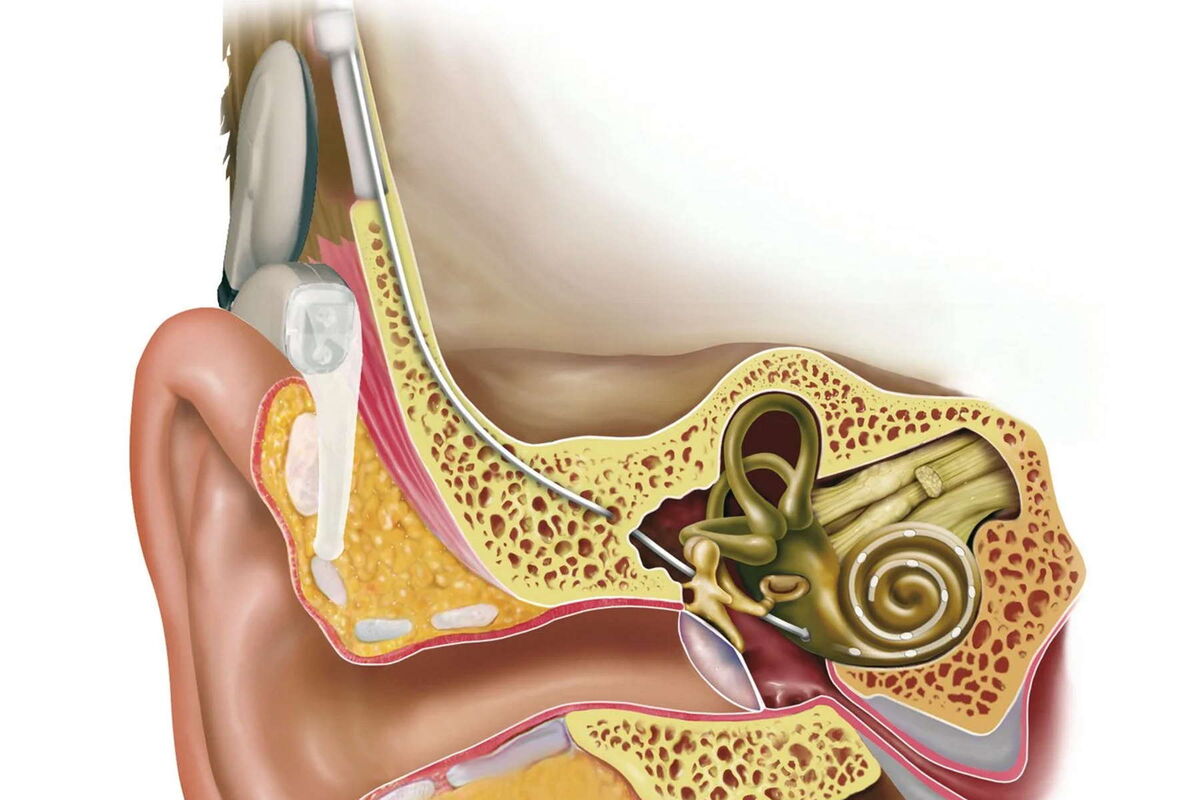
What is the cochlea? The cochlea is a spiral-shaped organ in the inner ear responsible for hearing. Shaped like a snail shell, it converts sound waves into nerve signals sent to the brain. This tiny structure, no bigger than a pea, plays a crucial role in how we perceive sound. Without it, our ability to hear would be impossible. The cochlea contains thousands of hair cells that detect different frequencies, allowing us to enjoy music, understand speech, and hear everyday sounds. Curious about more? Here are 34 fascinating facts about this incredible part of our auditory system.
What is the Cochlea?
The cochlea is a spiral-shaped organ found in the inner ear. It plays a crucial role in hearing by converting sound waves into nerve signals that the brain can interpret. Let's dive into some fascinating facts about this tiny yet mighty part of our auditory system.
- The cochlea resembles a snail shell, spiraling around itself about 2.5 times.
- It measures approximately 9 millimeters in diameter and 5 millimeters in height.
- The name "cochlea" comes from the Greek word "kokhlos," meaning spiral or snail shell.
- Inside the cochlea, there are three fluid-filled chambers: the scala vestibuli, scala media, and scala tympani.
- The organ of Corti, located within the cochlea, contains hair cells that act as sensory receptors for sound.
How Does the Cochlea Work?
Understanding the cochlea's function helps us appreciate its complexity. Here's how it transforms sound waves into electrical signals.
- Sound waves enter the ear canal and cause the eardrum to vibrate.
- These vibrations are transmitted through the ossicles, three tiny bones in the middle ear.
- The stapes, one of the ossicles, sends vibrations into the cochlea through the oval window.
- The fluid inside the cochlea moves in response to these vibrations.
- This fluid movement causes the basilar membrane to oscillate, stimulating hair cells in the organ of Corti.
The Role of Hair Cells
Hair cells are essential for hearing. They convert mechanical energy into electrical signals that the brain can understand.
- There are two types of hair cells: inner hair cells and outer hair cells.
- Inner hair cells are primarily responsible for sending auditory information to the brain.
- Outer hair cells amplify sound vibrations and improve the sensitivity of inner hair cells.
- Humans have about 3,500 inner hair cells and 12,000 outer hair cells in each cochlea.
- Damage to hair cells can lead to hearing loss, as they do not regenerate in humans.
Cochlear Implants
Cochlear implants are medical devices that can help people with severe hearing loss. They bypass damaged hair cells and directly stimulate the auditory nerve.
- The first cochlear implant was successfully implanted in 1961.
- Modern cochlear implants consist of an external microphone, speech processor, and internal electrodes.
- These devices can provide a sense of sound to individuals who are profoundly deaf or severely hard of hearing.
- Cochlear implants are most effective when implanted at a young age, as early intervention can improve language development.
- Over 700,000 people worldwide have received cochlear implants.
Interesting Facts About Cochlea
The cochlea is not just a marvel of biology but also a subject of ongoing research and curiosity.
- The cochlea can detect sounds ranging from 20 Hz to 20,000 Hz.
- It can distinguish between sounds that differ by as little as 0.1% in frequency.
- The cochlea's spiral shape helps it to separate different frequencies of sound.
- Each region of the cochlea is tuned to a specific frequency, with high frequencies detected at the base and low frequencies at the apex.
- The cochlea's ability to process complex sounds is crucial for understanding speech and music.
Cochlea in Other Animals
The cochlea is not unique to humans; many animals have similar structures that allow them to hear.
- Mammals are the only animals with a true cochlea.
- Birds have a simpler structure called the basilar papilla, which functions similarly to the cochlea.
- Reptiles and amphibians have a structure called the lagena, which is less complex than the cochlea.
- The size and shape of the cochlea can vary significantly between species, depending on their hearing needs.
- Some animals, like bats and dolphins, have highly specialized cochleae that allow them to hear ultrasonic frequencies.
Cochlear Health
Maintaining cochlear health is vital for preserving hearing ability. Here are some tips and facts related to cochlear health.
- Prolonged exposure to loud noises can damage hair cells and lead to permanent hearing loss.
- Wearing ear protection in noisy environments can help prevent cochlear damage.
- Regular hearing check-ups can detect early signs of cochlear damage.
- Certain medications, known as ototoxic drugs, can harm the cochlea and should be used with caution.
The Final Note on Cochlear Facts
Cochleae are fascinating parts of our auditory system. These spiral-shaped organs play a crucial role in how we hear and process sounds. From their intricate structure to their vital function in converting sound waves into nerve signals, cochleae are nothing short of amazing. They’re not just important for hearing; they also help maintain balance.
Understanding cochlear facts can deepen our appreciation for the complexity of human biology. Whether you’re a student, a teacher, or just curious, knowing these details can be both enlightening and useful.
So next time you hear a favorite song or enjoy a quiet moment, remember the cochlea’s role in making those experiences possible. It’s a small but mighty part of our bodies, deserving of recognition and care. Keep these facts in mind, and you’ll never take your hearing for granted again.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
