Transduction is a fascinating process that plays a crucial role in both biology and technology. But what exactly is it? Transduction refers to the conversion of one form of energy or signal into another. In biology, it often involves the transfer of genetic material from one bacterium to another via a virus. This process can lead to significant genetic changes and adaptations. In technology, transduction is used in devices like microphones and sensors, converting sound waves or physical stimuli into electrical signals. Understanding transduction can help us grasp how organisms evolve and how our gadgets work. Ready to learn more? Let's dive into 31 intriguing facts about transduction!
What is Transduction?
Transduction is a fascinating process where one form of energy gets converted into another. This phenomenon is crucial in various fields, including biology, physics, and technology. Let's dive into some intriguing facts about transduction.
-
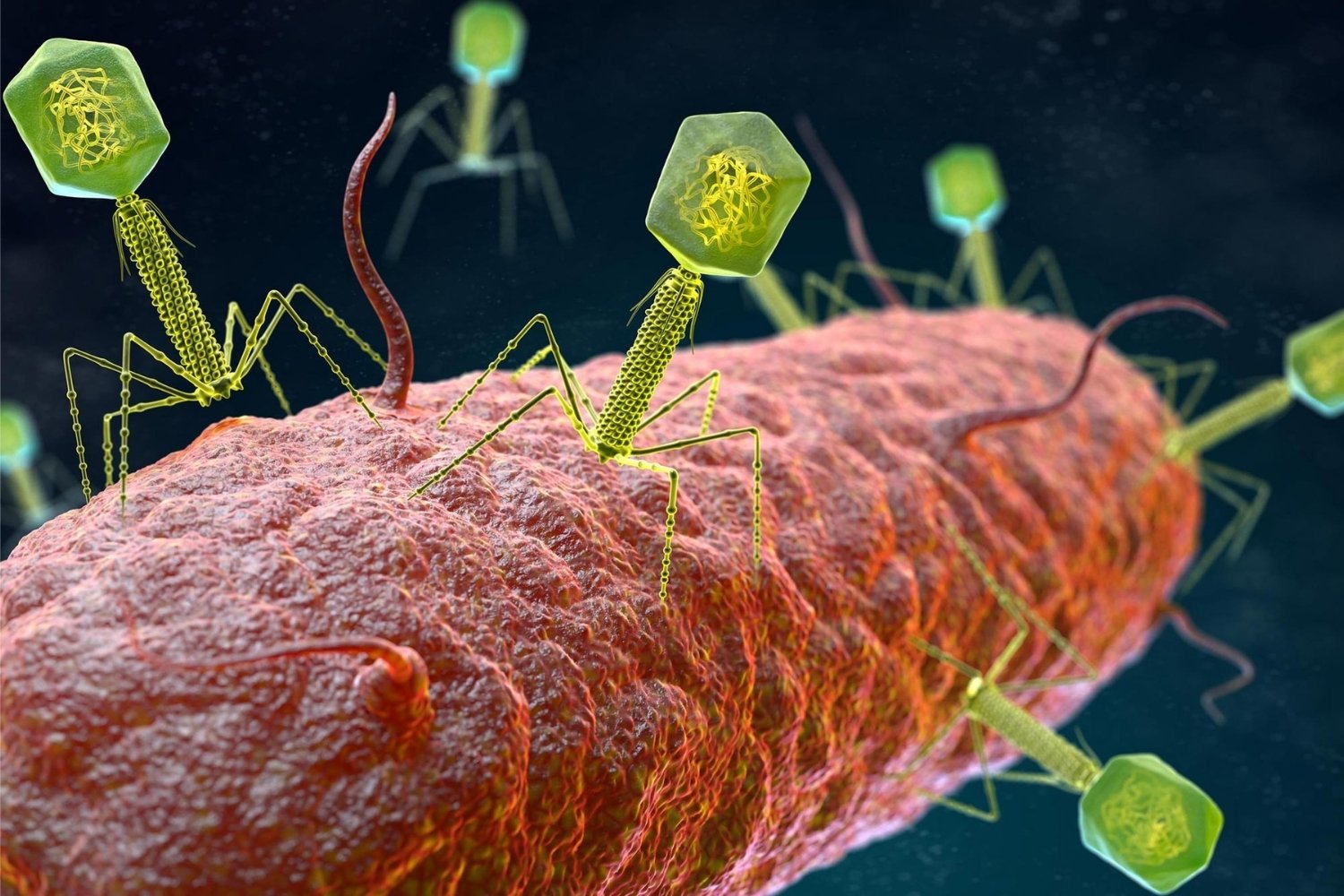
Biological Transduction: In biology, transduction refers to the process by which a virus transfers genetic material from one bacterium to another. This can lead to genetic variation in bacterial populations.
-
Sensory Transduction: Our senses rely on transduction. For example, in the human eye, photoreceptor cells convert light into electrical signals that the brain interprets as vision.
-
Sound Transduction: In the ear, sound waves are transformed into electrical signals by hair cells in the cochlea, allowing us to hear.
-
Signal Transduction Pathways: Cells use signal transduction pathways to respond to external stimuli. These pathways involve a series of molecular events that lead to a cellular response.
-
Transduction in Technology: Microphones use transduction to convert sound waves into electrical signals, which can then be amplified or recorded.
Historical Background of Transduction
Understanding the history of transduction helps appreciate its significance in modern science and technology.
-
Discovery of Bacterial Transduction: The phenomenon of bacterial transduction was first discovered by Joshua Lederberg and Norton Zinder in 1952.
-
Early Studies on Sensory Transduction: Research on sensory transduction dates back to the 19th century, with significant contributions from scientists like Hermann von Helmholtz.
-
Development of Signal Transduction Theory: The concept of signal transduction in cells was developed in the mid-20th century, with key contributions from researchers like Earl Sutherland.
Applications of Transduction
Transduction has numerous applications across different fields, making it a cornerstone of modern science and technology.
-
Medical Diagnostics: Biosensors use transduction to detect biological molecules, aiding in medical diagnostics.
-
Hearing Aids: These devices rely on transduction to amplify sound for individuals with hearing loss.
-
Telecommunications: Fiber optic technology uses transduction to convert electrical signals into light signals for data transmission.
-
Environmental Monitoring: Sensors that detect pollutants often use transduction to convert chemical signals into readable data.
Interesting Facts About Transduction
Here are some lesser-known yet fascinating facts about transduction that highlight its versatility and importance.
-
Transduction in Plants: Plants use signal transduction to respond to environmental changes, such as light and gravity.
-
Artificial Transduction: Scientists are developing artificial transduction systems to mimic biological processes for medical and technological applications.
-
Transduction in Robotics: Robots use transducers to convert physical movements into electrical signals, enabling precise control.
-
Energy Harvesting: Transduction is used in energy harvesting technologies to convert ambient energy (like vibrations) into electrical power.
-
Quantum Transduction: In quantum computing, transduction can convert quantum information from one form to another, facilitating communication between different types of quantum systems.
Challenges in Transduction Research
Despite its many applications, transduction research faces several challenges that scientists are working to overcome.
-
Efficiency Issues: Improving the efficiency of transduction processes is a major research focus, particularly in energy conversion technologies.
-
Signal Interference: In signal transduction pathways, unwanted interference can disrupt cellular communication, posing a challenge for researchers.
-
Miniaturization: Developing smaller and more efficient transducers for use in compact devices remains a significant challenge.
-
Cost: High costs associated with advanced transduction technologies can limit their widespread adoption.
Future of Transduction
The future of transduction holds exciting possibilities, with ongoing research promising to unlock new applications and improve existing technologies.
-
Smart Sensors: Future smart sensors will use advanced transduction methods to provide more accurate and real-time data.
-
Biomedical Engineering: Innovations in transduction could lead to new medical devices that better mimic natural biological processes.
-
Renewable Energy: Improved transduction technologies could enhance the efficiency of renewable energy systems, such as solar panels and wind turbines.
-
Quantum Computing: Advances in quantum transduction could revolutionize computing by enabling more efficient quantum information processing.
Fun Facts About Transduction
Let's end with some fun and quirky facts about transduction that you might not have known.
-
Transduction in Jellyfish: Some jellyfish use bioluminescence, a form of transduction, to convert chemical energy into light.
-
Transduction in Art: Artists have used transduction principles to create interactive installations that respond to sound or movement.
-
Transduction in Space: Spacecraft use transducers to convert physical measurements, like temperature and pressure, into data that can be transmitted back to Earth.
-
DIY Transduction: Hobbyists and makers often use simple transducers in DIY electronics projects, such as building homemade radios or sensors.
-
Transduction in Gaming: Modern gaming controllers use transduction to convert physical inputs (like button presses) into digital signals that control gameplay.
-
Transduction in Nature: Fireflies use a natural form of transduction to produce light through a chemical reaction in their bodies.
The Marvel of Transduction
Transduction is a fascinating process that bridges the gap between different forms of energy and biological responses. From bacterial transformation to sensory perception, it plays a crucial role in various biological systems. Understanding transduction helps us grasp how cells communicate, adapt, and respond to their environment. This knowledge is not just academic; it has practical applications in medicine, biotechnology, and neuroscience.
Whether it's the way our eyes convert light into visual signals or how bacteria acquire new genes, transduction is a cornerstone of life sciences. It’s amazing how such a fundamental process can have such diverse and far-reaching impacts. So next time you blink, smell a flower, or hear a song, remember that transduction is at work, making these experiences possible. Keep exploring, stay curious, and let the marvels of science continue to inspire you.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
