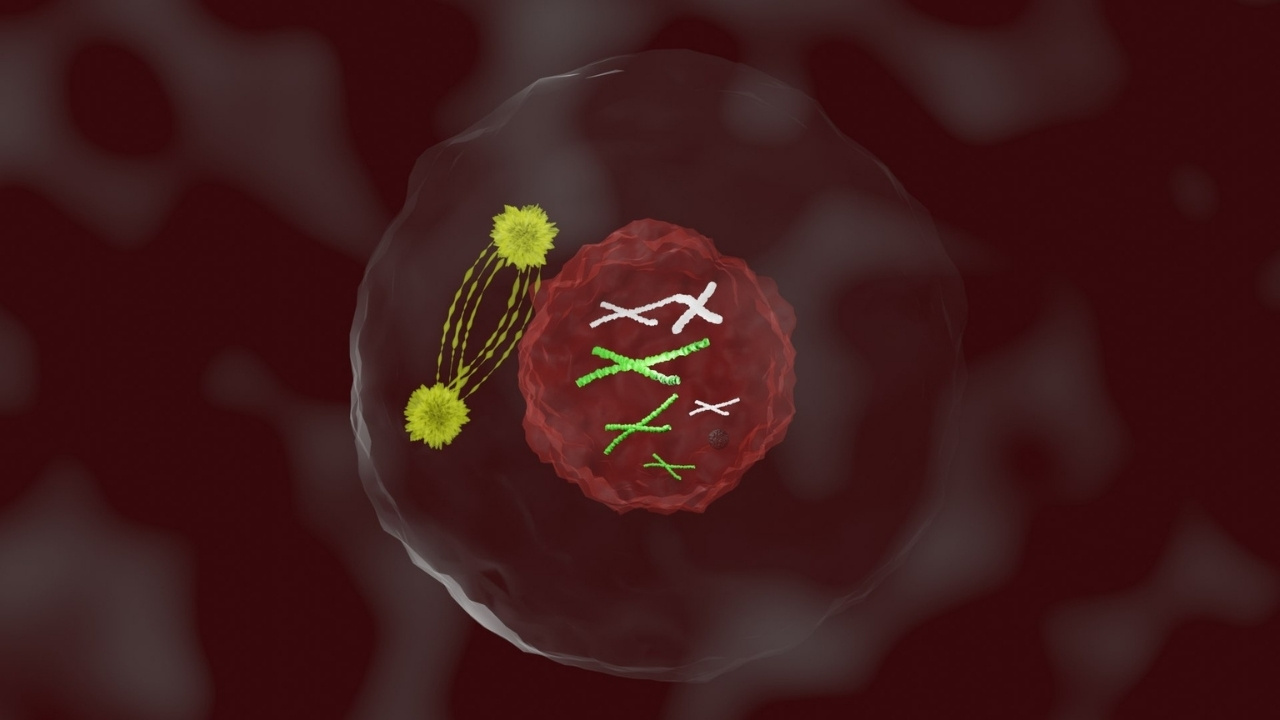
Prophase is the first stage of mitosis, a process crucial for cell division. During this phase, chromatin condenses into visible chromosomes, each consisting of two sister chromatids joined at a centromere. The nuclear envelope begins to break down, allowing spindle fibers to interact with chromosomes. Centrosomes move to opposite poles of the cell, organizing the spindle apparatus. This stage sets the groundwork for the accurate distribution of genetic material to daughter cells. Understanding prophase is essential for grasping how cells replicate and maintain genetic integrity. Dive into these 35 fascinating facts about prophase to deepen your knowledge of this vital cellular process.
What is Prophase?
Prophase is the first stage of cell division in both mitosis and meiosis. During this phase, several critical processes occur to prepare the cell for division. Let's dive into some fascinating facts about prophase.
-
Chromatin Condensation: During prophase, chromatin fibers condense into visible chromosomes. This makes it easier for the cell to manage and distribute genetic material.
-
Chromosome Structure: Each chromosome consists of two sister chromatids joined at a region called the centromere.
-
Nuclear Envelope Breakdown: The nuclear envelope, which encloses the nucleus, begins to disintegrate, allowing the chromosomes to interact with the mitotic spindle.
-
Spindle Formation: Microtubules start forming the mitotic spindle, a structure essential for separating chromosomes.
-
Centrosome Movement: Centrosomes, which help organize the spindle, move to opposite poles of the cell.
Prophase in Mitosis
Prophase in mitosis is all about preparing the cell to divide into two identical daughter cells. Here are some key facts specific to mitotic prophase.
-
Duration: Prophase is the longest phase of mitosis, often taking up to half of the total time of mitosis.
-
Chromosome Visibility: Chromosomes become visible under a light microscope during prophase.
-
Nucleolus Disappearance: The nucleolus, a structure within the nucleus, disappears as the cell prepares for division.
-
Histone Modification: Histones, proteins around which DNA is wrapped, undergo modifications to facilitate chromatin condensation.
-
Microtubule Attachment: Microtubules attach to the kinetochores, protein structures on the centromeres, to help pull the chromosomes apart.
Prophase in Meiosis
Prophase in meiosis is more complex than in mitosis, as it involves two rounds of division. Here are some intriguing facts about meiotic prophase.
-
Prophase I and II: Meiosis has two prophase stages, Prophase I and Prophase II, each with distinct events.
-
Synapsis: During Prophase I, homologous chromosomes pair up in a process called synapsis.
-
Crossing Over: Homologous chromosomes exchange genetic material in a process known as crossing over, increasing genetic diversity.
-
Chiasmata Formation: The points where crossing over occurs are called chiasmata.
-
Tetrad Formation: Homologous chromosomes form structures called tetrads, consisting of four chromatids.
Molecular Events in Prophase
Prophase involves several molecular changes that are crucial for successful cell division. Let's explore some of these events.
-
Cohesin Proteins: Cohesin proteins hold sister chromatids together until they are ready to be separated.
-
Condensin Complex: The condensin complex helps in the condensation of chromosomes, making them more compact.
-
Phosphorylation: Various proteins undergo phosphorylation, a chemical modification that activates or deactivates them.
-
Aurora Kinases: These enzymes play a crucial role in chromosome alignment and segregation.
-
Cyclin-Dependent Kinases: These kinases regulate the progression of the cell cycle, including the transition from prophase to metaphase.
Visualizing Prophase
Understanding prophase can be easier with visual aids. Here are some facts about how scientists study this phase.
-
Fluorescence Microscopy: This technique uses fluorescent dyes to stain chromosomes, making them visible under a microscope.
-
Electron Microscopy: Provides detailed images of the cell's internal structures during prophase.
-
Live-Cell Imaging: Allows scientists to observe prophase in real-time in living cells.
-
Chromosome Painting: Uses fluorescent probes to highlight specific chromosomes, aiding in the study of chromosomal behavior.
-
3D Imaging: Advanced imaging techniques create three-dimensional models of chromosomes during prophase.
Prophase in Different Organisms
Prophase can vary slightly among different organisms. Here are some interesting facts about these variations.
-
Plant Cells: In plant cells, the preprophase band, a ring of microtubules, forms before prophase begins.
-
Animal Cells: Animal cells rely heavily on centrosomes for spindle formation, unlike plant cells.
-
Fungi: Some fungi undergo a closed mitosis, where the nuclear envelope does not break down during prophase.
-
Protists: Certain protists have unique spindle structures that differ from those in plant and animal cells.
-
Bacteria: Although bacteria do not undergo mitosis, they have a similar process called binary fission.
Fun Facts About Prophase
Let's end with some fun and lesser-known facts about prophase.
-
Historical Discovery: The term "prophase" was coined by German scientist Walther Flemming in the late 19th century.
-
Prophase in Cancer: Cancer cells often have abnormalities in prophase, leading to uncontrolled cell division.
-
Educational Models: Many educational kits include models of prophase to help students understand this complex process.
-
Prophase in Pop Culture: Prophase has even made appearances in popular science fiction, symbolizing the complexity of life.
-
Research Advances: Ongoing research continues to uncover new details about prophase, contributing to our understanding of cell biology.
The Final Stretch
Prophase is a fascinating stage of cell division. It sets the stage for the complex dance of chromosomes, ensuring genetic material is accurately divided. From the condensation of chromatin into visible chromosomes to the breakdown of the nuclear envelope, each step is crucial. Understanding prophase helps us appreciate the intricacies of life at a cellular level.
Whether you're a student, a teacher, or just curious about biology, knowing these facts can deepen your appreciation for the microscopic processes that sustain life. So next time you think about cell division, remember the vital role prophase plays. It's not just a phase; it's a key player in the continuity of life. Keep exploring, keep learning, and stay curious about the wonders of biology.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
