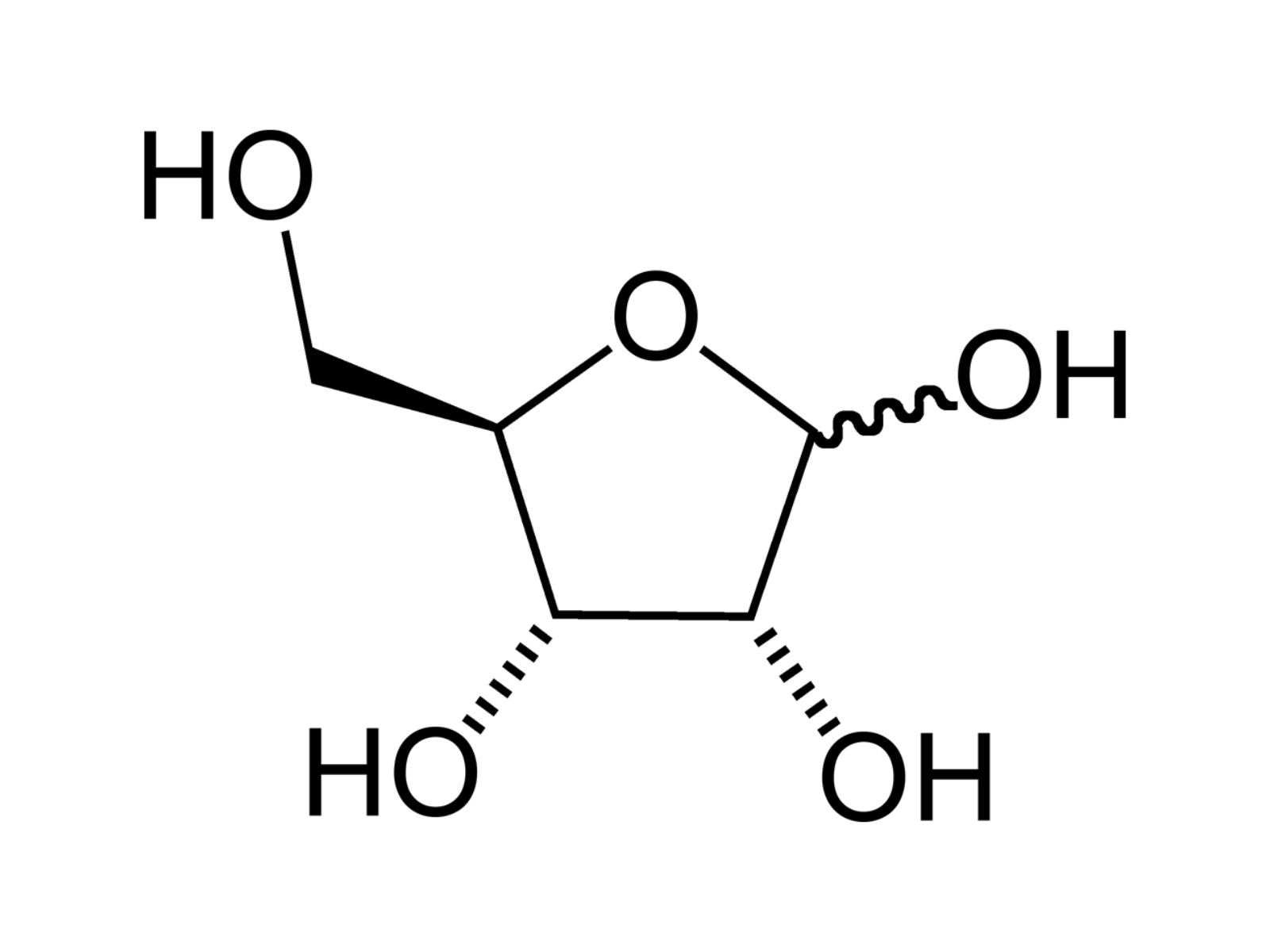
Ribofuranose, commonly known as ribose, plays a crucial role in biology. This simple sugar forms part of the backbone of RNA, the molecule essential for coding, decoding, regulation, and expression of genes. Without ribose, life as we know it wouldn't exist. But what exactly makes ribose so special? How does it function in our bodies, and why should we care? This article dives into 30 fascinating facts about ribose, shedding light on its structure, functions, and significance. From its discovery to its role in energy production, you'll gain a deeper understanding of this vital sugar. Ready to learn more? Let's get started!
Key Takeaways:
- Ribose, a vital sugar in our bodies, helps make energy, repair muscles, and support heart health. It's found in foods like meat, dairy, nuts, and vegetables, and can also be taken as a supplement.
- Research shows ribose may improve conditions like chronic fatigue syndrome and fibromyalgia, and even help older adults with cognitive function. It's a versatile sugar with many potential health benefits.
What is Ribofuranose?
Ribofuranose, commonly known as ribose, is a simple sugar with a crucial role in biology. This five-carbon sugar is a building block for many essential molecules in the body.
- Ribose is a pentose sugar, meaning it has five carbon atoms.
- It exists in two forms: D-ribose and L-ribose, with D-ribose being the biologically active form.
- Ribose is a component of RNA (ribonucleic acid), which is vital for coding, decoding, regulation, and expression of genes.
- It also forms part of ATP (adenosine triphosphate), the primary energy carrier in cells.
- Ribose is involved in the synthesis of NADH (nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide), a coenzyme essential for metabolism.
Ribose in Metabolism
Ribose plays a significant role in the body's metabolic processes, influencing energy production and overall cellular function.
- Ribose is synthesized in the body through the pentose phosphate pathway.
- It helps in the formation of nucleotides, the building blocks of DNA and RNA.
- Ribose supplementation can enhance ATP production, potentially improving energy levels.
- It is crucial for the regeneration of ATP during intense physical activity.
- Ribose aids in the recovery of muscle tissue after exercise by replenishing ATP stores.
Health Benefits of Ribose
Ribose offers several health benefits, particularly for those with certain medical conditions or those engaged in high-intensity physical activities.
- Ribose supplementation may help individuals with chronic fatigue syndrome by boosting energy levels.
- It can improve exercise performance and reduce muscle soreness.
- Ribose has been studied for its potential to support heart health, particularly in patients with heart disease.
- It may enhance cellular repair processes, aiding in faster recovery from injuries.
- Ribose can improve sleep quality by reducing fatigue and promoting relaxation.
Sources of Ribose
Ribose can be obtained from various dietary sources, although the body can also produce it naturally.
- Meat and poultry are good sources of ribose.
- It is found in dairy products like milk and cheese.
- Nuts and seeds contain small amounts of ribose.
- Certain vegetables like spinach and broccoli have ribose.
- Ribose supplements are available in powder and capsule forms for those needing higher doses.
Ribose in Scientific Research
Ribose continues to be a subject of scientific research, with studies exploring its various applications and benefits.
- Research indicates ribose may help in managing fibromyalgia symptoms.
- Studies suggest ribose could improve cognitive function in older adults.
- Ribose is being investigated for its role in mitochondrial health.
- It may have potential in treating metabolic disorders.
- Ongoing research is examining ribose's impact on athletic performance and recovery.
Interesting Facts about Ribose
Here are some intriguing facts about ribose that highlight its importance and versatility.
- Ribose was first discovered in 1905 by German chemist Emil Fischer.
- It is a key component of riboflavin (vitamin B2), essential for energy production.
- Ribose can form a cyclic structure, known as ribofuranose, in aqueous solutions.
- It is used in the production of flavor enhancers and sweeteners in the food industry.
- Ribose is a precursor for the synthesis of coenzyme A, crucial for fatty acid metabolism.
Ribofuranose: A Sweet Insight
Ribofuranose, or ribose, plays a crucial role in biology. This simple sugar forms the backbone of RNA, making it essential for genetic coding and protein synthesis. Without ribose, cells couldn't function properly. It's also a key player in energy production, being a part of ATP, the energy currency of cells. Athletes and those with chronic fatigue often use ribose supplements to boost energy levels. Found naturally in foods like meat, dairy, and certain vegetables, ribose is more than just a sugar. Its impact on health and cellular function can't be overstated. Understanding ribose helps us appreciate the complexity of life at a molecular level. Whether you're a science enthusiast or just curious, knowing about ribofuranose enriches your grasp of biology. So next time you think about sugars, remember ribose and its vital contributions.
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
