What are proto-oncogenes? Proto-oncogenes are normal genes that play a crucial role in cell growth and division. When these genes mutate, they can become oncogenes, which may lead to cancer. Think of proto-oncogenes as the gas pedal in a car, controlling how fast cells grow and divide. If the gas pedal gets stuck, cells can grow uncontrollably, leading to tumors. Understanding proto-oncogenes helps scientists develop treatments targeting cancer at its root. These genes are essential for normal cellular functions but can be dangerous when altered. Knowing more about proto-oncogenes can provide insights into cancer prevention and therapy.
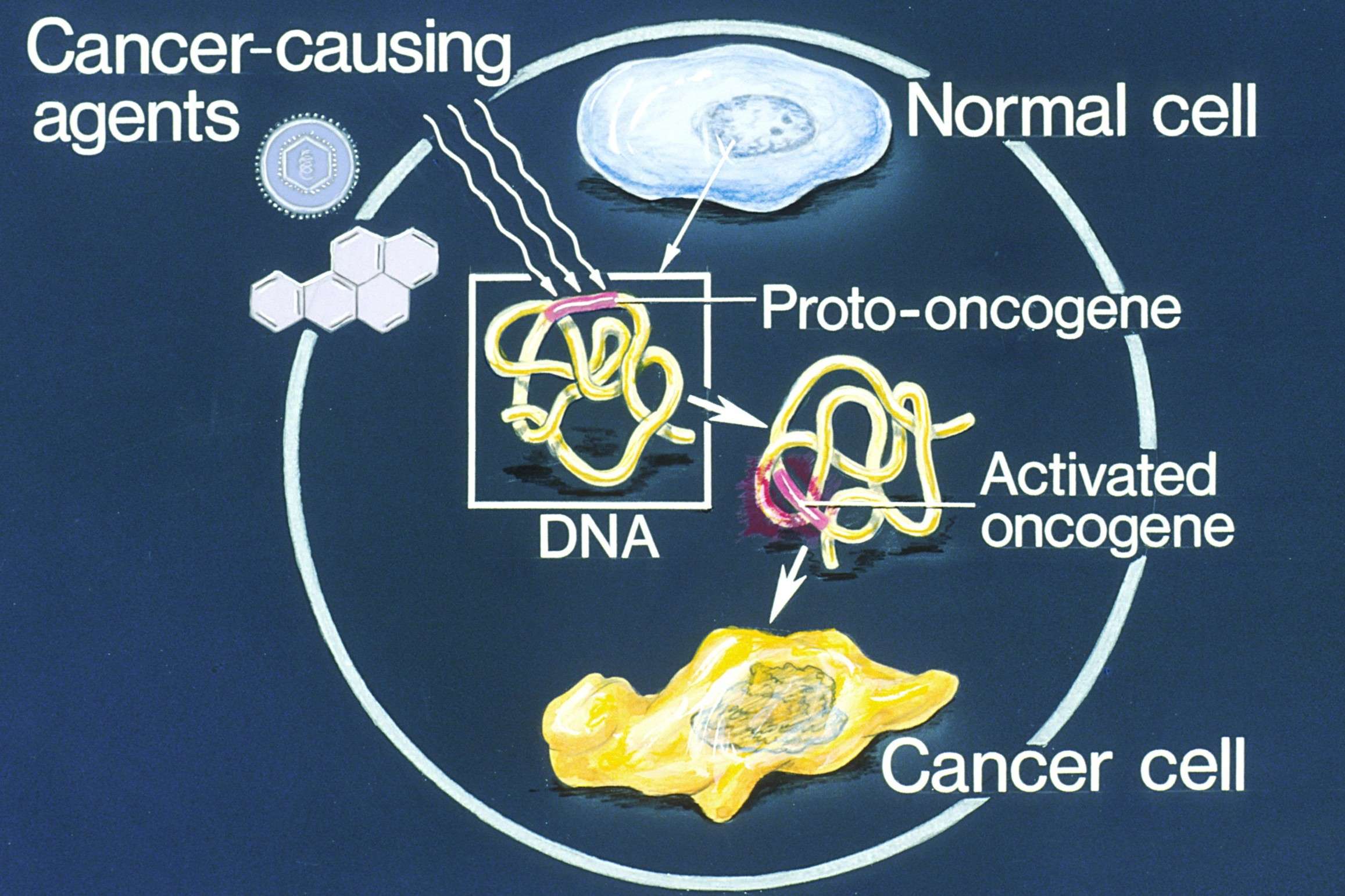
What is a Proto-oncogene?
Proto-oncogenes are genes that play a crucial role in normal cell growth and division. When these genes mutate, they can become oncogenes, which can lead to cancer. Understanding proto-oncogenes is essential for grasping how cancer develops and progresses.
- Proto-oncogenes are normal genes that help cells grow.
- When a proto-oncogene mutates, it can become an oncogene.
- Oncogenes can cause cells to grow uncontrollably, leading to cancer.
- Proto-oncogenes are involved in various cellular functions, including cell division, differentiation, and apoptosis.
- The term "proto-oncogene" was first coined in the 1970s.
How Do Proto-oncogenes Work?
Proto-oncogenes produce proteins that regulate cell growth and division. These proteins ensure that cells divide only when necessary and that they stop dividing when they should.
- Proto-oncogenes encode proteins that act as growth factors, receptors, and signal transducers.
- Growth factors produced by proto-oncogenes stimulate cell division.
- Receptors on the cell surface receive signals from growth factors.
- Signal transducers relay signals from receptors to the cell's nucleus.
- Transcription factors in the nucleus activate genes involved in cell division.
Examples of Proto-oncogenes
Several well-known proto-oncogenes have been extensively studied. These genes are often involved in critical cellular processes and can become oncogenes when mutated.
- The RAS gene family is one of the most studied proto-oncogenes.
- Mutations in RAS genes are found in about 30% of all cancers.
- The MYC gene is another important proto-oncogene.
- MYC mutations are associated with various cancers, including breast and lung cancer.
- The HER2 gene is a proto-oncogene involved in breast cancer.
How Do Proto-oncogenes Become Oncogenes?
Mutations in proto-oncogenes can occur due to various factors, including environmental influences and genetic predispositions. These mutations can lead to the uncontrolled growth of cells.
- Point mutations can activate proto-oncogenes.
- Gene amplification can lead to an increased number of proto-oncogenes.
- Chromosomal translocations can place proto-oncogenes next to highly active genes.
- Viral infections can insert oncogenes into the host genome.
- Environmental factors like radiation and chemicals can cause mutations in proto-oncogenes.
The Role of Proto-oncogenes in Cancer
Proto-oncogenes play a significant role in the development of cancer. When these genes become oncogenes, they can lead to the formation of tumors.
- Oncogenes can cause cells to bypass normal growth controls.
- Tumors can form when cells grow and divide uncontrollably.
- Oncogenes can also prevent cells from undergoing apoptosis, or programmed cell death.
- Cancer treatments often target oncogenes to stop tumor growth.
- Understanding proto-oncogenes helps researchers develop new cancer therapies.
Research and Future Directions
Ongoing research aims to better understand proto-oncogenes and their role in cancer. This research could lead to new treatments and preventive measures.
- Researchers are studying how proto-oncogenes interact with other genes.
- New technologies like CRISPR are being used to study proto-oncogenes.
- Personalized medicine approaches are being developed to target specific oncogenes.
- Early detection of proto-oncogene mutations could lead to better cancer prevention.
- Future research may uncover new proto-oncogenes involved in cancer.
Final Thoughts on Proto-oncogenes
Proto-oncogenes play a crucial role in cell growth and division. When they mutate, they can turn into oncogenes, leading to uncontrolled cell proliferation and cancer. Understanding these genes helps researchers develop targeted cancer therapies, offering hope for more effective treatments.
Scientists continue to study proto-oncogenes to unlock new ways to combat cancer. By identifying how these genes function and mutate, medical professionals can better predict cancer risks and create personalized treatment plans.
Staying informed about proto-oncogenes and their impact on health is essential. This knowledge empowers individuals to make informed decisions about their health and supports ongoing research efforts.
Proto-oncogenes are a key piece of the puzzle in the fight against cancer. Their study not only advances scientific understanding but also brings us closer to a future where cancer is more manageable and less feared.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
