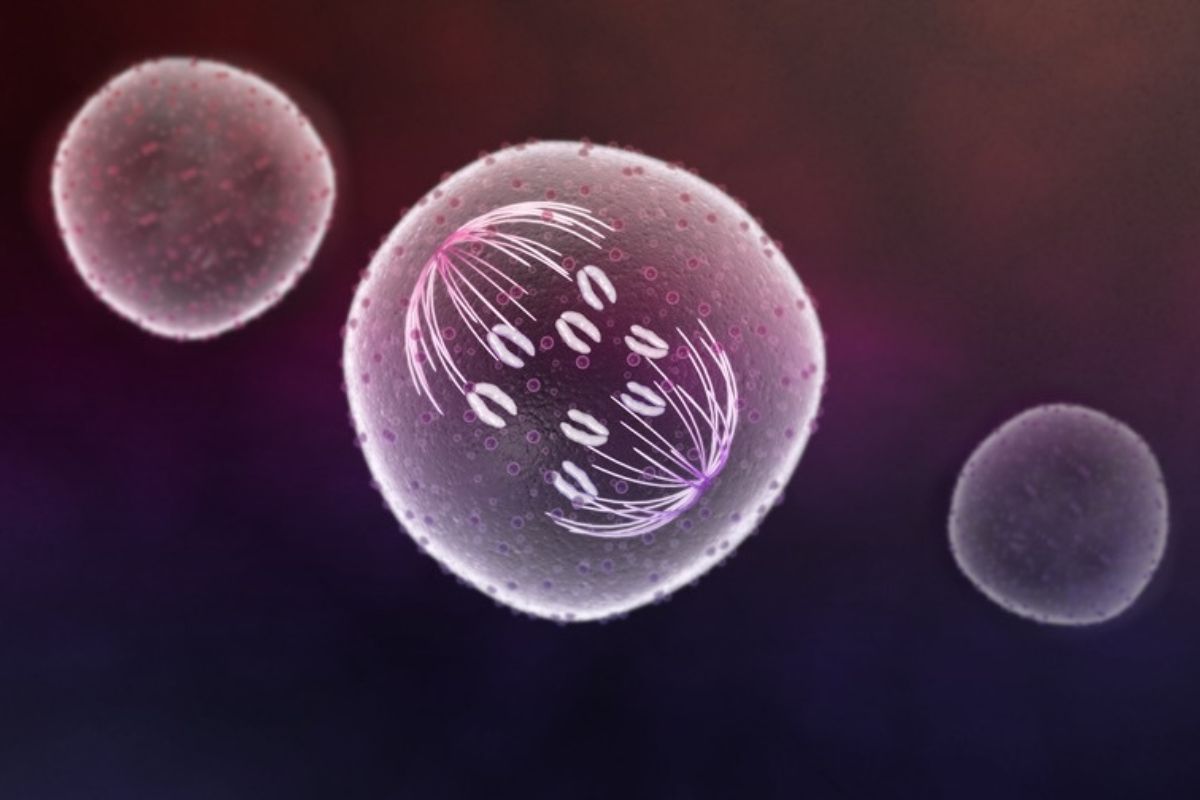
Anaphase is a crucial stage in cell division, specifically during mitosis and meiosis. But what exactly happens during anaphase? In this phase, the sister chromatids, which were previously paired up, are pulled apart to opposite ends of the cell. This ensures that each new cell will have an identical set of chromosomes. Why is this important? Proper chromosome separation is vital for genetic stability. Mistakes during anaphase can lead to genetic disorders or cell malfunction. Understanding anaphase helps us grasp how cells reproduce and maintain genetic integrity. Ready to dive into 33 fascinating facts about anaphase? Let's get started!
What is Anaphase?
Anaphase is a crucial stage in cell division where chromosomes are separated into two identical sets. This phase ensures that each new cell receives an accurate copy of the genetic material. Let's dive into some fascinating facts about anaphase.
Key Events During Anaphase
Understanding the key events of anaphase helps grasp its importance in cell division.
- Chromosome Separation: During anaphase, sister chromatids are pulled apart to opposite poles of the cell.
- Spindle Fibers: Spindle fibers, made of microtubules, play a vital role in moving the chromatids.
- Centromere Splitting: The centromere, which holds sister chromatids together, splits, allowing them to move apart.
- Kinetochore Movement: Kinetochore proteins attached to chromatids help in their movement along spindle fibers.
- Poleward Movement: Chromatids move towards the cell poles, ensuring each new cell will have a complete set of chromosomes.
The Role of Proteins in Anaphase
Proteins are essential for the successful execution of anaphase.
- Cohesin Proteins: Cohesin proteins hold sister chromatids together until anaphase begins.
- Separase Enzyme: Separase cuts cohesin proteins, allowing chromatids to separate.
- Anaphase-Promoting Complex (APC): APC triggers the transition from metaphase to anaphase by marking proteins for degradation.
- Motor Proteins: Motor proteins like dynein and kinesin help move chromatids along spindle fibers.
- Aurora Kinase: Aurora kinase ensures proper chromosome alignment and segregation.
Anaphase in Different Types of Cell Division
Anaphase occurs in both mitosis and meiosis, but there are differences.
- Mitosis Anaphase: In mitosis, anaphase results in two identical daughter cells.
- Meiosis I Anaphase: In meiosis I, homologous chromosomes are separated, not sister chromatids.
- Meiosis II Anaphase: Meiosis II anaphase resembles mitosis, where sister chromatids are separated.
- Reductional Division: Meiosis I is a reductional division, reducing chromosome number by half.
- Equational Division: Meiosis II is an equational division, maintaining chromosome number.
Errors and Anaphase
Errors during anaphase can lead to serious consequences.
- Nondisjunction: Failure of chromatids to separate can cause nondisjunction, leading to aneuploidy.
- Aneuploidy: Aneuploidy is the presence of an abnormal number of chromosomes, causing conditions like Down syndrome.
- Cancer: Errors in anaphase can contribute to cancer development by causing genetic instability.
- Checkpoint Proteins: Checkpoint proteins monitor anaphase to prevent errors.
- Mitotic Spindle Checkpoint: This checkpoint ensures all chromosomes are properly attached to spindle fibers before separation.
Visualizing Anaphase
Microscopy techniques help visualize anaphase in action.
- Fluorescence Microscopy: Fluorescence microscopy can highlight chromosomes and spindle fibers.
- Live-Cell Imaging: Live-cell imaging allows observation of anaphase in real-time.
- Confocal Microscopy: Confocal microscopy provides detailed images of chromosome movement.
- Electron Microscopy: Electron microscopy offers high-resolution images of cellular structures during anaphase.
- Time-Lapse Photography: Time-lapse photography captures the dynamic process of anaphase.
Historical Discoveries
The study of anaphase has a rich history of scientific discoveries.
- Walther Flemming: Walther Flemming first described the stages of mitosis, including anaphase, in the late 19th century.
- Theodor Boveri: Theodor Boveri's work on sea urchin eggs helped understand chromosome behavior during cell division.
- Hermann Fol: Hermann Fol observed the first clear images of chromosome separation in the 19th century.
- Microscopy Advances: Advances in microscopy have continually improved our understanding of anaphase.
- Genetic Research: Genetic research has revealed the molecular mechanisms behind anaphase.
Anaphase in Modern Research
Modern research continues to uncover new aspects of anaphase.
- Cancer Therapy: Understanding anaphase can lead to better cancer therapies targeting cell division.
- Genetic Disorders: Research on anaphase helps in diagnosing and treating genetic disorders.
- Stem Cell Research: Anaphase studies contribute to advancements in stem cell research and regenerative medicine.
The Final Stretch of Anaphase
Anaphase, a crucial phase of cell division, ensures genetic material is accurately distributed to daughter cells. During this stage, chromosomes split and move to opposite poles, driven by spindle fibers. This process is vital for growth, repair, and reproduction in living organisms.
Understanding anaphase helps grasp how cells function and maintain genetic stability. Errors in this phase can lead to genetic disorders or diseases like cancer. Scientists study anaphase to develop treatments and improve health outcomes.
In essence, anaphase is a key player in life's continuity. Its precise execution ensures cells divide correctly, supporting life's complex processes. By appreciating anaphase, we gain insight into the intricate dance of cellular division, highlighting the marvel of biological systems.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
