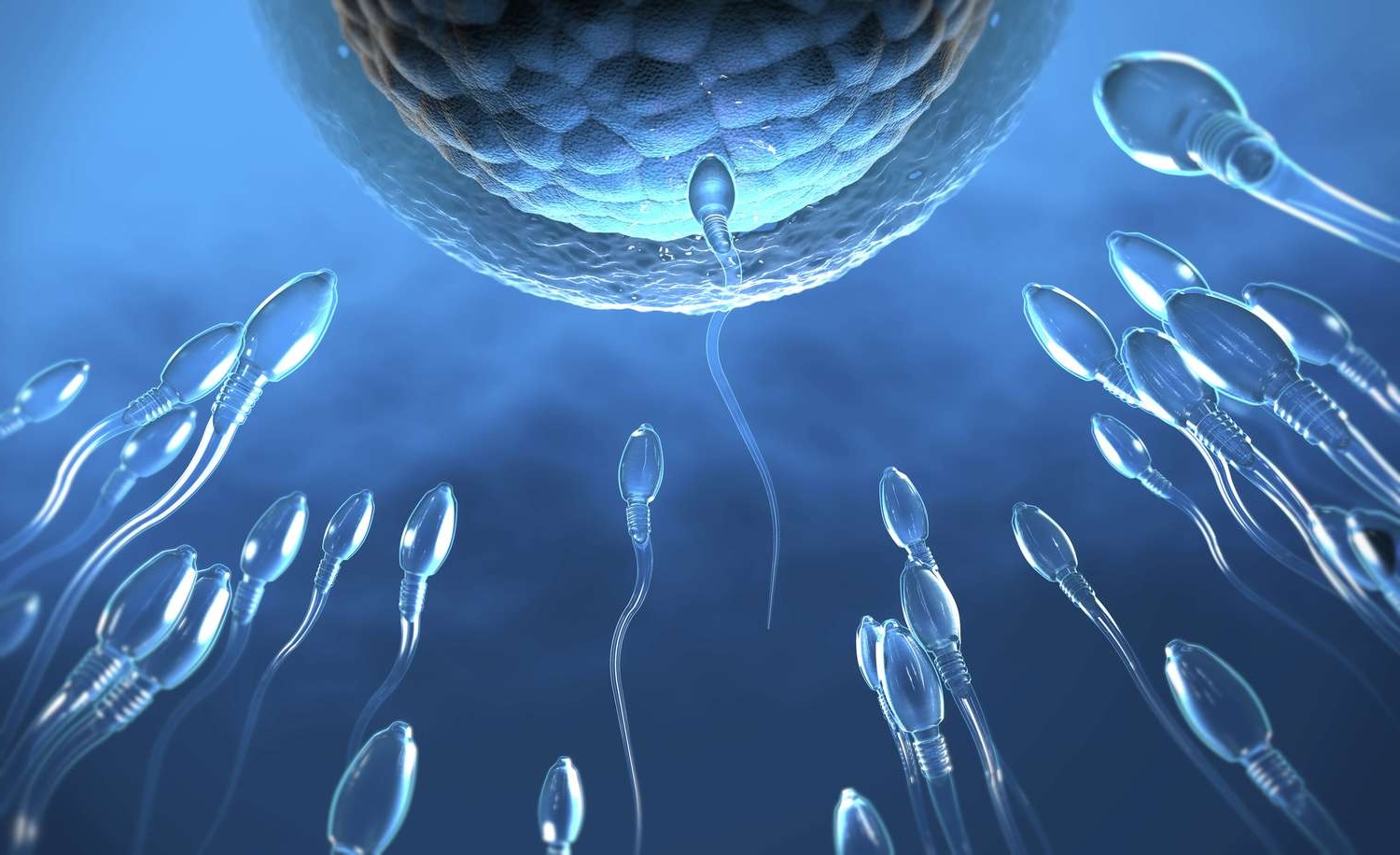
What exactly is a zygote? A zygote is the very first cell formed when a sperm cell fertilizes an egg cell. This tiny cell holds all the genetic information needed to create a new organism. Think of it as the blueprint for life. From this single cell, an entire human being will develop through a series of complex processes. The zygote undergoes rapid cell division, eventually forming a blastocyst, which then implants in the uterus. This marks the beginning of pregnancy. Understanding zygotes can help us grasp the basics of genetics, development, and even medical advancements like IVF. Ready to learn more? Let's dive into 28 fascinating facts about zygotes!
What is a Zygote?
A zygote is the initial cell formed when a sperm cell fertilizes an egg cell. This tiny cell marks the beginning of a new organism's development. Let's dive into some fascinating facts about zygotes.
-
The term "zygote" comes from the Greek word "zygotos," meaning "joined" or "yoked."
-
A zygote contains a complete set of chromosomes, half from the sperm and half from the egg.
-
This cell is the first stage of human development, eventually growing into a fetus.
-
Zygotes undergo rapid cell division, a process called cleavage, shortly after fertilization.
Formation and Development
Understanding how a zygote forms and develops can be quite intriguing. Here are some key points about its formation and early stages.
-
Fertilization typically occurs in the fallopian tube of the female reproductive system.
-
The zygote's first division happens within 24 to 30 hours after fertilization.
-
By the time it reaches the uterus, the zygote has divided multiple times, forming a structure called a blastocyst.
-
The blastocyst implants itself into the uterine wall, a crucial step for pregnancy to continue.
Genetic Makeup
The genetic composition of a zygote is a blend of both parents' DNA. This mix determines many characteristics of the future organism.
-
Each zygote has 46 chromosomes, 23 from each parent.
-
The combination of genes from both parents contributes to the unique traits of the offspring.
-
Genetic disorders can sometimes be traced back to abnormalities in the zygote's chromosomes.
-
The sex of the baby is determined at the zygote stage, depending on whether the sperm carries an X or Y chromosome.
Role in Reproduction
Zygotes play a critical role in sexual reproduction, ensuring the continuation of species. Here are some interesting aspects of their role.
-
In humans, the zygote stage lasts about four days before it becomes a blastocyst.
-
Zygotes are also found in plants, fungi, and some algae, playing a similar role in their reproductive cycles.
-
In vitro fertilization (IVF) involves creating zygotes outside the body and then implanting them into the uterus.
-
Some animals, like certain fish and amphibians, release eggs and sperm into the water, where zygotes form externally.
Scientific Discoveries
Scientific research on zygotes has led to many groundbreaking discoveries in genetics and reproductive health.
-
The first successful IVF baby, Louise Brown, was born in 1978, marking a milestone in reproductive medicine.
-
Scientists can now edit genes in zygotes using CRISPR technology, potentially preventing genetic disorders.
-
Research on zygotes has improved our understanding of early human development and congenital disabilities.
-
Stem cell research often involves studying zygotes to understand how cells differentiate into various tissues.
Ethical Considerations
The study and manipulation of zygotes raise several ethical questions, especially in the context of reproductive technologies and genetic engineering.
-
Debates continue over the moral status of zygotes, particularly in discussions about abortion and stem cell research.
-
Some countries have strict regulations on the use of zygotes in scientific research.
-
Ethical concerns also arise with genetic editing, as it could lead to "designer babies."
-
The potential for cloning humans from zygotes has sparked significant ethical and moral debates.
Fun Facts
Let's end with some lighter, fun facts about zygotes that might surprise you.
-
Identical twins form when a single zygote splits into two separate embryos.
-
Fraternal twins result from two different eggs being fertilized by two different sperm cells, creating two zygotes.
-
Some animals, like certain sharks, can reproduce through parthenogenesis, where an egg develops into a zygote without fertilization.
-
The study of zygotes has even influenced science fiction, inspiring stories about cloning and genetic engineering.
The Final Word on Zygotes
Zygotes are the starting point of all complex life. They form when sperm and egg cells unite, creating a single cell with a complete set of DNA. This tiny cell then divides and grows, eventually forming a new organism. Understanding zygotes helps us grasp the basics of genetics, reproduction, and development. From the moment of fertilization, the journey of a zygote is a fascinating process that lays the foundation for life. Whether you're a student, a teacher, or just curious, knowing about zygotes gives insight into the miracle of life. So next time you think about where life begins, remember the humble zygote. It's more than just a cell; it's the start of something amazing.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
